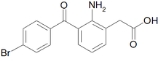
Bromfenac
Encyclopedia
Bromfenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
(NSAID) marketed in the US as an ophthalmic
solution (current brand name Bromday, prior formulation brand name Xibrom, which has since been discontinued.) by ISTA Pharmaceuticals
for short-term, local use. Bromday is the once-daily formulation of Bromfenac, while Xibrom, which has since been discontinued, was the twice-daily formulation. Bromfenac is indicated for the treatment of ocular inflammation and pain after cataract surgery, though it may be prescribed in an off-label manner by the physician.
For ophthalmic use, Bromfenac has been prescibed more than 20,000,000 times across the world. As an eye drop, it has been availalbe since 2000, starting in Japan where it was sold as Bronuck. It was first FDA approved for use in the United States in 2005 and it was marketed as Xibrom, twice-daily. October 2010 was the FDA approval of the new once-daily formulation of Bromfenac called Bromday. The Bromfenac molecule will be marketed in Europe and other worldwide markets with agreements from Bausch & Lomb, Croma Pharma, and other companies.
Bromfenac was formerly marketed in the United States by Wyeth-Ayerst in an oral formulation called Duract for short-term relief of pain (less than 10 days at a time). It was brought to market in July, 1997, and was withdrawn June 22, 1998 following numerous reports of liver failure
in patients who had taken the medication for longer than the recommended 10-day period. The dose was one 25mg capsule every 6 to 8 hours, or two capsules if taken with a high-fat
meal, up to a maximum of 150mg per day.
The Bromfenac Comparative trial was done to determine the optimal concentration for a once daily formulation. Interestingly, the standard 0.09% concentration performed as well as a double strength 0.18% concentration indicating that the COX enzyme receptors were already saturated and blocked by the bromfenac molecule.
In the Bromday FDA Pivotal Trial patients were evaluated with two end-points: a primary efficacy endpoint of the summed ocular inflammation score (SOIS) at post-operative day 15 and a secondary efficacy endpoint of patients reporting a pain score of “none” on post-operative day 1. Note that both arms of this study, the Bromday arm and the placebo arm, were not given any sort of corticosteroid to control inflammation. All anti-inflammatory activity for these post-op cataract patients was from the Bromday NSAID alone.
For post-operative inflammation at day 15, the patients receiving Bromday had an SOIS level of just 1.1 compared to 2.8 for the patients in the placebo arm. This was statistically significant with a superb P value of <0.0001 for day 3, day 8, day 15, and day 22. When patients were asked about their pain level the day after surgery, after having received a total of just three drops of Bromday (pre-op day, day of surgery, post-op day 1), an amazing 94.8% of patients reported “none”, compared to 70.5% for placebo.
Patients who had lack of efficacy were allowed to exit the trial as a safety and comfort measure. For patients receiving Bromday, only 2.9% of Bromday patients elected to do so. This is more than 10 times better than the placebo group where nearly 33% of patients discontinued their participation in the study. These results show that Bromday given just once per day, as a sole anti-inflammatory agent was clinically effective at reducing post-operative inflammation and pain.
Bromday is the first of a new generation of post-operative medications with convenient once daily dosing. More importantly, Bromday brings the same high level of penetration and potency seen previously in Xibrom with half the dosing, half the medication load, and half the level of BAK (benzalkonium chloride) preservative.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
(NSAID) marketed in the US as an ophthalmic
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology and diseases of the eye. An ophthalmologist is a specialist in medical and surgical eye problems...
solution (current brand name Bromday, prior formulation brand name Xibrom, which has since been discontinued.) by ISTA Pharmaceuticals
ISTA Pharmaceuticals
ISTA Pharmaceuticals, Inc, is a US based pharmaceutical company that specializes in ophthalmic pharmaceutical products and discovers, develops, and markets therapies for inflammation, ocular pain, glaucoma, allergy, and dry eye.-Profile:...
for short-term, local use. Bromday is the once-daily formulation of Bromfenac, while Xibrom, which has since been discontinued, was the twice-daily formulation. Bromfenac is indicated for the treatment of ocular inflammation and pain after cataract surgery, though it may be prescribed in an off-label manner by the physician.
For ophthalmic use, Bromfenac has been prescibed more than 20,000,000 times across the world. As an eye drop, it has been availalbe since 2000, starting in Japan where it was sold as Bronuck. It was first FDA approved for use in the United States in 2005 and it was marketed as Xibrom, twice-daily. October 2010 was the FDA approval of the new once-daily formulation of Bromfenac called Bromday. The Bromfenac molecule will be marketed in Europe and other worldwide markets with agreements from Bausch & Lomb, Croma Pharma, and other companies.
Bromfenac was formerly marketed in the United States by Wyeth-Ayerst in an oral formulation called Duract for short-term relief of pain (less than 10 days at a time). It was brought to market in July, 1997, and was withdrawn June 22, 1998 following numerous reports of liver failure
Liver failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs of liver disease , and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage . The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis...
in patients who had taken the medication for longer than the recommended 10-day period. The dose was one 25mg capsule every 6 to 8 hours, or two capsules if taken with a high-fat
Fat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
meal, up to a maximum of 150mg per day.
Clinical use
The FDA approval for Bromday, which is the only currently available formulation of Bromfenac available in the USA, is for use one day before and two weeks following cataract surgery for the treatment of ocular inflammation and pain.Pharmacology and clinical studies
The high degree of penetration and potency of Bromday can be attributed to the halogenation of the molecule: by adding a bromine moiety the NSAID becomes highly lipophilic which allows for rapid, sustained drug levels in the ocular tissues.The Bromfenac Comparative trial was done to determine the optimal concentration for a once daily formulation. Interestingly, the standard 0.09% concentration performed as well as a double strength 0.18% concentration indicating that the COX enzyme receptors were already saturated and blocked by the bromfenac molecule.
In the Bromday FDA Pivotal Trial patients were evaluated with two end-points: a primary efficacy endpoint of the summed ocular inflammation score (SOIS) at post-operative day 15 and a secondary efficacy endpoint of patients reporting a pain score of “none” on post-operative day 1. Note that both arms of this study, the Bromday arm and the placebo arm, were not given any sort of corticosteroid to control inflammation. All anti-inflammatory activity for these post-op cataract patients was from the Bromday NSAID alone.
For post-operative inflammation at day 15, the patients receiving Bromday had an SOIS level of just 1.1 compared to 2.8 for the patients in the placebo arm. This was statistically significant with a superb P value of <0.0001 for day 3, day 8, day 15, and day 22. When patients were asked about their pain level the day after surgery, after having received a total of just three drops of Bromday (pre-op day, day of surgery, post-op day 1), an amazing 94.8% of patients reported “none”, compared to 70.5% for placebo.
Patients who had lack of efficacy were allowed to exit the trial as a safety and comfort measure. For patients receiving Bromday, only 2.9% of Bromday patients elected to do so. This is more than 10 times better than the placebo group where nearly 33% of patients discontinued their participation in the study. These results show that Bromday given just once per day, as a sole anti-inflammatory agent was clinically effective at reducing post-operative inflammation and pain.
Bromday is the first of a new generation of post-operative medications with convenient once daily dosing. More importantly, Bromday brings the same high level of penetration and potency seen previously in Xibrom with half the dosing, half the medication load, and half the level of BAK (benzalkonium chloride) preservative.

