Brownian noise
Encyclopedia
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
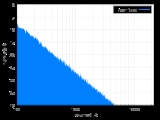
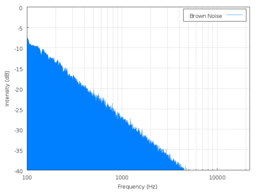
, Brownian noise , also known as Brown noise or red noise, is the kind of signal noise produced by Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
, hence its alternative name of random walk noise. The term "Brown noise" comes not from the color
Brown
Brown is a color term, denoting a range of composite colors produced by a mixture of orange, red, rose, or yellow with black or gray. The term is from Old English brún, in origin for any dusky or dark shade of color....
, but after Robert Brown
Robert Brown (botanist)
Robert Brown was a Scottish botanist and palaeobotanist who made important contributions to botany largely through his pioneering use of the microscope...
, the discoverer of Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
.
Explanation
The graphic representation of the sound signal mimics a Brownian pattern. Its spectral densitySpectral density
In statistical signal processing and physics, the spectral density, power spectral density , or energy spectral density , is a positive real function of a frequency variable associated with a stationary stochastic process, or a deterministic function of time, which has dimensions of power per hertz...
is inversely proportional to f², meaning it has more energy at lower frequencies, even more so than pink noise
Pink noise
Pink noise or 1/ƒ noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density is inversely proportional to the frequency. In pink noise, each octave carries an equal amount of noise power...
. It decreases in power by 6 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
per octave
Octave
In music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
and, when heard, has a "damped" or "soft" quality compared to white
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
and pink noise
Pink noise
Pink noise or 1/ƒ noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density is inversely proportional to the frequency. In pink noise, each octave carries an equal amount of noise power...
. The sound is a low roar resembling a waterfall or heavy rainfall. See also purple noise, which is a 6 dB increase per octave.
Power spectrum
A Brownian signal is expressed mathematically as the integral of a white noiseWhite noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
signal,
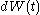 , namely a Wiener process
, namely a Wiener processWiener process
In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown...
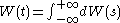
White noise has a constant spectrum
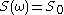 . The Fourier transform
. The Fourier transformFourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
has the general property
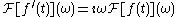
Since white noise is the derivative of Brownian motion (more accurately, Brownian motion is the integral of white noise, as the derivative of a random function is not defined cf.) we conclude that the spectrum for Brownian noise is
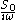 , therefore the power spectrum is given by
, therefore the power spectrum is given by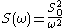
Production
Brown noise can be produced by integratingIntegral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
white noise
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
. That is, whereas (digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
) white noise can be produced by randomly choosing each sample independently, Brown noise can be produced by adding a random offset to each sample to obtain the next one.
Sample
External links
- Brown noise in wave(.wav) format, 1 minute long
- PlayNoise, a free online white, pink, and brown noise generator, uses Javascript/HTML5.

