
Bryant Tuckerman
Encyclopedia
Louis Bryant Tuckerman, III (November 28, 1915 – May 19, 2002) was an American mathematician, born in Lincoln, Nebraska
. He was a member of the team that developed the Data Encryption Standard
(DES).
He studied topology
at Princeton
, where he invented the Tuckerman traverse method for revealing all the faces of a flexagon
.
He was also the discoverer, on March 4, 1971, of the 24th Mersenne prime
, a titanic prime
, with a value of
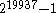 .
.
Lincoln, Nebraska
The City of Lincoln is the capital and the second-most populous city of the US state of Nebraska. Lincoln is also the county seat of Lancaster County and the home of the University of Nebraska. Lincoln's 2010 Census population was 258,379....
. He was a member of the team that developed the Data Encryption Standard
Data Encryption Standard
The Data Encryption Standard is a block cipher that uses shared secret encryption. It was selected by the National Bureau of Standards as an official Federal Information Processing Standard for the United States in 1976 and which has subsequently enjoyed widespread use internationally. It is...
(DES).
He studied topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
at Princeton
Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university located in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. The school is one of the eight universities of the Ivy League, and is one of the nine Colonial Colleges founded before the American Revolution....
, where he invented the Tuckerman traverse method for revealing all the faces of a flexagon
Flexagon
In geometry, flexagons are flat models, usually constructed by folding strips of paper, that can be flexed or folded in certain ways to reveal faces besides the two that were originally on the back and front....
.
He was also the discoverer, on March 4, 1971, of the 24th Mersenne prime
Mersenne prime
In mathematics, a Mersenne number, named after Marin Mersenne , is a positive integer that is one less than a power of two: M_p=2^p-1.\,...
, a titanic prime
Titanic prime
Titanic prime is a term coined by Samuel Yates in the 1980s, denoting a prime number of at least 1000 decimal digits. Few such primes were known then, but the required size is trivial for modern computers.The first 30 titanic primes are of the form:...
, with a value of
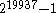 .
.
