Business-Agile Enterprise
Encyclopedia
A B-AE is an amalgam of different business & IT methods that work together to create an agile and competitive business model. These disciplines include business technology management
, service-oriented architecture
, IT governance
, SOA governance
, IT portfolio management
, business process management
, Control objectives for information and related technology (CobiT)
, enterprise architecture
, business architecture
, project management
, Information Technology Infrastructure Library
, ITIL V3 (Alignment of IT to business), IT service management
, information management
, matrix management
, and business process modeling
.
A B-AE improves financial measurements such as;
Agile companies make more money with less resources and lower costs
These figures are not limited to any one area within the enterprise and are not "IT-specific." They also do not measure returns on any single project, rather, they measure enterprise-wide returns, and reflect the EBITDA of the entire enterprise. The financial effects are enterprise-wide, since the key management capabilities are interconnected, and because both the business and technology professionals in a B-AE actively share ownership of decision-making and execution.
Between agile and staid companies there is a 50% profit difference.
MIT has proven that IT departments that have a cost focus spend more and get less than those of an agility focus.
Business Technology Management
Business technology management is a management science that seeks to unify business and technology decision-making at every level in an enterprise. BTM delivers a set of guiding principles, known as BTM capabilities. These capabilities are combined to form BTM solutions, around which a company's...
, service-oriented architecture
Service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
, IT governance
Information technology governance
Information Technology Governance, IT Governance is a subset discipline of Corporate Governance focused on information technology systems and their performance and risk management...
, SOA governance
SOA Governance
SOA governance is a concept used for activities related to exercising control over services in a service-oriented architecture . SOA governance can be seen as a subset of IT governance which itself is a subset of corporate governance. The focus is on those resources to be leveraged for SOA to...
, IT portfolio management
IT portfolio management
IT portfolio management is the application of systematic management to large classes of items managed by enterprise Information Technology capabilities. Examples of IT portfolios would be planned initiatives, projects, and ongoing IT services...
, business process management
Business process management
Business process management is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It promotes business effectiveness and efficiency while striving for innovation, flexibility, and integration with technology. BPM attempts to...
, Control objectives for information and related technology (CobiT)
COBIT
COBIT is a framework created by ISACA for information technology management and IT Governance. It is a supporting toolset that allows managers to bridge the gap between control requirements, technical issues and business risks.-Overview:...
, enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
, business architecture
Business architecture
A business architecture is a part of an enterprise architecture related to corporate business, and the documents and diagrams that describe that architectural structure of business...
, project management
Project management
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals. A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end , undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or added value...
, Information Technology Infrastructure Library
Information Technology Infrastructure Library
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library , is a set of good practices for IT service management that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. In its current form , ITIL is published in a series of five core publications, each of which covers an ITSM lifecycle stage...
, ITIL V3 (Alignment of IT to business), IT service management
IT Service Management
IT service management is a discipline for managing information technology systems, philosophically centered on the customer's perspective of IT's contribution to the business. ITSM stands in deliberate contrast to technology-centered approaches to IT management and business interaction...
, information management
Information management
Information management is the collection and management of information from one or more sources and the distribution of that information to one or more audiences. This sometimes involves those who have a stake in, or a right to that information...
, matrix management
Matrix management
Matrix management is a type of organizational management in which people with similar skills are pooled for work assignments. For example, all engineers may be in one engineering department and report to an engineering manager, but these same engineers may be assigned to different projects and...
, and business process modeling
Process modeling
The term process model is used in various contexts. For example, in business process modeling the enterprise process model is often referred to as the business process model. Process models are core concepts in the discipline of process engineering....
.
A B-AE improves financial measurements such as;
- margins
- profitability
- time to market
- revenue growth
- earnings per share
- ebitda (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation & amortization
- return on equity
- return on assets
- return on investments
Agile companies make more money with less resources and lower costs
Business Technology Management Institute Agility research
BTM conducted 5 years of business agility research across 50 industries worldwide. Their document, "Business Technology Convergence Index," summarizes the financial benefits a firm can accrue in converging their business & IT groups..
Agile companies have converged their business & IT worlds and consistently exhibit superior revenue growth and net margins relative to their industry groups.

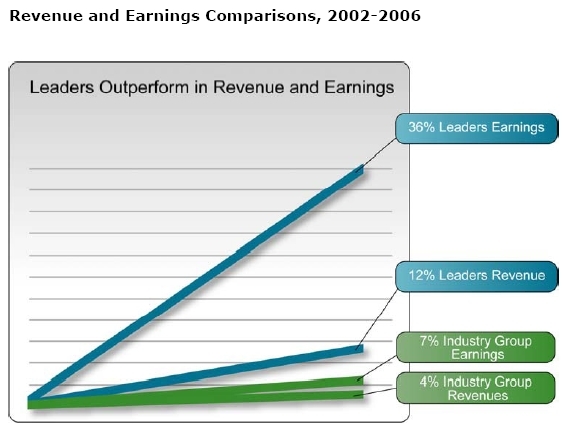
- Annual Revenue Growth – 12% growth vs 4% for their industry groups
- Average Annual Earnings per Share – 36% growth vs 7% for their industry groups
Agile Companies not only grow at a faster pace than their peers, but they also exhibit consistently greater returns than those of their direct competitors.
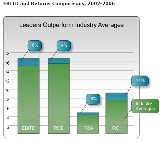
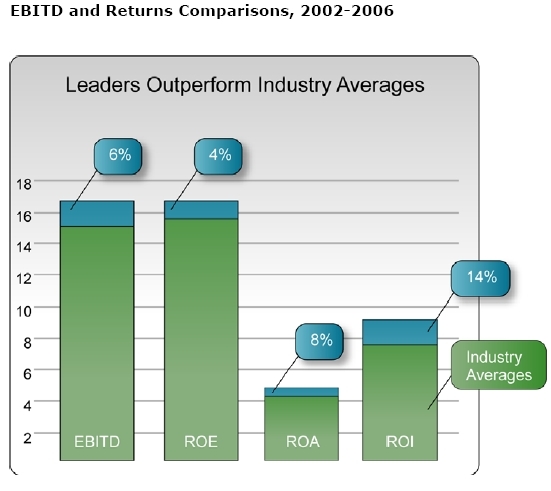
- Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation & amortization – 6% higher EBITDA than those delivered by their industry groups
- Return on equity – 4% higher
- Return on assets – 8% higher
- Return on investments – 14% higher
These figures are not limited to any one area within the enterprise and are not "IT-specific." They also do not measure returns on any single project, rather, they measure enterprise-wide returns, and reflect the EBITDA of the entire enterprise. The financial effects are enterprise-wide, since the key management capabilities are interconnected, and because both the business and technology professionals in a B-AE actively share ownership of decision-making and execution.
MIT Sloan School of Management's Center for Information Systems Research Agility research
In the book, "Leveraging the New Infrastructure", the idea of treating IT as a portfolio of investments, just as corporate finance handles their investment portfolios, is documented as a way to assess IT business value. Agility is a major contributor to these financial benefits.Agile companies show higher profit growth.
| Performance | Agile | Staid | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| New products | 8.8 | 3.2 | Percent of 2004 sales from new products introduced in previous three years. Average = 5.6% |
| Modified products | 35 | 13 | Average percent of 2004 sales from modified products introduced in previous three years. Average = 22.5% |
| Growth | +7 | −10 | Average annual percentage growth 2002–2004 (relative to industry average). Average growth = 6.8% per annum |
| Profit growth | +37 | −13 | Average annual percent change in ROE 2002–2004 (relative to industry average). Average = 0.5% |
Between agile and staid companies there is a 50% profit difference.
Agile Companies exhibit superior Business Value relative to their industry groups.
Agile companies are IT Savvy. An IT Savvy firm uses a digital platform to integrate a set of electronic business processes and the technologies, applications, and data supporting these processes. Managers in these companies elevate their firm's performance by a consistent use of IT. They use disciplined core processes and then apply the resulting data to both operational and strategic decision-making tasks.- Business Value – firms with above average IT spending & IT Savvy had net margins 20% above their industry's median
- Profitability via sharing – firms with above average percentage of shared applications & it savvy have return on assets 30% above their industry's median
- Time to market – firms with above average IT infrastructure spending & IT savvy grew 3 percentage points higher than their industry's average
- IT-enabled business investments – top-performing companies (IT savvy) can get up to 40% more value
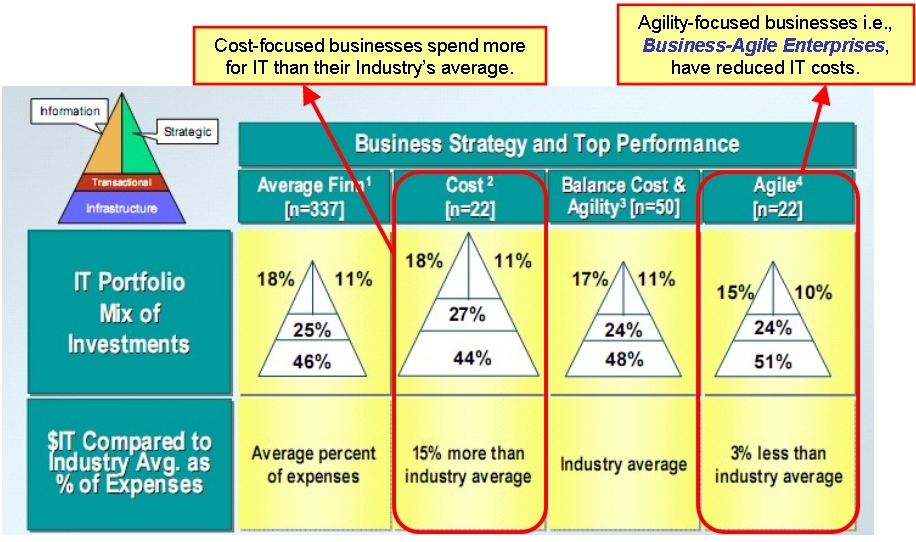
Agility-focused businesses have reduced IT costs
Weill and Broadbent's results show;
MIT has proven that IT departments that have a cost focus spend more and get less than those of an agility focus.
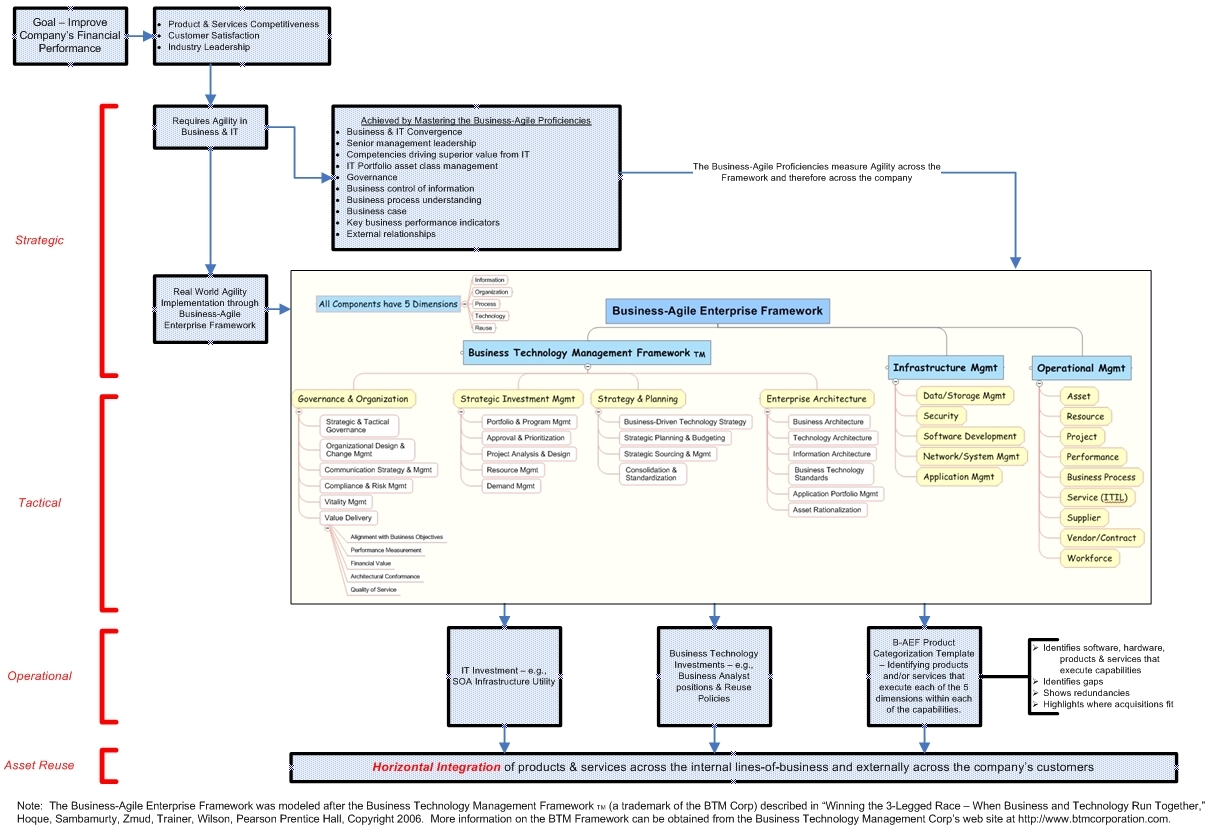
The business-agile enterprise approach
A business-agile enterprise is an ongoing journey to a state of greater industry competitiveness. A B-AE strives to achieve larger degrees of agility to match their industry's competitive requirements rather than using a reorganization to improve competitiveness.Technique
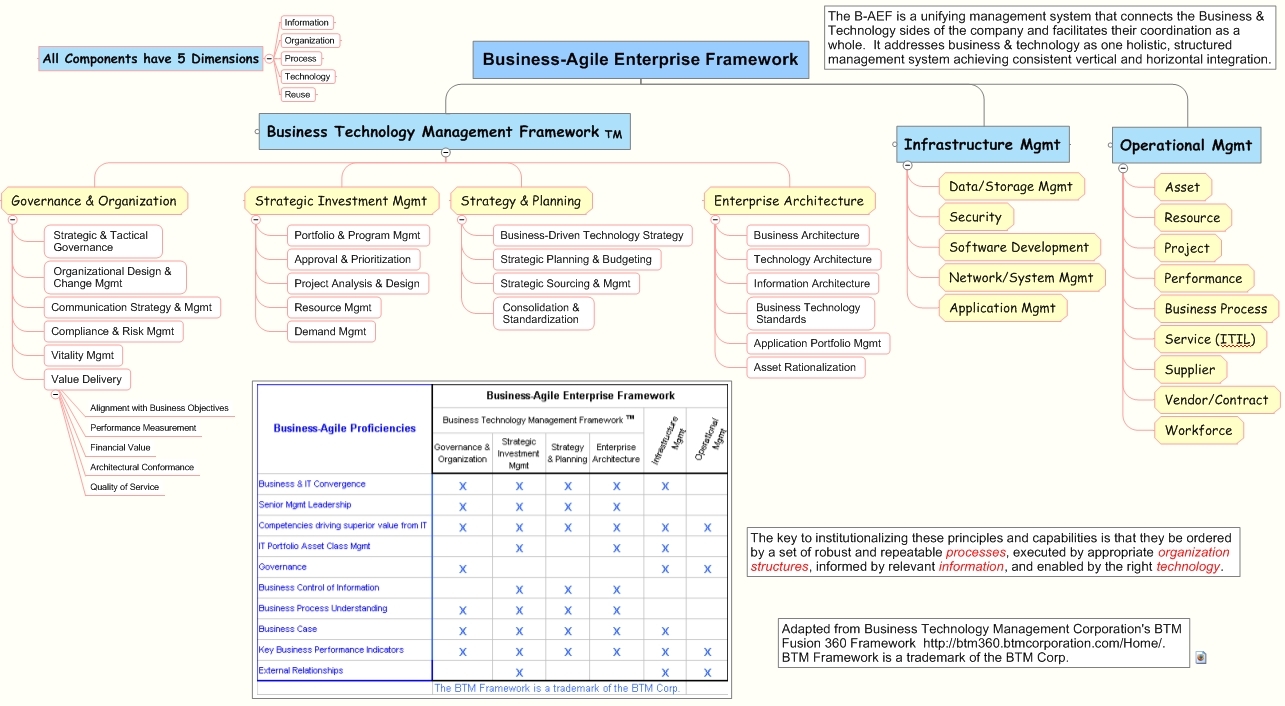
The B-AE is a top–down, business approach that summarizes in one place the joint business & IT elements necessary to compete.- It starts with the Business-Agile Proficiencies (B-AP). The B-APs measure agility (and therefore financial performance) across the Business-Agile Enterprise Framework (B-AEF).
- The B-APs are driven down into the business-agile enterprise framework where the practical everyday requirements needed to conduct business are referenced, executed & measured.
- The B-AEF requires two investments;
- IT investments – e.g., service-oriented architectureService-oriented architectureIn software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
infrastructure so stable and ubiquitous as to become a utility - Business technology investments – e.g., reuse policies and new roles such as the business service champion and the business service analyst
- IT investments – e.g., service-oriented architecture
- The B-AE Product Categorization Template is a work product of the B-AE Framework. It contains 190 "slots" that describe the execution environment of each of the 5 dimensions (information, organization, process, technology, reuse) within each of the capabilities (e.g., strategic & tactical governance, portfolio & program management, etc...). The filled-in template;
- Identifies software, hardware, products & services that execute the particular capability
- Identifies business & technology gaps
- Shows business & technology redundancies
- Highlights where acquisitions fit
Business-Agile Proficiencies
The B-APs are a set of ten (10) practices and competencies that define agility from a practical standpoint.- Business & IT Convergence (Asset Sharing & Mega-Alignment)
- Competencies that drive Superior Value from IT (IT Savvy)
- IT portfolio asset class management (enterprise architecture)
- Governance (direction, control & distributed authority for decision making)
- Senior management leadership (management involvement)
- Business control of information (intellectual capital & information visibility)
- Business process understanding (component business modeling)
- Business case (business value documentation throughout lifecycle)
- Key business performance indicators (consistent & continuous benefits valuation)
- External relationships (external assets, skills & competencies to act on opportunities)
Business-agile enterprise framework
The business-agile enterprise framework describes how a B-AF functions in real-world operations. It highlights the big picture and shows how business and IT can work together. The B-AEF is a unifying management system that connects the business & technology sides of the company and facilitates their coordination as a whole. It addresses business & technology as one holistic, structured management system achieving consistent vertical and horizontal integration.
Business-agile enterprise business architecture

See also
- Business technology managementBusiness Technology ManagementBusiness technology management is a management science that seeks to unify business and technology decision-making at every level in an enterprise. BTM delivers a set of guiding principles, known as BTM capabilities. These capabilities are combined to form BTM solutions, around which a company's...
- Strategic planningStrategic planningStrategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy. In order to determine the direction of the organization, it is necessary to understand its current position and the possible avenues...
- Marketing strategyMarketing strategyMarketing strategy is a process that can allow an organization to concentrate its limited resources on the greatest opportunities to increase sales and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage.-Developing a marketing strategy:...
- Business modelBusiness modelA business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
- Business planBusiness planA business plan is a formal statement of a set of business goals, the reasons why they are believed attainable, and the plan for reaching those goals. It may also contain background information about the organization or team attempting to reach those goals....
- Business model designBusiness model designBusiness model design refers to the activity of designing a company's business model. It is part of the business development and business strategy process and involves design methods.Business model design includes the modeling and description of a company's:...
- Business process modelingBusiness process modelingBusiness Process Modeling in systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current process may be analyzed and improved. BPM is typically performed by business analysts and managers who are seeking to improve process efficiency and quality...
Further reading
- "Agility in Information Systems: Enabling Capabilities for the IT Function," George Hobbs & Rens Scheepers, Pacific Asia Journal of the Association for Information Systems: 2010 Vol. 2: Iss. 4, Article 2. Link

