
Business process modeling
Encyclopedia
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
is the activity of representing processes
Process modeling
The term process model is used in various contexts. For example, in business process modeling the enterprise process model is often referred to as the business process model. Process models are core concepts in the discipline of process engineering....
of an enterprise, so that the current process may be analyzed and improved. BPM is typically performed by business analysts and managers who are seeking to improve process efficiency and quality. The process improvements identified by BPM may or may not require Information Technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
involvement, although that is a common driver for the need to model a business process, by creating a process master.
Change management
Change management
Change management is a structured approach to shifting/transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state. It is an organizational process aimed at helping employees to accept and embrace changes in their current business environment....
programs are typically involved to put the improved business processes into practice. With advances in technology from large platform vendors, the vision of BPM models becoming fully executable (and capable of simulations and round-trip engineering) is coming closer to reality every day.
History
Techniques to model business process such as the flow chart, functional flow block diagramFunctional flow block diagram
A Functional Flow Block Diagram is a multi-tier, time-sequenced, step-by-step flow diagram of a system’s functional flow.The FFBD notation was developed in the 1950s, and is widely used in classical systems engineering...
, control flow diagram
Control flow diagram
A control flow diagram is a diagram to describe the control flow of a business process, process or program.Control flow diagrams were developed in the 1950s, and are widely used in multiple engineering disciplines...
, Gantt chart
Gantt chart
A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. Gantt charts illustrate the start and finish dates of the terminal elements and summary elements of a project. Terminal elements and summary elements comprise the work breakdown structure of the project. Some Gantt charts...
, PERT diagram, and IDEF
IDEF
IDEF, an abbreviation of Integration Definition, refers to a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses, from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis/design and knowledge acquisition. These "definition...
have emerged since the beginning of the 20th century. The Gantt charts were among the first to arrive around 1899, the flow charts in the 1920s, Functional Flow Block Diagram and PERT in the 1950s, Data Flow Diagrams and IDEF in the 1970s. Among the modern methods are Unified Modeling Language
Unified Modeling Language
Unified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
and Business Process Modeling Notation
Business Process Modeling Notation
Business Process Model and Notation is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. It was previously known as Business Process Modeling Notation....
. Still, these represent just a fraction of the methodologies used over the years to document business processes. The term "business process modeling" itself was coined in the 1960s in the field of systems engineering
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
by S. Williams in his 1967 article "Business Process Modeling Improves Administrative Control". His idea was that techniques for obtaining a better understanding of physical control systems could be used in a similar way for business process
Business process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
es. It took until the 1990s before the term became popular.
In the 1990s the term "process
Business process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
" became a new productivity paradigm. Companies were encouraged to think in processes instead of functions and procedures. Process thinking looks at the chain of events in the company from purchase to supply, from order retrieval to sales etc. The traditional modeling tools were developed to picture time and costs, while modern methods focus on cross-function activities. These cross-functional activities have increased severely in number and importance due to the growth of complexity and dependencies. New methodologies such as business process redesign, business process innovation, business process management
Business process management
Business process management is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It promotes business effectiveness and efficiency while striving for innovation, flexibility, and integration with technology. BPM attempts to...
, integrated business planning
Integrated business planning
Integrated business planning refers to the technologies, applications and processes of connecting the planning function across the enterprise to improve organizational alignment and financial performance...
among others all "aiming at improving processes across the traditional functions that comprise a company".
In the field of software engineering
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
the term "business process modeling" opposed the common software process modeling, aiming to focus more on the state of the practice during software development
Software development
Software development is the development of a software product...
. In that time early 1990s all existing and new modeling techniques to picture business processes were considered and called "business process modeling languages." In the Object Oriented approach, it was considered to be an essential step in the specification of Business Application Systems. Business process modeling became the base of new methodologies, that for example also supported data collection, data flow analysis, process flow diagrams and reporting facilities. Around 1995 the first visually oriented tools for business process modeling and implementation were being presented.
Business model
A business modelBusiness model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
is a framework for creating economic, social, and/or other forms of value. The term 'business model' is thus used for a broad range of informal and formal descriptions to represent core aspects of a business, including purpose, offerings, strategies, infrastructure, organizational structures, trading practices, and operational processes and policies.
In the most basic sense, a business model is the method of doing business by which a company can sustain itself. That is, generate revenue. The business model spells-out how a company makes money by specifying where it is positioned in the value chain
Value chain
The value chain, is a concept from business management that was first described and popularized by Michael Porter in his 1985 best-seller, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance.-Firm Level:...
.
Business process
A business processBusiness process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks
Task (project management)
In project management a task is an activity that needs to be accomplished within a defined period of time. An assignment is a task under the responsibility of an assignee which should have a start and end date defined. One or more assignments on a task puts the task under execution. Completion of...
that produce a specific service or product (serve a particular goal) for a particular customer or customers. There are three main types of business processes:
- Management processes, the processes that govern the operation of a system. Typical management processes include "Corporate GovernanceCorporate governanceCorporate governance is a number of processes, customs, policies, laws, and institutions which have impact on the way a company is controlled...
" and "Strategic ManagementStrategic managementStrategic management is a field that deals with the major intended and emergent initiatives taken by general managers on behalf of owners, involving utilization of resources, to enhance the performance of firms in their external environments...
". - Operational processes, processes that constitute the core businessCore businessThe core business of an organization is an idealized construct intended to express that organization's "main" or "essential" activity.The corporate trend in the mid-20th Century of acquiring new enterprises and forming conglomerates enabled corporations to reduce costs funds and similar investment...
and create the primary value stream. Typical operational processes are PurchasingPurchasingPurchasing refers to a business or organization attempting for acquiring goods or services to accomplish the goals of the enterprise. Though there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations...
, ManufacturingManufacturingManufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
, MarketingMarketingMarketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, and SalesSalesA sale is the act of selling a product or service in return for money or other compensation. It is an act of completion of a commercial activity....
. - Supporting processes, which support the core processes. Examples include Accounting, RecruitmentRecruitmentRecruitment refers to the process of attracting, screening, and selecting qualified people for a job. For some components of the recruitment process, mid- and large-size organizations often retain professional recruiters or outsource some of the process to recruitment agencies.The recruitment...
, Technical supportTechnical supportTechnical support or tech support refers to a range of services by which enterprises provide assistance to users of technology products such as mobile phones, televisions, computers, software products or other electronic or mechanical goods...
.
A business process can be decomposed into several sub-processes, which have their own attributes, but also contribute to achieving the goal of the super-process. The analysis of business processes typically includes the mapping of processes and sub-processes down to activity level. A business process model is a model
Scientific modelling
Scientific modelling is the process of generating abstract, conceptual, graphical and/or mathematical models. Science offers a growing collection of methods, techniques and theory about all kinds of specialized scientific modelling...
of one or more business processes, and defines the ways in which operations are carried out to accomplish the intended objectives of an organization. Such a model remains an abstraction and depends on the intended use of the model. It can describe the workflow or the integration between business processes. It can be constructed in multiple levels.
A workflow
Workflow
A workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...
is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, work of a simple or complex mechanism, work of a group of persons, work of an organization of staff, or machines. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work, segregated in workshare, work split or whatever types of ordering. For control purposes, workflow may be a view on real work under a chosen aspect.
Artifact-centric Business process
The Artifact-centric business process modelArtifact-centric business process model
Artifact-centric Business Process Model represents an operational model of business processes in which the changes and evolutions of business data, or business entities, are considered as the main driver of the processes...
has emerged as a new promising approach for modeling business processes, as it provides a highly flexible solution to capture operational specifications of business processes. It particularly focuses on describing the data of business processes, known as “artifacts”, by characterizing business-relevant data objects, their lifecycles, and related services. The artifact-centric process modelling approach fosters the automation of the business operations and supports the flexibility of the workflow enactment and evolution.
Business process modeling tools
Business process modeling tools provide business users with the ability to model their business processes, implement and execute those models, and refine the models based on as-executed data. As a result, business process modeling tools can provide transparency into business processes, as well as the centralization of corporate business process models and execution metrics.Modeling and simulation
Modeling and simulation functionality allows for pre-execution “what-if” modeling and simulation. Post-execution optimization is available based on the analysis of actual as-performed metrics.Business process modeling diagrams are:
- Use case diagramUse case diagramA use case diagram in the Unified Modeling Language is a type of behavioral diagram defined by and created from a Use-case analysis. Its purpose is to present a graphical overview of the functionality provided by a system in terms of actors, their goals , and any dependencies between those use...
s created by Ivar JacobsonIvar JacobsonIvar Hjalmar Jacobson is a Swedish computer scientist, known as major contributor to UML, Objectory, RUP and aspect-oriented software development.- Biography :...
, 1992. Currently integrated in UMLUnified Modeling LanguageUnified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group... - Activity diagramActivity diagramActivity diagrams are graphical representations of workflows of stepwise activities and actions with support for choice, iteration and concurrency. In the Unified Modeling Language, activity diagrams can be used to describe the business and operational step-by-step workflows of components in a system...
s, also currently adopted by UML
Some business process modeling techniques are:
- Business Process Modeling NotationBusiness Process Modeling NotationBusiness Process Model and Notation is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. It was previously known as Business Process Modeling Notation....
(BPMN) - Cognition enhanced Natural language Information Analysis Method (CogNIAM)
- Extended Business Modeling Language (xBML)
- Event-driven process chainEvent-driven process chainAn Event-driven Process Chain is a type of flowchart used for business process modelling. EPC's can be used for configuring an enterprise resource planning implementation, and for business process improvement.- Overview :...
(EPC) - ICAM DEFinitionIDEFIDEF, an abbreviation of Integration Definition, refers to a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses, from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis/design and knowledge acquisition. These "definition...
(IDEF0IDEF0IDEF0 is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeling language for the analysis, development, reengineering, and integration of information systems; business processes; or software engineering analysis.IDEF0 is part of the IDEF family...
) - Unified Modeling LanguageUnified Modeling LanguageUnified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
(UML), extensions for business process such as Eriksson-Penker's
Programming language tools for BPM
BPM suite software provides programming interfaces (web services, application program interfaces (APIs)) which allow enterprise applications to be built to leverage the BPM engine. This component is often referenced as the engine of the BPM suite.Programming languages that are being introduced for BPM include:
- BPMNBusiness Process Modeling NotationBusiness Process Model and Notation is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. It was previously known as Business Process Modeling Notation....
- Business Process Execution LanguageBusiness Process Execution LanguageBusiness Process Execution Language , short for Web Services Business Process Execution Language is an OASIS standard executable language for specifying actions within business processes with web services...
(BPEL), - Web Services Choreography Description Language (WS-CDLWS-CDLThe Web Services Choreography Description Language is a W3C candidate recommendation. It is a language for describing how peer-to-peer participants collaborate...
). - XML Process Definition Language (XPDLXPDLThe XML Process Definition Language is a format standardized by the Workflow Management Coalition to interchange business process definitions between different workflow products, i.e...
),
Some vendor-specific languages:
- Architecture of Integrated Information SystemsArchitecture of Integrated Information SystemsARIS is an approach to enterprise modeling. It offers methods for analyzing processes and taking a holistic view of process design, management, work flow, and application processing....
(ARIS) supports EPC, - Java Process Definition Language (JBPMJBPMjBPM is an open-source workflow engine written in Java that can execute business processes described in BPMN 2.0 . It is released under the ASL by the JBoss community.In essence jBPM takes graphical process descriptions as input...
),
Other technologies related to business process modeling include model-driven architecture
Model-driven architecture
Model-driven architecture is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model-driven architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of...
and service-oriented architecture
Service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
.
Business reference model
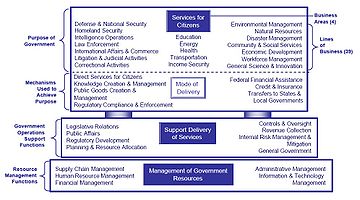
Business reference model
Business reference model is a reference model, concentrating on the functional and organizational aspects of the core business of an enterprise, service organization or government agency....
is a reference model, concentrating on the functional and organizational aspects of an enterprise
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
, service organization or government agency
Government agency
A government or state agency is a permanent or semi-permanent organization in the machinery of government that is responsible for the oversight and administration of specific functions, such as an intelligence agency. There is a notable variety of agency types...
. In general a reference model
Reference Model
A reference model in systems, enterprise, and software engineering is a model of something that embodies the basic goal or idea of something and can then be looked at as a reference for various purposes.- Overview :...
is a model of something that embodies the basic goal or idea of something and can then be looked at as a reference for various purposes. A business reference model is a means to describe the business operations of an organization, independent of the organizational structure that perform them. Other types of business reference model can also depict the relationship between the business processes, business functions, and the business area’s business reference model. These reference model
Reference Model
A reference model in systems, enterprise, and software engineering is a model of something that embodies the basic goal or idea of something and can then be looked at as a reference for various purposes.- Overview :...
s can be constructed in layers, and offer a foundation for the analysis of service components, technology, data, and performance.
The most familiar business reference model is the Business Reference Model of the US Federal Government. That model is a function-driven
Function model
A function model or functional model in systems engineering and software engineering is a structured representation of the functions within the modeled system or subject area....
framework for describing the business operations of the Federal Government independent of the agencies that perform them. The Business Reference Model provides an organized, hierarchical construct for describing the day-to-day business operations of the Federal government. While many models exist for describing organizations - organizational chart
Organizational chart
An organizational chart is a diagram that shows the structure of an organization and the relationships and relative ranks of its parts and positions/jobs...
s, location maps, etc. - this model presents the business using a functionally driven approach.
Business process integration
A business modelBusiness model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
, which may be considered an elaboration of a business process model, typically shows business data and business organizations as well as business processes. By showing business processes and their information flows a business model allows business stakeholders to define, understand, and validate their business enterprise. The data model
Data model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
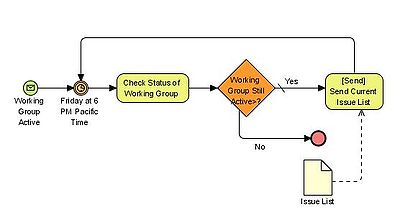
part of the business model shows how business information is stored, which is useful for developing software code. See the figure on the right for an example of the interaction between business process models and data models.
Usually a business model is created after conducting an interview, which is part of the business analysis
Business Analysis
Business analysis is the discipline of identifying business needs and determining solutions to business problems. Solutions often include a systems development component, but may also consist of process improvement, organizational change or strategic planning and policy development...
process. The interview consists of a facilitator asking a series of questions to extract information about the subject business process. The interviewer is referred to as a facilitator to emphasize that it is the participants, not the facilitator, who provide the business process information. Although the facilitator should have some knowledge of the subject business process, but this is not as important as the mastery of a pragmatic and rigorous method interviewing business experts. The method is important because for most enterprises a team of facilitators is needed to collect information across the enterprise, and the findings of all the interviewers must be compiled and integrated once completed.
Business models are developed as defining either the current state of the process, in which case the final product is called the "as is" snapshot model, or a concept of what the process should become, resulting in a "to be" model. By comparing and contrasting "as is" and "to be" models the business analysts can determine if the existing business processes and information systems are sound and only need minor modifications, or if reengineering is required to correct problems or improve efficiency. Consequently, business process modeling and subsequent analysis can be used to fundamentally reshape the way an enterprise conducts its operations.
Business process reengineering
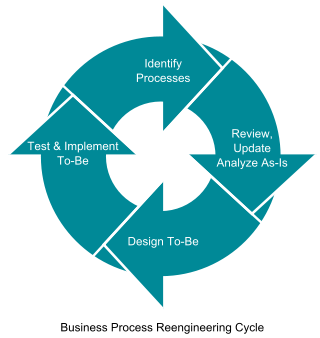
Business process reengineering
Business process re-engineering is the analysis and design of workflows and processes within an organization.According to Davenport a business process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome....
(BPR) is an approach aiming at improvements by means of elevating efficiency and effectiveness of the processes
Business process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
that exist within and across organizations. The key to business process reengineering is for organizations to look at their business processes from a "clean slate" perspective and determine how they can best construct these processes to improve how they conduct business.
Business process reengineering (BPR) began as a private sector technique to help organizations fundamentally rethink how they do their work in order to dramatically improve customer service, cut operational costs, and become world-class competitors. A key stimulus for reengineering has been the continuing development and deployment of sophisticated information systems and networks. Leading organizations are becoming bolder in using this technology to support innovative business processes, rather than refining current ways of doing work.
Business process management
Business process managementBusiness process management
Business process management is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It promotes business effectiveness and efficiency while striving for innovation, flexibility, and integration with technology. BPM attempts to...
is a field of management
Management
Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively...
focused on aligning organizations with the wants and needs of clients. It is a holistic management
Holism
Holism is the idea that all the properties of a given system cannot be determined or explained by its component parts alone...
approach that promotes business effectiveness and efficiency while striving for innovation, flexibility and integration with technology. As organizations strive for attainment of their objectives, business process management attempts to continuously improve processes - the process to define, measure and improve your processes – a "process optimization" process.
See also
- Business architectureBusiness architectureA business architecture is a part of an enterprise architecture related to corporate business, and the documents and diagrams that describe that architectural structure of business...
- Business Model CanvasBusiness Model CanvasThe Business Model Canvas is a strategic management template for developing new or documenting existing business models. It is a visual chart with elements describing a firm's value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances...
- Business planBusiness planA business plan is a formal statement of a set of business goals, the reasons why they are believed attainable, and the plan for reaching those goals. It may also contain background information about the organization or team attempting to reach those goals....
- Business process illustrationBusiness process illustrationIn order that business processes can be improved they must first be illustrated. The hardest task in business process mapping is getting everyone to agree what the process looks like. The starting point is an illustration of the process. The production of a process illustration is an iterative...
- Business process mappingBusiness Process MappingBusiness process mapping refers to activities involved in defining exactly what a business entity does, who is responsible, to what standard a process should be completed and how the success of a business process can be determined. Once this is done, there can be no uncertainty as to the...
- Business Process Modeling NotationBusiness Process Modeling NotationBusiness Process Model and Notation is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. It was previously known as Business Process Modeling Notation....
- Artifact-centric business process modelArtifact-centric business process modelArtifact-centric Business Process Model represents an operational model of business processes in which the changes and evolutions of business data, or business entities, are considered as the main driver of the processes...
- Capability Maturity Model IntegrationCapability Maturity Model IntegrationCapability Maturity Model Integration is a process improvement approach whose goal is to help organizations improve their performance. CMMI can be used to guide process improvement across a project, a division, or an entire organization...
- Extended Enterprise Modeling LanguageExtended Enterprise Modeling LanguageExtended Enterprise Modeling Language in software engineering is a modelling language used for Enterprise modelling across a number of layers.-Overview:...
- Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and MethodologyGeneralised Enterprise Reference Architecture and MethodologyGeneralised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology is a generalised Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering.This framework is developed in the 1990s...
- Model Driven Engineering
Further reading
- Lambertus Johannes Hommes, Bart-Jan Hommes (2004). The Evaluation of Business Process Modeling Techniques. Doctoral thesis. Technische Universiteit Delft.
- Håvard D. Jørgensen (2004). Interactive Process Models. Thesis Norwegian University of Science and Technology Trondheim, Norway.
- Manuel Laguna, Johan Marklund (2004). Business Process Modeling, Simulation, and Design. Pearson/Prentice Hall, 2004.
- Ovidiu S. Noran (2000). Business Modelling: UML vs. IDEF Paper Griffh University
- Jan Recker (2005). "Process Modeling in the 21st Century". In: BP Trends, May 2005.
- Ryan K. L. Ko, Stephen S. G. Lee, Eng Wah Lee (2009) Business Process Management (BPM) Standards: A Survey. In: Business Process Management Journal, Emerald Group Publishing Limited. Volume 15 Issue 5. ISSN 1463-7154.
- Jan VanthienenJan VanthienenJan Vanthienen is a Belgium organizational theorist and Professor of Information systems at Leuven University , known for his contributions to Business Process Modeling and Business Engineering.- Biography :...
, S. Goedertier and R. Haesen (2007). "EM-BrA2CE v0.1: A vocabulary and execution model for declarative business process modeling". DTEW - KBI_0728.

