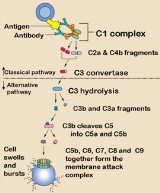
C1Q complex
Encyclopedia
The C1q complex is potentially multivalent
for attachment to the complement fixation sites of immunoglobulin.
The sites are on the CH2 domain of IgG and, it is thought, on the CH4 domain of IgM
.
The appropriate peptide sequence
of the complement fixing site might become exposed following complexing of the immunoglobulin, or the sites might always be available, but might require multiple attachment by C1q with critical geometry in order to achieve the necessary avidity
.
The 80-amino acid helical component of each triple peptide contain many Gly-X-Y sequences, where X and Y are proline
, isoleucine
, or hydroxylysine
; they, therefore, strongly resemble collagen
fibrils.
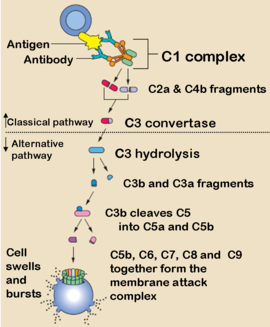 It is assumed that the globular ends are the sites for multivalent attachment to the complement fixing sites in immune complexed immunoglobulin. Patients suffering from Lupus erythematosus often have deficient expression of C1q.
It is assumed that the globular ends are the sites for multivalent attachment to the complement fixing sites in immune complexed immunoglobulin. Patients suffering from Lupus erythematosus often have deficient expression of C1q.
Multivalent
Multivalent may refer to:*Multivalent , the property of having multiple valences*Polyvalent: something which has many values, meanings, or appeals*Multivalent , a Java-based web browser...
for attachment to the complement fixation sites of immunoglobulin.
The sites are on the CH2 domain of IgG and, it is thought, on the CH4 domain of IgM
IGM
IGM as an acronym or abbreviation can refer to:* Immunoglobulin M , the primary antibody against A and B antigens on red blood cells* International Grandmaster, a chess ranking* intergalactic medium* Intragroup medium - see: Intracluster medium...
.
The appropriate peptide sequence
Peptide sequence
Peptide sequence or amino acid sequence is the order in which amino acid residues, connected by peptide bonds, lie in the chain in peptides and proteins. The sequence is generally reported from the N-terminal end containing free amino group to the C-terminal end containing free carboxyl group...
of the complement fixing site might become exposed following complexing of the immunoglobulin, or the sites might always be available, but might require multiple attachment by C1q with critical geometry in order to achieve the necessary avidity
Avidity
In proteins, avidity is a term used to describe the combined strength of multiple bond interactions. Avidity is distinct from affinity, which is a term used to describe the strength of a single bond...
.
Structure
C1q is a 400kDa protein formed from 18 peptide chains in 3 subunits of 6. Each 6 peptide subunit consists of a Y-shaped pair of triple peptide helices joined at the stem and ending in a globular non-helical head.The 80-amino acid helical component of each triple peptide contain many Gly-X-Y sequences, where X and Y are proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
, or hydroxylysine
Hydroxylysine
5-Hydroxylysine is an amino acid with the molecular formula C6H14N2O3. It was first discovered in 1921 by Donald Van Slyke. It is a hydroxy derivative of lysine. It is most widely known as a component of collagen....
; they, therefore, strongly resemble collagen
Collagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
fibrils.
Function


