
CJK Unified Ideographs
Encyclopedia
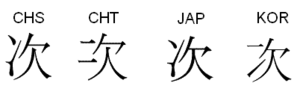
Han unification
Han unification is an effort by the authors of Unicode and the Universal Character Set to map multiple character sets of the so-called CJK languages into a single set of unified characters. Han characters are a common feature of written Chinese , Japanese , Korean , and—at least historically—other...
the common (shared) characters were identified, and named "CJK Unified Ideographs". As of version 6.0, Unicode defines a total of 74,616 CJK Unified Ideographs.
The terms ideographs or ideograms may be misleading, since the Chinese script is not strictly a picture writing system.
Historically, the Vietnamese writing system Chữ Nôm uses Chinese ideographs too, so sometimes the abbreviation "CJKV" is used. Since the 16th century, an extended Latin alphabet has been used in Vietnam.
CJK Unified Ideographs
The basic CJK Unified Ideographs block (4E00-9FFF) contains 20,940 basic Chinese characters, not only those used in the Chinese writing system but also the KanjiKanji
Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet...
used in the Japanese writing system
Japanese writing system
The modern Japanese writing system uses three main scripts:*Kanji, adopted Chinese characters*Kana, a pair of syllabaries , consisting of:...
and the Hanja
Hanja
Hanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation...
, whose use is diminishing in Korea
Korean mixed script
Korean mixed script is a form of writing that uses both Hangul and hanja .The script has never been used for languages other than Korean. In North Korea, writing in mixed script was replaced by writing only in Hangul in the middle of the 20th century and has not been used since...
. Many characters in this block are used in all three writing system
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
s, while others are in only one or two of the three. Chinese characters were also used in the Vietnamese
Vietnamese language
Vietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam...
Chữ nôm script (now obsolete). The first 20,902 characters in the block are arranged according to the Kangxi Dictionary
Kangxi dictionary
The Kangxi Dictionary was the standard Chinese dictionary during the 18th and 19th centuries. The Kangxi Emperor of the Manchu Qing Dynasty ordered its compilation in 1710. The creator innovated greatly by reusing and confirming the new Zihui system of 596 radicals, since then known as 596 Kangxi...
ordering of radical
Radical (Chinese character)
A Chinese radical is a component of a Chinese character. The term may variously refer to the original semantic element of a character, or to any semantic element, or, loosely, to any element whatever its origin or purpose...
s. In this system the characters written with the fewest strokes are listed first. The remaining characters were added later, and so are not in radical sequence.
The block is the result of Han unification
Han unification
Han unification is an effort by the authors of Unicode and the Universal Character Set to map multiple character sets of the so-called CJK languages into a single set of unified characters. Han characters are a common feature of written Chinese , Japanese , Korean , and—at least historically—other...
, which was somewhat controversial in the Far East. Since Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters were coded in the same location, the appearance of a selected glyph could depend on the particular font being used. However, the source separation rule states that characters encoded separately in an earlier character set would remain separate in the new Unicode encoding.
Using variation selectors it is possible to specify certain variant CJK ideograms within Unicode. The Adobe-Japan1 character set proposal, which actually calls for 14,658 ideographic variation sequences, is an extreme example of the use of variation selectors.
Charts
4E00-62FF,6300-77FF,
7800-8CFF,
8D00-9FFF.
Sources
The code points in this block are assigned under Source Separation Rule.China
| Code | Standard | Character count | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| G0 | GB 2312-80 GB 2312 GB2312 is the registered internet name for a key official character set of the People's Republic of China, used for simplified Chinese characters... |
6763 | |
| G1 | GB 12345-90 | 2352 | |
| G3 | GB 7589-87 unsimplified form | 7237 | |
| G5 | GB 7590-87 unsimplified form | 7039 | |
| G7 | Modern Chinese general character chart | 642 | |
| G8 | GB 8565-89 | 290 | |
Taiwan
| Code | Standard | Character count | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | CNS 11643-1986 plane 1 | 5401+9 | |
| T2 | CNS 11643-1986 plane 2 | 7650 | |
| TE | CNS 11643-1986 plane 14 | 6319+239+10 | 239 from CCIII, 10 from XCCS |
Japan
| Code | Standard | Character count | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| J0 | JIS X 0208-90 JIS X 0208 JIS X 0208 is a 2-byte character set specified as a Japanese Industrial Standard, containing 6879 graphic characters suitable for writing text, place names, personal names, and so forth in the Japanese language. The official title of the current standard is... |
6335+1 | |
| J1 | JIS X 0212-90 JIS X 0212 JIS X 0212 is a Japanese Industrial Standard defining coded character set for encoding the characters used in Japanese. This standard extends JIS X 0208.-History:... |
5801 | |
South Korea
| Code | Standard | Character count | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| K0 | KS C 5601-87 | 4888 | includes 268 duplicates |
| K1 | KS C 5657-91 | 2856 | |
Others
- ANSI Z39.64-1989
- Big5Big5Big-5 or Big5 is a character encoding method used in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau for Traditional Chinese characters.Mainland China, which uses Simplified Chinese Characters, uses the GB instead.- Organization :...
- CCCII plane 1
- GB 12052-89
- JEFJefis a fast-food chain on Okinawa Island, with five restaurants in and around Naha . They sport a menu featuring many homebrewn Okinawan specialties such as the Nūyaru burger and the Gōyā burger, hamburgers with a filling of SPAM and bitter melon omelet. They also have fried gōyā rings, similar to...
- Chinese telegraph codeChinese telegraph codeThe Chinese Telegraph Code, Chinese Telegraphic Code, or Chinese Commercial Code is a four-digit decimal code for electrically telegraphing messages written with Chinese characters.- Encoding and decoding :...
- Taiwan telegraph code
- Xerox Chinese
In Unicode 4.1, 14 HKSCS-2004
HKSCS
The Hong Kong Supplementary Character Set is a set of Chinese characters -- 4,702 in total in the initial release—used in Cantonese, as well as when writing the names of some places in Hong Kong . It evolved from the preceding Government Chinese Character Set or GCCS...
characters and 8 GB 18030
GB 18030
GB18030 is a Chinese government standard describing the required language and character support necessary for software in China. In addition to the "GB18030 code page" this standard contains requirements about which scripts must be supported, font support, etc....
characters were assigned to between U+9FA6 and U+9FBB code points.

