
Carolinas Campaign
Encyclopedia
The Carolinas Campaign was the final campaign in the Western Theater
of the American Civil War
. In January 1865, Union
Maj. Gen.
William Tecumseh Sherman
advanced north from Savannah, Georgia
, through the Carolinas
, with the intention of linking up with Union forces in Virginia
. The defeat of Confederate
Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
's army at the Battle of Bentonville
in March, and its surrender in April, represented the loss of the final major army of the Confederacy.
, he was ordered by Union Army general-in-chief Lt. Gen.
Ulysses S. Grant
to embark his army on ships to reinforce the Army of the Potomac
and the Army of the James
in Virginia, where Grant was bogged down in the Siege of Petersburg
against Confederate General Robert E. Lee
. Sherman had bigger things in mind. He predicted on January 5, 1865: "I do think that in the several grand epochs of this war, my name will have a prominent part." He persuaded Grant that he should march north through the Carolinas instead, destroying everything of military value along the way, similar to his march to the sea through Georgia
. Sherman was particularly interested in targeting South Carolina
, the first state to secede
from the Union, for the effect it would have on Southern morale.
Sherman's army commenced toward Columbia, South Carolina
, in late January 1865. His 60,079 men were divided into three wings: the Army of the Tennessee
, under Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard
, the Army of the Ohio
under Maj. Gen. John M. Schofield, and two corps, the XIV and XX, under Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum, which was later formally designated the Army of Georgia
. Reinforcements arrived regularly during his march north, and by April 1 he commanded 88,948 men.
Sherman's opponents on the Confederate side had considerably fewer men. The primary force in the Carolinas was the battered Army of Tennessee, again under the command of General Joseph E. Johnston (who had been relieved of duty by Confederate President Jefferson Davis
during the Atlanta Campaign
against Sherman). His strength was recorded in mid-March at 9,513 and 15,188 by mid-April. The army was organized into three corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. William J. Hardee
, Lt. Gen. Alexander P. Stewart
, and Lt. Gen. Stephen D. Lee
. Also in the Carolinas were cavalry forces from the division
of Maj. Gen. Wade Hampton
and a small number in Wilmington
under Gen. Braxton Bragg
.
Sherman's plan was to bypass the minor Confederate troop concentrations at Augusta, Georgia
, and Charleston, South Carolina
, and reach Goldsboro, North Carolina
, by March 15. As with his Georgia operations, Sherman marched his armies in multiple directions simultaneously, confusing the scattered Confederate defenders as to his first true objective, which was the state capital of Columbia.
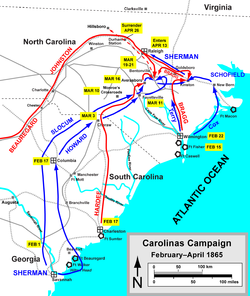 The following battles were fought in the Carolinas Campaign.
The following battles were fought in the Carolinas Campaign.
attempted to prevent the crossing of the Salkehatchie River
by the right wing of Sherman's army. The Union division under Maj. Gen. Francis P. Blair (Howard's army) crossed the river and assaulted McLaws's flank. McLaws withdrew to Branchville
, causing only one day's delay in the Union advance.
On February 17, Columbia surrendered to Sherman, and Hampton's cavalry retreated from the city. Union forces were overwhelmed by throngs of liberated Federal prisoners and emancipated African American
s. Many soldiers took advantage of ample supplies of liquor in the city and began to drink. Fires began in the city, and high winds spread the flames across a wide area. Most of the central city was destroyed, and the city's fire companies found it difficult to operate in conjunction with the invading Union army, many of whom were also trying to put out the fire. The burning of Columbia has engendered controversy ever since, with some claiming the fires were accidental, others stating they were a deliberate act of vengeance, and others claiming that the fires were set by retreating Confederate soldiers who lit bales of cotton on their way out of town. On that same day, the Confederates evacuated Charleston. On February 18, Sherman's forces destroyed virtually anything of military value in Columbia, including railroad depots, warehouses, arsenals, and machine shops. On February 22, Wilmington surrendered.
toward Goldsboro. On March 7, Cox's advance was stopped by divisions under Gen. Braxton Bragg's command at Southwest Creek south of Kinston, North Carolina
. On March 8, the Confederates attempted to seize the initiative by attacking the Union flanks. After initial success, their attacks stalled because of faulty communications. On March 9, the Union forces were reinforced and beat back Bragg's renewed attacks on March 10 after heavy fighting. Bragg withdrew across the Neuse River
and was unable to prevent the fall of Kinston on March 14.
) County. Early on March 10, Hampton's Confederate cavalry surprised the Federals in their camps, driving them back in confusion and capturing wagons and artillery. The Federals regrouped and counterattacked, regaining their artillery and camps after a desperate fight. With Union reinforcements on the way, the Confederates withdrew.
.
in Greensboro
in mid-April, he told the Confederate president:
On April 18, three days after the death of President
Abraham Lincoln
, Johnston signed an armistice
with Sherman at Bennett Place
, a farmhouse near Durham Station
. Sherman got himself into political hot water by offering terms of surrender to Johnston that encompassed political issues as well as military, without authorization from General Grant or the United States government. The confusion on this issue lasted until April 26, when Johnston agreed to purely military terms and formally surrendered his army and all Confederate forces in the Carolinas, Georgia, and Florida
. It was the second significant surrender that month; on April 9, Robert E. Lee had surrendered the Army of Northern Virginia
at Appomattox Court House
. It was the virtual end for the Confederacy, although some smaller forces held out, particularly in the Trans-Mississippi
region, into the summer.
Western Theater of the American Civil War
This article presents an overview of major military and naval operations in the Western Theater of the American Civil War.-Theater of operations:...
of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
. In January 1865, Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
Maj. Gen.
Major general (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, and United States Air Force, major general is a two-star general-officer rank, with the pay grade of O-8. Major general ranks above brigadier general and below lieutenant general...
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman was an American soldier, businessman, educator and author. He served as a General in the Union Army during the American Civil War , for which he received recognition for his outstanding command of military strategy as well as criticism for the harshness of the "scorched...
advanced north from Savannah, Georgia
Savannah, Georgia
Savannah is the largest city and the county seat of Chatham County, in the U.S. state of Georgia. Established in 1733, the city of Savannah was the colonial capital of the Province of Georgia and later the first state capital of Georgia. Today Savannah is an industrial center and an important...
, through the Carolinas
The Carolinas
The Carolinas is a term used in the United States to refer collectively to the states of North and South Carolina. Together, the two states + have a population of 13,942,126. "Carolina" would be the fifth most populous state behind California, Texas, New York, and Florida...
, with the intention of linking up with Union forces in Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
. The defeat of Confederate
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston was a career U.S. Army officer, serving with distinction in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars, and was also one of the most senior general officers in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
's army at the Battle of Bentonville
Battle of Bentonville
At 3 p.m., Confederate infantry from the Army of Tennessee launched an attack and drove the Union left flank back in confusion, nearly capturing Carlin in the process and overrunning the XIV Corps field hospital. Confederates under Maj. Gen. D.H. Hill filled the vacuum left by the retreating...
in March, and its surrender in April, represented the loss of the final major army of the Confederacy.
Background and opposing forces
After Sherman captured Savannah, the culmination of his march to the seaSherman's March to the Sea
Sherman's March to the Sea is the name commonly given to the Savannah Campaign conducted around Georgia from November 15, 1864 to December 21, 1864 by Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman of the Union Army in the American Civil War...
, he was ordered by Union Army general-in-chief Lt. Gen.
Lieutenant General (United States)
In the United States Army, the United States Air Force and the United States Marine Corps, lieutenant general is a three-star general officer rank, with the pay grade of O-9. Lieutenant general ranks above major general and below general...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant was the 18th President of the United States as well as military commander during the Civil War and post-war Reconstruction periods. Under Grant's command, the Union Army defeated the Confederate military and ended the Confederate States of America...
to embark his army on ships to reinforce the Army of the Potomac
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the major Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.-History:The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861, but was then only the size of a corps . Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen...
and the Army of the James
Army of the James
The Army of the James was a Union Army that was composed of units from the Department of Virginia and North Carolina and served along the James River during the final operations of the American Civil War in Virginia.-History:...
in Virginia, where Grant was bogged down in the Siege of Petersburg
Siege of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg Campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War...
against Confederate General Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
. Sherman had bigger things in mind. He predicted on January 5, 1865: "I do think that in the several grand epochs of this war, my name will have a prominent part." He persuaded Grant that he should march north through the Carolinas instead, destroying everything of military value along the way, similar to his march to the sea through Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
. Sherman was particularly interested in targeting South Carolina
South Carolina
South Carolina is a state in the Deep South of the United States that borders Georgia to the south, North Carolina to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Originally part of the Province of Carolina, the Province of South Carolina was one of the 13 colonies that declared independence...
, the first state to secede
Secession
Secession is the act of withdrawing from an organization, union, or especially a political entity. Threats of secession also can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.-Secession theory:...
from the Union, for the effect it would have on Southern morale.
Sherman's army commenced toward Columbia, South Carolina
Columbia, South Carolina
Columbia is the state capital and largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The population was 129,272 according to the 2010 census. Columbia is the county seat of Richland County, but a portion of the city extends into neighboring Lexington County. The city is the center of a metropolitan...
, in late January 1865. His 60,079 men were divided into three wings: the Army of the Tennessee
Army of the Tennessee
The Army of the Tennessee was a Union army in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, named for the Tennessee River. It should not be confused with the similarly named Army of Tennessee, a Confederate army named after the State of Tennessee....
, under Maj. Gen. Oliver O. Howard
Oliver O. Howard
Oliver Otis Howard was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War...
, the Army of the Ohio
Army of the Ohio
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.-History:...
under Maj. Gen. John M. Schofield, and two corps, the XIV and XX, under Maj. Gen. Henry W. Slocum, which was later formally designated the Army of Georgia
Army of Georgia
The Army of Georgia was a Union army that constituted the Left Wing of Major General William T. Sherman's Army Group during the March to the Sea and the Carolinas Campaign.-History:...
. Reinforcements arrived regularly during his march north, and by April 1 he commanded 88,948 men.
Sherman's opponents on the Confederate side had considerably fewer men. The primary force in the Carolinas was the battered Army of Tennessee, again under the command of General Joseph E. Johnston (who had been relieved of duty by Confederate President Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Finis Davis , also known as Jeff Davis, was an American statesman and leader of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, serving as President for its entire history. He was born in Kentucky to Samuel and Jane Davis...
during the Atlanta Campaign
Atlanta Campaign
The Atlanta Campaign was a series of battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War throughout northwest Georgia and the area around Atlanta during the summer of 1864. Union Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman invaded Georgia from the vicinity of Chattanooga, Tennessee, beginning in May...
against Sherman). His strength was recorded in mid-March at 9,513 and 15,188 by mid-April. The army was organized into three corps, commanded by Lt. Gen. William J. Hardee
William J. Hardee
William Joseph Hardee was a career U.S. Army officer, serving during the Second Seminole War and fighting in the Mexican-American War...
, Lt. Gen. Alexander P. Stewart
Alexander P. Stewart
Alexander Peter Stewart was a career United States Army officer, college professor, and a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.-Early life and career:...
, and Lt. Gen. Stephen D. Lee
Stephen D. Lee
Stephen Dill Lee was an American soldier, planter, legislator, and author. He was the youngest Confederate lieutenant general during the American Civil War, and later served as the first president of Mississippi A&M College...
. Also in the Carolinas were cavalry forces from the division
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
of Maj. Gen. Wade Hampton
Wade Hampton III
Wade Hampton III was a Confederate cavalry leader during the American Civil War and afterward a politician from South Carolina, serving as its 77th Governor and as a U.S...
and a small number in Wilmington
Wilmington, North Carolina
Wilmington is a port city in and is the county seat of New Hanover County, North Carolina, United States. The population is 106,476 according to the 2010 Census, making it the eighth most populous city in the state of North Carolina...
under Gen. Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg
Braxton Bragg was a career United States Army officer, and then a general in the Confederate States Army—a principal commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War and later the military adviser to Confederate President Jefferson Davis.Bragg, a native of North Carolina, was...
.
Sherman's plan was to bypass the minor Confederate troop concentrations at Augusta, Georgia
Augusta, Georgia
Augusta is a consolidated city in the U.S. state of Georgia, located along the Savannah River. As of the 2010 census, the Augusta–Richmond County population was 195,844 not counting the unconsolidated cities of Hephzibah and Blythe.Augusta is the principal city of the Augusta-Richmond County...
, and Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the second largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It was made the county seat of Charleston County in 1901 when Charleston County was founded. The city's original name was Charles Towne in 1670, and it moved to its present location from a location on the west bank of the...
, and reach Goldsboro, North Carolina
Goldsboro, North Carolina
Goldsboro is a city in Wayne County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 37,597 at the 2008 census estimate. It is the principal city of and is included in the Goldsboro, North Carolina Metropolitan Statistical Area. The nearby town of Waynesboro was founded in 1787 and Goldsboro was...
, by March 15. As with his Georgia operations, Sherman marched his armies in multiple directions simultaneously, confusing the scattered Confederate defenders as to his first true objective, which was the state capital of Columbia.
Battles

Rivers' Bridge (February 3, 1865)
The Confederate division of Maj. Gen. Lafayette McLawsLafayette McLaws
Lafayette McLaws was a United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War.-Early life:...
attempted to prevent the crossing of the Salkehatchie River
Salkehatchie River
The Salkehatchie River originates near the City of Barnwell, South Carolina and accepts drainage from Turkey Creek and Whippy Swamp before merging with the Little Salkehatchie River to form the Combahee River Basin, which empties into Saint Helena Sound and the Atlantic Ocean...
by the right wing of Sherman's army. The Union division under Maj. Gen. Francis P. Blair (Howard's army) crossed the river and assaulted McLaws's flank. McLaws withdrew to Branchville
Branchville, South Carolina
Branchville is a town in Orangeburg County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 1,083 at the 2000 census.When the train depot was in use, three presidents stopped by the depot: William H...
, causing only one day's delay in the Union advance.
On February 17, Columbia surrendered to Sherman, and Hampton's cavalry retreated from the city. Union forces were overwhelmed by throngs of liberated Federal prisoners and emancipated African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
s. Many soldiers took advantage of ample supplies of liquor in the city and began to drink. Fires began in the city, and high winds spread the flames across a wide area. Most of the central city was destroyed, and the city's fire companies found it difficult to operate in conjunction with the invading Union army, many of whom were also trying to put out the fire. The burning of Columbia has engendered controversy ever since, with some claiming the fires were accidental, others stating they were a deliberate act of vengeance, and others claiming that the fires were set by retreating Confederate soldiers who lit bales of cotton on their way out of town. On that same day, the Confederates evacuated Charleston. On February 18, Sherman's forces destroyed virtually anything of military value in Columbia, including railroad depots, warehouses, arsenals, and machine shops. On February 22, Wilmington surrendered.
Wyse Fork (March 7–10)
Schofield planned to advance inland from Wilmington in February. At the same time, he assigned Maj. Gen. Jacob D. Cox to direct Union forces from New BernNew Bern, North Carolina
New Bern is a city in Craven County, North Carolina with a population of 29,524 as of the 2010 census.. It is located at the confluence of the Trent and the Neuse rivers...
toward Goldsboro. On March 7, Cox's advance was stopped by divisions under Gen. Braxton Bragg's command at Southwest Creek south of Kinston, North Carolina
Kinston, North Carolina
Kinston is a city in Lenoir County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 23,688 at the 2000 census. The population was estimated at 22,360 in 2008. It has been the county seat of Lenoir County since its formation in 1791 . Kinston is located in North Carolina's Inner Banks...
. On March 8, the Confederates attempted to seize the initiative by attacking the Union flanks. After initial success, their attacks stalled because of faulty communications. On March 9, the Union forces were reinforced and beat back Bragg's renewed attacks on March 10 after heavy fighting. Bragg withdrew across the Neuse River
Neuse River
The Neuse River is a river rising in the Piedmont of North Carolina and emptying into Pamlico Sound below New Bern. Its total length is approximately , making it the longest river entirely contained in North Carolina. The Trent River joins it at New Bern. Its drainage basin, measuring in area,...
and was unable to prevent the fall of Kinston on March 14.
Monroe's Cross Roads (March 10)
As Sherman's army advanced into North Carolina, Maj. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick's Cavalry Division screened its left flank. On the evening of March 9, two of Kilpatrick's brigades encamped near the Charles Monroe House in Cumberland (now HokeHoke County, North Carolina
-Demographics:As of the census of 2010, there were 46,952 people, 11,373 households, and 8,745 families residing in the county. The population density was 86 people per square mile . There were 12,518 housing units at an average density of 32 per square mile...
) County. Early on March 10, Hampton's Confederate cavalry surprised the Federals in their camps, driving them back in confusion and capturing wagons and artillery. The Federals regrouped and counterattacked, regaining their artillery and camps after a desperate fight. With Union reinforcements on the way, the Confederates withdrew.
Averasborough (March 16)
On the afternoon of March 15, Kilpatrick's cavalry came up against Hardee's corps deployed across the Raleigh Road near Smithville. After feeling out the Confederate defenses, Kilpatrick withdrew and called for infantry support. During the night, four divisions of the XX Corps arrived to confront the Confederates. At dawn, March 16, the Federals advanced on a division front, driving back skirmishers, but they were stopped by the main Confederate line and a counterattack. Mid-morning, the Federals renewed their advance with strong reinforcements and drove the Confederates from two lines of works, but they were repulsed at a third line. Late afternoon, the Union XIV Corps began to arrive on the field but was unable to deploy before dark because of the swampy ground. Hardee retreated during the night after holding up the Union advance for nearly two days.Bentonville (March 19–21)
While Slocum's advance was stalled at Averasborough by Hardee's troops, the right wing of Sherman's army under Howard marched toward Goldsboro. On March 19, Slocum encountered the entrenched Confederates of Gen. Joseph E. Johnston who had concentrated to meet his advance at Bentonville. Johnston had increased his forces to about 21,000 men by absorbing the troops under Bragg who had abandoned Wilmington. Late afternoon, Johnston attacked, crushing the line of the XIV Corps. Only strong counterattacks and desperate fighting south of the Goldsborough Road blunted the Confederate offensive. Elements of the XX Corps were thrown into the action as they arrived on the field. Five Confederate attacks failed to dislodge the Federal defenders, and darkness ended the first day's fighting. During the night, Johnston contracted his line into a "V" to protect his flanks with Mill Creek to his rear. On March 20, Slocum was heavily reinforced, but fighting was sporadic. Sherman was inclined to let Johnston retreat. On March 21, however, Johnston remained in position while he removed his wounded. Skirmishing heated up along the entire front. In the afternoon, Maj. Gen. Joseph Mower led his Union division along a narrow trace that carried it across Mill Creek into Johnston's rear. Confederate counterattacks stopped Mower's advance, saving the army's only line of communication and retreat. Mower withdrew, ending fighting for the day. During the night, Johnston retreated across the bridge at Bentonville. Union forces pursued at first light, driving back Wheeler's rearguard and saving the bridge. Federal pursuit was halted at Hannah's Creek after a severe skirmish. Sherman, after regrouping at Goldsboro, pursued Johnston toward RaleighRaleigh, North Carolina
Raleigh is the capital and the second largest city in the state of North Carolina as well as the seat of Wake County. Raleigh is known as the "City of Oaks" for its many oak trees. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the city's 2010 population was 403,892, over an area of , making Raleigh...
.
Aftermath
Sherman's Carolina Campaign, in which his troops marched 425 miles (684 km) in 50 days, had been similar to his march to the sea through Georgia, although physically more demanding. However, the Confederate forces opposing him were much smaller and more dispirited. When Joseph E. Johnston met with Jefferson DavisJefferson Davis
Jefferson Finis Davis , also known as Jeff Davis, was an American statesman and leader of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, serving as President for its entire history. He was born in Kentucky to Samuel and Jane Davis...
in Greensboro
Greensboro, North Carolina
Greensboro is a city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is the third-largest city by population in North Carolina and the largest city in Guilford County and the surrounding Piedmont Triad metropolitan region. According to the 2010 U.S...
in mid-April, he told the Confederate president:
On April 18, three days after the death of President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
, Johnston signed an armistice
Armistice
An armistice is a situation in a war where the warring parties agree to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, but may be just a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace...
with Sherman at Bennett Place
Bennett Place
Bennett Place, sometimes known as Bennett Farm, in Durham, North Carolina was the site of the largest surrender of Confederate soldiers ending the American Civil War, on April 26, 1865.-History:...
, a farmhouse near Durham Station
Durham, North Carolina
Durham is a city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is the county seat of Durham County and also extends into Wake County. It is the fifth-largest city in the state, and the 85th-largest in the United States by population, with 228,330 residents as of the 2010 United States census...
. Sherman got himself into political hot water by offering terms of surrender to Johnston that encompassed political issues as well as military, without authorization from General Grant or the United States government. The confusion on this issue lasted until April 26, when Johnston agreed to purely military terms and formally surrendered his army and all Confederate forces in the Carolinas, Georgia, and Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
. It was the second significant surrender that month; on April 9, Robert E. Lee had surrendered the Army of Northern Virginia
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, as well as the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac...
at Appomattox Court House
Appomattox Court House
The Appomattox Courthouse is the current courthouse in Appomattox, Virginia built in 1892. It is located in the middle of the state about three miles northwest of the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park, once known as Clover Hill - home of the original Old Appomattox Court House...
. It was the virtual end for the Confederacy, although some smaller forces held out, particularly in the Trans-Mississippi
Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War
The Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War was the major military and naval operations west of the Mississippi River. The area excluded the states and territories bordering the Pacific Ocean, which formed the Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War.The campaign classification...
region, into the summer.
Further reading
- Taylor, Paul. Orlando M. Poe: Civil War General and Great Lakes Engineer. Kent, OH: Kent State University Press, 2009. ISBN 978-1-60635-040-9.

