
Cavity Perturbation Theory
Encyclopedia
Cavity
perturbation theory
describes methods for derivation of perturbation
formula
e for performance changes of a cavity resonator. These performance changes are assumed to be caused by either introduction of a small foreign object into the cavity or a small deformation of its boundary.
for original and perturbed cavities can be used to derive expressions for resulting resonant frequency shifts.
and/or permeability
), a corresponding change in resonant frequency can be approximated as :
where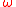 is the angular
is the angular
resonant frequency of the perturbed cavity,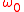 is the resonant frequency of the original cavity,
is the resonant frequency of the original cavity, 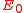 and
and 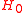 represent original electric
represent original electric
and magnetic field
respectively,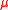 and
and  are original permeability
are original permeability
and permittivity
respectively, while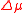 and
and 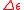 are changes in original permeability and permittivity
are changes in original permeability and permittivity
introduced by material change.
Expression can be rewritten in terms of stored energies
as :
where W is the total energy stored in the original cavity and and
and 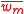 are electric
are electric
and magnetic energy densities respectively.
Expression for change in resonant frequency can additionally be written in terms of time-average stored energies as :
where and
and 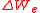 represent time-average electric and magnetic energies contained in
represent time-average electric and magnetic energies contained in 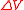 .
.
This expression can also be written in terms of energy densities as:
s. Since ex-ante knowledge of the resonant frequency, resonant frequency shift and electromagnetic field
s is necessary in order to extrapolate material properties, these measurement techniques generally make use of standard resonant cavities where resonant frequencies and electromagnetic fields are well known. Two examples of such standard resonant cavities are rectangular and circular waveguide
cavities and coaxial cable
s resonators . Cavity perturbation measurement techniques for material characterization are used in many fields ranging from physics and material science to medicine and biology .
For rectangular waveguide cavity, field distribution of dominant 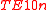 mode is well known. Ideally, the material to be measured is introduced into the cavity at the position of maximum electric or magnetic field. When the material is introduced at the position of maximum electric field, then the contribution of magnetic field to perturbed frequency shift is very small and can be ignored. In this case, we can use perturbation theory to derive expressions for real and imaginary components of complex material permittivity
mode is well known. Ideally, the material to be measured is introduced into the cavity at the position of maximum electric or magnetic field. When the material is introduced at the position of maximum electric field, then the contribution of magnetic field to perturbed frequency shift is very small and can be ignored. In this case, we can use perturbation theory to derive expressions for real and imaginary components of complex material permittivity
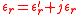 as :
as :
where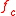 and
and 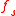 represent resonant frequencies of original cavity and perturbed cavity respectively,
represent resonant frequencies of original cavity and perturbed cavity respectively, 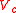 and
and 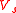 represent volumes of original cavity and material sample respectively,
represent volumes of original cavity and material sample respectively, 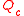 and
and 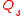 represent quality factors
represent quality factors
of original and perturbed cavities respectively.
Once the complex permittivity of the material is known, we can easily calculate its effective conductivity
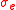 and dielectric
and dielectric
loss tangent
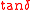 as :
as :
where f is the frequency of interest and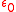 is the free space permittivity.
is the free space permittivity.
Similarly, if the material is introduced into the cavity at the position of maximum magnetic field, then the contribution of electric field to perturbed frequency shift is very small and can be ignored. In this case, we can use perturbation theory to derive expressions for complex material permeability
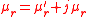 as :
as :
where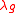 is the guide wavelength (calculated as
is the guide wavelength (calculated as  ).
).
Resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior, that is, it naturally oscillates at some frequencies, called its resonant frequencies, with greater amplitude than at others. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical...
perturbation theory
Perturbation theory
Perturbation theory comprises mathematical methods that are used to find an approximate solution to a problem which cannot be solved exactly, by starting from the exact solution of a related problem...
describes methods for derivation of perturbation
Perturbation
Perturbation or perturb may refer to any of numerous concepts in several fields:* Perturbation theory, mathematical methods that give approximate solutions to problems that cannot be solved exactly...
formula
Formula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
e for performance changes of a cavity resonator. These performance changes are assumed to be caused by either introduction of a small foreign object into the cavity or a small deformation of its boundary.
General theory
When a resonant cavity is perturbed, i.e. when a foreign object with distinct material properties is introduced into the cavity or when a general shape of the cavity is changed, electromagnetic fields inside the cavity change accordingly. The underlying assumption of cavity perturbation theory is that electromagnetic fields inside the cavity after the change differ by a very small amount from the fields before the change. Then Maxwell's equationsMaxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations are a set of partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electrodynamics, classical optics, and electric circuits. These fields in turn underlie modern electrical and communications technologies.Maxwell's equations...
for original and perturbed cavities can be used to derive expressions for resulting resonant frequency shifts.
Material perturbation
When a material within a cavity is changed (permittivityPermittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
and/or permeability
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
), a corresponding change in resonant frequency can be approximated as :
where
 is the angular
is the angularAngular frequency
In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
resonant frequency of the perturbed cavity,
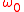 is the resonant frequency of the original cavity,
is the resonant frequency of the original cavity, 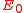 and
and 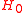 represent original electric
represent original electricElectric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
and magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
respectively,
 and
and  are original permeability
are original permeabilityPermeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
and permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
respectively, while
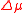 and
and 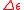 are changes in original permeability and permittivity
are changes in original permeability and permittivityPermittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
introduced by material change.
Expression can be rewritten in terms of stored energies
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
as :
where W is the total energy stored in the original cavity and
 and
and 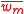 are electric
are electricElectric potential energy
Electric potential energy, or electrostatic potential energy, is a potential energy that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a defined system...
and magnetic energy densities respectively.
Shape perturbation
When a general shape of a resonant cavity is changed, a corresponding change in resonant frequency can be approximated as :Expression for change in resonant frequency can additionally be written in terms of time-average stored energies as :
where
 and
and 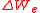 represent time-average electric and magnetic energies contained in
represent time-average electric and magnetic energies contained in 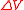 .
.This expression can also be written in terms of energy densities as:
Applications
Microwave measurement techniques based on cavity perturbation theory are generally used to determine the dielectric and magnetic parameters of materials and various circuit components such as dielectric resonatorDielectric resonator
A dielectric resonator is an electronic component that exhibits resonance for a narrow range of frequencies, generally in the microwave band. The resonance is similar to that of a circular hollow metallic waveguide, except that the boundary is defined by large change in permittivity rather than by...
s. Since ex-ante knowledge of the resonant frequency, resonant frequency shift and electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
s is necessary in order to extrapolate material properties, these measurement techniques generally make use of standard resonant cavities where resonant frequencies and electromagnetic fields are well known. Two examples of such standard resonant cavities are rectangular and circular waveguide
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure which guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. There are different types of waveguides for each type of wave...
cavities and coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
s resonators . Cavity perturbation measurement techniques for material characterization are used in many fields ranging from physics and material science to medicine and biology .
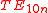 rectangular waveguide cavity
rectangular waveguide cavity
For rectangular waveguide cavity, field distribution of dominant 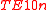 mode is well known. Ideally, the material to be measured is introduced into the cavity at the position of maximum electric or magnetic field. When the material is introduced at the position of maximum electric field, then the contribution of magnetic field to perturbed frequency shift is very small and can be ignored. In this case, we can use perturbation theory to derive expressions for real and imaginary components of complex material permittivity
mode is well known. Ideally, the material to be measured is introduced into the cavity at the position of maximum electric or magnetic field. When the material is introduced at the position of maximum electric field, then the contribution of magnetic field to perturbed frequency shift is very small and can be ignored. In this case, we can use perturbation theory to derive expressions for real and imaginary components of complex material permittivityPermittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
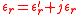 as :
as :where
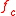 and
and 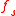 represent resonant frequencies of original cavity and perturbed cavity respectively,
represent resonant frequencies of original cavity and perturbed cavity respectively, 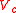 and
and 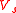 represent volumes of original cavity and material sample respectively,
represent volumes of original cavity and material sample respectively,  and
and  represent quality factors
represent quality factorsQ factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
of original and perturbed cavities respectively.
Once the complex permittivity of the material is known, we can easily calculate its effective conductivity
Conductivity
Conductivity may refer to:*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current*Conductivity , also the specific conductance, is a measurement of the electrical conductance per unit distance in an electrolytic or aqueous solution*Ionic conductivity, a measure of...
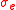 and dielectric
and dielectricDielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
loss tangent
Loss tangent
The loss tangent is a parameter of a dielectric material that quantifies its inherent dissipation of electromagnetic energy. The term refers to the tangent of the angle in a complex plane between the resistive component of an electromagnetic field and its reactive component.-Electromagnetic...
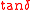 as :
as :where f is the frequency of interest and
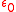 is the free space permittivity.
is the free space permittivity.Similarly, if the material is introduced into the cavity at the position of maximum magnetic field, then the contribution of electric field to perturbed frequency shift is very small and can be ignored. In this case, we can use perturbation theory to derive expressions for complex material permeability
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
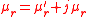 as :
as :where
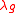 is the guide wavelength (calculated as
is the guide wavelength (calculated as  ).
).

