
Dielectric resonator
Encyclopedia
A dielectric
resonator (also dielectric resonator oscillator, DRO) is an electronic
component that exhibits resonance
for a narrow range of frequencies, generally in the microwave
band. The resonance
is similar to that of a circular hollow metallic waveguide
, except that the boundary is defined by large change in permittivity
rather than by a conductor. Dielectric resonators generally consist of a "puck" of ceramic that has a large dielectric constant
and a low dissipation factor
. The resonance frequency
is determined by the overall physical dimensions of the puck and the dielectric constant
of the material.
published a study in which he showed that dielectric structures can act just as metallic cavity resonators. He appropriately named these structures dielectric resonators. Richtmyer also demonstrated that, if exposed to free space, dielectic resonators must radiate because of the boundary conditions at the dielectric-to-air interface. These results were later used in development of DRA
(Dielectric Resonator Antenna
). Due to World War II
, lack of advanced materials and adequate manufacturing techniques, dielectric resonators fell in relative obscurity for another two decades after Richtmyer's study was published. However, in the 1960s, as high-frequency electronics and modern communications industry started to take off, dielectric resonators gained in significance. They offered a size-reducing design alternative to bulky waveguide filters
and lower-cost alternatives for electronic oscillator
, frequency selective limiter
and slow-wave circuits. In addition to cost and size, other advantages that dielectric resonators have over conventional metal cavity resonators are lower weight, material availability, and ease of manufacturing. There is a vast availability of different dielectric resonators on the market today with unloaded Q factor
on the order of 10000s.
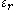 . Dielectric resonators can exhibit extremely high Q factor
. Dielectric resonators can exhibit extremely high Q factor
that is comparable to a metal walled cavity.
There are three types of resonant modes that can be excited in dielectric resonators: transverse electric
(TE), transverse magnetic (TM) or hybrid electromagnetic (HEM) modes. Theoretically, there is an infinite number of modes in each of the three groups, and desired mode is usually selected based on the application requirements. Generally,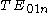 mode is used in most non-radiating applications, but other modes can have certain advantages for specific applications.
mode is used in most non-radiating applications, but other modes can have certain advantages for specific applications.
Approximate resonant frequency of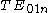 mode for an isolated cylindrical dielectric resonator can be calculated as :
mode for an isolated cylindrical dielectric resonator can be calculated as :
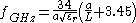
Where is the radius of the cylindrical resonator and
is the radius of the cylindrical resonator and 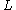 is its length. Both
is its length. Both  and
and 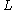 are in millimeters. Resonant frequency
are in millimeters. Resonant frequency 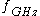 is in gigahertz. This formula is accurate to about 2% in the range:
is in gigahertz. This formula is accurate to about 2% in the range:
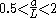
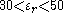
However, since a dielectric resonator is usually enclosed in a conducting cavity for most applications, the real resonant frequencies are different from the one calculated above. As conducting walls of the enclosing cavity approach the resonator, change in boundary conditions and field containment start to affect resonant frequencies. The size and type of the material encapsulating the cavity can drastically impact the performance of the resonant circuit. This phenomenon can be explained using cavity perturbation theory
. If a resonator is enclosed in a metallic cavity, resonant frequencies change in following fashion :
- if the stored energy of the displaced field is mostly electric, its resonant frequency will decrease;
- if the stored energy of the displaced field is mostly magnetic, its resonant frequency will increase. This happens to be the case for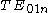 mode.
mode.
Most common problem exhibited by dielectric resonator circuits is their sensitivity to temperature variation and mechanical vibrations. Even though recent improvements in materials science and manufacturing mitigated some of these issues, compensating techniques still may be required to stabilize the circuit performance over temperature and frequency.
- Filtering applications (most common are bandpass and bandstop filters),
- Oscillators (diode
, feedback-, reflection-, transmission- and reaction-type oscillators),
- Frequency-selective limiters,
- Dielectric Resonator Antenna
(DRA) elements.
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
resonator (also dielectric resonator oscillator, DRO) is an electronic
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
component that exhibits resonance
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
for a narrow range of frequencies, generally in the microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
band. The resonance
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
is similar to that of a circular hollow metallic waveguide
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure which guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound waves. There are different types of waveguides for each type of wave...
, except that the boundary is defined by large change in permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
rather than by a conductor. Dielectric resonators generally consist of a "puck" of ceramic that has a large dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
and a low dissipation factor
Dissipation factor
In physics, the dissipation factor is a measure of loss-rate of energy of a mode of oscillation in a dissipative system. It is the reciprocal of Quality factor, which represents the quality of oscillation....
. The resonance frequency
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
is determined by the overall physical dimensions of the puck and the dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
of the material.
Historical Overview
In the late 19th century, Lord Rayleigh demonstrated that an infinitely long cylindrical rod made up of dielectric material could serve as a waveguide. Additional theoretical and experimental work done in Germany in early 20th century, offered further insight into the behavior of electromagnetic waves in dielectic rod waveguides. Since a dielectric resonator can be thought of as a truncated dielectric rod waveguide, this research was essential for scientific understanding of electromagnetic phenomena in dielectric resonators. In 1939 Robert D. RichtmyerRobert D. Richtmyer
Robert Davis Richtmyer was an American physicist, mathematician, educator, author, and musician.-Biography:Richtmyer was born on October 10, 1910 in Ithaca, New York.His father was physicist Floyd K...
published a study in which he showed that dielectric structures can act just as metallic cavity resonators. He appropriately named these structures dielectric resonators. Richtmyer also demonstrated that, if exposed to free space, dielectic resonators must radiate because of the boundary conditions at the dielectric-to-air interface. These results were later used in development of DRA
Dielectric Resonator Antenna
If the dielectric resonator is placed in an open environment, power is lost in the radiated fields. This fact makes dielectric resonators useful as antenna elements.Dielectric resonator antennas offer following attractive features:...
(Dielectric Resonator Antenna
Dielectric Resonator Antenna
If the dielectric resonator is placed in an open environment, power is lost in the radiated fields. This fact makes dielectric resonators useful as antenna elements.Dielectric resonator antennas offer following attractive features:...
). Due to World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, lack of advanced materials and adequate manufacturing techniques, dielectric resonators fell in relative obscurity for another two decades after Richtmyer's study was published. However, in the 1960s, as high-frequency electronics and modern communications industry started to take off, dielectric resonators gained in significance. They offered a size-reducing design alternative to bulky waveguide filters
RF and microwave filter
Radio frequency and microwave filters represent a class of electronic filter, designed to operate on signals in the megahertz to gigahertz frequency ranges...
and lower-cost alternatives for electronic oscillator
Electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices...
, frequency selective limiter
Limiter
In electronics, a limiter is a circuit that allows signals below a specified input power to pass unaffected while attenuating the peaks of stronger signals that exceed this input power....
and slow-wave circuits. In addition to cost and size, other advantages that dielectric resonators have over conventional metal cavity resonators are lower weight, material availability, and ease of manufacturing. There is a vast availability of different dielectric resonators on the market today with unloaded Q factor
Q factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
on the order of 10000s.
Theory of Operation
Although dielectric resonators display many similarities to resonant metal cavities, there is one important difference between the two: while the electric and magnetic fields are zero outside the walls of the metal cavity (i.e. open circuit boundary conditions are fully satisfied), these fields are not zero outside the dielectric walls of the resonator (i.e. open circuit boundary conditions are approximately satisfied). Even so, electric and magnetic fields decay from their maximum values considerably when they are away from the resonator walls. Most of the energy is stored in the resonator at a given resonant frequency for a sufficiently high dielectric constantDielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
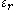 . Dielectric resonators can exhibit extremely high Q factor
. Dielectric resonators can exhibit extremely high Q factorQ factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
that is comparable to a metal walled cavity.
There are three types of resonant modes that can be excited in dielectric resonators: transverse electric
Transverse mode
A transverse mode of a beam of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of radiation measured in a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction of the beam...
(TE), transverse magnetic (TM) or hybrid electromagnetic (HEM) modes. Theoretically, there is an infinite number of modes in each of the three groups, and desired mode is usually selected based on the application requirements. Generally,
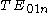 mode is used in most non-radiating applications, but other modes can have certain advantages for specific applications.
mode is used in most non-radiating applications, but other modes can have certain advantages for specific applications.Approximate resonant frequency of
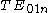 mode for an isolated cylindrical dielectric resonator can be calculated as :
mode for an isolated cylindrical dielectric resonator can be calculated as :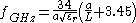
Where
 is the radius of the cylindrical resonator and
is the radius of the cylindrical resonator and 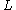 is its length. Both
is its length. Both  and
and 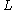 are in millimeters. Resonant frequency
are in millimeters. Resonant frequency 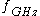 is in gigahertz. This formula is accurate to about 2% in the range:
is in gigahertz. This formula is accurate to about 2% in the range: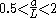
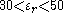
However, since a dielectric resonator is usually enclosed in a conducting cavity for most applications, the real resonant frequencies are different from the one calculated above. As conducting walls of the enclosing cavity approach the resonator, change in boundary conditions and field containment start to affect resonant frequencies. The size and type of the material encapsulating the cavity can drastically impact the performance of the resonant circuit. This phenomenon can be explained using cavity perturbation theory
Cavity Perturbation Theory
Cavity perturbation theorydescribes methods for derivation of perturbation formulae for performance changes of a cavity resonator. These performance changes are assumed to be caused by either introduction of a small foreign object into the cavity or a small deformation of its boundary.-General...
. If a resonator is enclosed in a metallic cavity, resonant frequencies change in following fashion :
- if the stored energy of the displaced field is mostly electric, its resonant frequency will decrease;
- if the stored energy of the displaced field is mostly magnetic, its resonant frequency will increase. This happens to be the case for
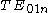 mode.
mode.Most common problem exhibited by dielectric resonator circuits is their sensitivity to temperature variation and mechanical vibrations. Even though recent improvements in materials science and manufacturing mitigated some of these issues, compensating techniques still may be required to stabilize the circuit performance over temperature and frequency.
Common Applications
Most common applications, of dielectric resonators are:- Filtering applications (most common are bandpass and bandstop filters),
- Oscillators (diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
, feedback-, reflection-, transmission- and reaction-type oscillators),
- Frequency-selective limiters,
- Dielectric Resonator Antenna
Dielectric Resonator Antenna
If the dielectric resonator is placed in an open environment, power is lost in the radiated fields. This fact makes dielectric resonators useful as antenna elements.Dielectric resonator antennas offer following attractive features:...
(DRA) elements.

