
Cell counting
Encyclopedia
Cell counting is a general name for various methods for the quantification of cell
s in molecular biology
and in medicine
.
of the cells which is required (for example: 5,000 cells per mililiter). By counting the cells in a known volume
of culture the concentration can be mediated. Here are several examples for the need for cell counting:
, whereas others rely on sophisticated electronic appliances.
 A counting chamber, also known as hemocytometer, is a microscope slide
A counting chamber, also known as hemocytometer, is a microscope slide
that is especially designed to enable cell counting. The slide has a sink in its middle; the area of the sink is marked with a grid. A drop of a cell culture
is placed in the sink. Looking at the sample under the microscope
, the researcher uses the grid to manually count the number of cells in a certain area. The depth of the sink is predefined, thus the volume of the counted culture can be calculated and with it the concentration of the cells.
Counting chambers are often used in clinical blood counts. Their advantage is being cheap and fast; this is makes them the preferred counting method in fast biological experiments in which it needs to be merely determined whether a cell culture has grown as expected. Usually the culture examined needs to be diluted, otherwise the high density of cells would make counting impossible. The need for dilution is a disadvantage, as every dilution adds inaccuracy to the measurement.
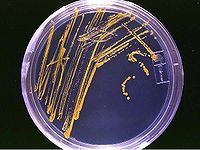 To quantify the number of cells in a culture, the cells can be simply plated on a petri dish
To quantify the number of cells in a culture, the cells can be simply plated on a petri dish
with growth medium
. If the cells are efficiently distributed on the plate, it can be generally assumed that each cell will give rise to a single colony
. The colonies can then counted, and based on the known volume of culture that was spread on the plate, the cell concentration can be calculated.
As is with counting chambers, cultures usually need to be heavily diluted prior to plating; otherwise, instead of obtaining single colonies that can be counted, a so-called "lawn" will form: thousands of colonies lying over each other. Additionally, plating is the slowest method of all: most microorganisms need at least 12 hours to form visible colonies.
and let the rest of it pass through. The higher the cell concentration is, the higher the turbidity. Spectrophotometer
s are electrical appliances that can measure turbidity very accurately. The culture is placed in a translucent cuvette
, the cuvette placed in the machine, and the turbidity measured immediately. Simple mathematical formulae help convert the detected turbidity to cell concentration. Using spectrophotometry for measuring the turbidity of cultures is known as turbidometry
.
In spectrophotometry, cultures usually do not need to be diluted, although above a certain cell density the results lose reliability. Of all the electrical appliances used for counting cells, a spectrophotometer is the cheapest and its operation the fastest and most straightforward. This has made spectrophotometry the methods of choice for quick measurements of bacterial growth and related applications. There are spectrophotometers in which several cuvettes can be inserted at one time, reducing work time even more. Additionally, there are spectrophotometers that require extremely small volumes of culture, as little as 1 microliter. This can be an advantage if the culture is precious and cannot be wasted. Spectrophotometry's drawback is its limited accuracy; it is the only method in which the cells are not counted directly—the machine measures light, not cells. This, combined with the stochastic
nature of liquid cultures, enables only an estimation of cell numbers.
 A Coulter counter
A Coulter counter
is an appliance that can counts cells as well as measure their volume. It is based on the fact that cells show great electrical resistance
; in other words, they conduct almost no electricity
. In a Coulter counter the cells, swimming in a solution that conducts electricity, are sucked one by one into a tiny gap. Flanking the gap are two electrode
s that conduct electricity. When no cell is in the gap, electricity flows unabated, but when a cell is sucked into the gap the current is resisted. The Coulter counter counts the number of such events and also measures the current (and hence the resistance), which directly correlates to the volume of the cell trapped. A similar system is the CASY cell counting technology
.
Coulter and CASY counters are much cheaper than flow cytometers, and for applications that require cell numbers and sizes, such as cell-cycle research, they are the method of choice. Its advantage over the methods above is the large number of cells that can be processed in a short time, namely: thousands of cells per second. This offers great accuracy and statistical significance
.
is by far the most sophisticated and expensive method for cell counting. In a flow cytometer the cells flow in a narrow stream in front of a laser
beam. The beam hits them one by one, and a light detector picks up the light that is reflected from the cells.
Flow cetometers have many other abilities, such as analyzing the shape of cells and their internal and external structures, as well as measuring the amount of specific protein
s and other biochemicals in the cells. Therefore, flow cytometers are rarely purchased for the sole purpose of counting cells.
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s in molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
and in medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
.
The need for cell counting
Numerous procedures in biology and medicine require the counting of cells. On most occasions it is actually the concentrationConcentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of the cells which is required (for example: 5,000 cells per mililiter). By counting the cells in a known volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
of culture the concentration can be mediated. Here are several examples for the need for cell counting:
- In medicine, the concentration of various blood cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, can give crucial information regarding the health situation of a person (see: complete blood countComplete blood countA complete blood count , also known as full blood count or full blood exam or blood panel, is a test panel requested by a doctor or other medical professional that gives information about the cells in a patient's blood...
). - Similarly, the concentration of bacteriaBacteriaBacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, viruses and other pathogenPathogenA pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
s in the bloodBloodBlood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
or in other bodily fluidBodily fluidBody fluid or bodily fluids are liquids originating from inside the bodies of living people. They include fluids that are excreted or secreted from the body as well as body water that normally is not.Body fluids include:-Body fluids and health:...
s can reveal information about the progress of an infectious diseaseInfectious diseaseInfectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
and about the degree of success with which the immune systemImmune systemAn immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
is dealing with the infectionInfectionAn infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
. - The cell concentration needs to be known for many experimentExperimentAn experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
s in molecular biology, in order to adjust accordingly the amount of reagentReagentA reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
s and chemicals that are to be applied in the experiment. - Studies that examine the growth rate of microorganismMicroorganismA microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
s (in other words: how fast they divideCell divisionCell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
to create new cells) require cell counting.
Methods
There are several methods for cell counting. Some are primitive and do not require special equipment which is not present at any average biological laboratoryLaboratory
A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories...
, whereas others rely on sophisticated electronic appliances.
Counting chamber

Microscope slide
A microscope slide is a thin flat piece of glass, typically 75 by 25 mm and about 1 mm thick, used to hold objects for examination under a microscope. Typically the object is placed or secured on the slide, and then both are inserted together in the microscope for viewing...
that is especially designed to enable cell counting. The slide has a sink in its middle; the area of the sink is marked with a grid. A drop of a cell culture
Cell culture
Cell culture is the complex process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions. In practice, the term "cell culture" has come to refer to the culturing of cells derived from singlecellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells. However, there are also cultures of plants, fungi and microbes,...
is placed in the sink. Looking at the sample under the microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
, the researcher uses the grid to manually count the number of cells in a certain area. The depth of the sink is predefined, thus the volume of the counted culture can be calculated and with it the concentration of the cells.
Counting chambers are often used in clinical blood counts. Their advantage is being cheap and fast; this is makes them the preferred counting method in fast biological experiments in which it needs to be merely determined whether a cell culture has grown as expected. Usually the culture examined needs to be diluted, otherwise the high density of cells would make counting impossible. The need for dilution is a disadvantage, as every dilution adds inaccuracy to the measurement.
Plating

Petri dish
A Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic cylindrical lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells or small moss plants. It was named after German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, who invented it when working as an assistant to Robert Koch...
with growth medium
Growth medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a liquid or gel designed to support the growth of microorganisms or cells, or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens.There are different types of media for growing different types of cells....
. If the cells are efficiently distributed on the plate, it can be generally assumed that each cell will give rise to a single colony
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony reference to several individual organisms of the same species living closely together, usually for mutual benefit, such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Some insects live only in colonies...
. The colonies can then counted, and based on the known volume of culture that was spread on the plate, the cell concentration can be calculated.
As is with counting chambers, cultures usually need to be heavily diluted prior to plating; otherwise, instead of obtaining single colonies that can be counted, a so-called "lawn" will form: thousands of colonies lying over each other. Additionally, plating is the slowest method of all: most microorganisms need at least 12 hours to form visible colonies.
Spectrophotometry
Cell cultures are turbid: they absorb some of the lightLight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
and let the rest of it pass through. The higher the cell concentration is, the higher the turbidity. Spectrophotometer
Spectrophotometry
In chemistry, spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength...
s are electrical appliances that can measure turbidity very accurately. The culture is placed in a translucent cuvette
Cuvette
A cuvette is a small tube of circular or square cross section, sealed at one end, made of plastic, glass, or fused quartz and designed to hold samples for spectroscopic experiments. The best cuvettes are as clear as possible, without impurities that might affect a spectroscopic reading...
, the cuvette placed in the machine, and the turbidity measured immediately. Simple mathematical formulae help convert the detected turbidity to cell concentration. Using spectrophotometry for measuring the turbidity of cultures is known as turbidometry
Turbidometry
Turbidometry is the process of measuring the amount of light that a solution absorbs. Light is passed through a filter creating a light of known wavelength which is then passed through a cuvette containing a solution. A photoelectric cell collects the light which passes through the cuvette...
.
In spectrophotometry, cultures usually do not need to be diluted, although above a certain cell density the results lose reliability. Of all the electrical appliances used for counting cells, a spectrophotometer is the cheapest and its operation the fastest and most straightforward. This has made spectrophotometry the methods of choice for quick measurements of bacterial growth and related applications. There are spectrophotometers in which several cuvettes can be inserted at one time, reducing work time even more. Additionally, there are spectrophotometers that require extremely small volumes of culture, as little as 1 microliter. This can be an advantage if the culture is precious and cannot be wasted. Spectrophotometry's drawback is its limited accuracy; it is the only method in which the cells are not counted directly—the machine measures light, not cells. This, combined with the stochastic
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
nature of liquid cultures, enables only an estimation of cell numbers.
Electrical resistance

Coulter counter
A Coulter counter is an apparatus for counting and sizing particles suspended in electrolytes. It is used for cells, bacteria, prokaryotic cells and virus particles....
is an appliance that can counts cells as well as measure their volume. It is based on the fact that cells show great electrical resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
; in other words, they conduct almost no electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
. In a Coulter counter the cells, swimming in a solution that conducts electricity, are sucked one by one into a tiny gap. Flanking the gap are two electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s that conduct electricity. When no cell is in the gap, electricity flows unabated, but when a cell is sucked into the gap the current is resisted. The Coulter counter counts the number of such events and also measures the current (and hence the resistance), which directly correlates to the volume of the cell trapped. A similar system is the CASY cell counting technology
CASY cell counting technology
CASY technology is an electric field multi-channel cell counting system. It was first marketed by Schärfe System GmbH in 1998. In 2006, Schärfe System was acquired by Innovatis, a company focused on cell culture analysis. CASY utilizes the techniques of electric current exclusion and pulse area...
.
Coulter and CASY counters are much cheaper than flow cytometers, and for applications that require cell numbers and sizes, such as cell-cycle research, they are the method of choice. Its advantage over the methods above is the large number of cells that can be processed in a short time, namely: thousands of cells per second. This offers great accuracy and statistical significance
Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
.
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometryFlow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique for counting and examining microscopic particles, such as cells and chromosomes, by suspending them in a stream of fluid and passing them by an electronic detection apparatus. It allows simultaneous multiparametric analysis of the physical and/or chemical...
is by far the most sophisticated and expensive method for cell counting. In a flow cytometer the cells flow in a narrow stream in front of a laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
beam. The beam hits them one by one, and a light detector picks up the light that is reflected from the cells.
Flow cetometers have many other abilities, such as analyzing the shape of cells and their internal and external structures, as well as measuring the amount of specific protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s and other biochemicals in the cells. Therefore, flow cytometers are rarely purchased for the sole purpose of counting cells.

