
Absorbance
Encyclopedia
In spectroscopy
, the absorbance A (also called optical density) is defined as:
 ,
,
where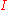 is the intensity of light at a specified wavelength
is the intensity of light at a specified wavelength
λ that has passed through a sample (transmitted light intensity) and is the intensity of the light before it enters the sample or incident light intensity
is the intensity of the light before it enters the sample or incident light intensity
(or power
). Absorbance measurements are often carried out in analytical chemistry
, since the absorbance of a sample is proportional to the thickness of the sample and the concentration of the absorbing species in the sample, in contrast to the transmittance
 of a sample, which varies exponentially with thickness and concentration.
of a sample, which varies exponentially with thickness and concentration.
 Absorptance (not absorbance) is defined as:
Absorptance (not absorbance) is defined as:
The ratio of the radiant flux absorbed by a body to that incident upon it. Also called [absorption] factor. Compare absorptivity
. Total absorptance refers to absorptance measured over all wavelengths. Spectral absorptance refers to absorptance measured at a specified wavelength.
Absorptance is explained, as it relates to absorbance, on the Color and Vision Research Laboratories, Institute of Ophthalmology, UCL, in this way:
Outside the field of analytical chemistry, e.g. when used with the Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS) technique, the absorbance is often defined using the natural logarithm
instead of the common logarithm
, i.e. as
 ,
,
See the Beer-Lambert law
for a more complete discussion.
refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance refers to the mathematical quantity. Also, absorbance does not always measure absorption: if a given sample is, for example, a dispersion, part of the incident light will in fact be scattered by the dispersed particles, and not really absorbed. However, in such cases, it is recommended that the term "attenuance" (formerly called "extinction") be used, which accounts for losses due to scattering and luminescence.
Although absorbance does not have true units, it is quite often reported in "Absorbance Units" or AU (not to be confused with the Astronomical unit
).
laser-based absorption techniques
can be used, since they have demonstrated detection limits that supersede those obtained by conventional non-laser-based instruments by many orders of magnitude (detections have been demonstrated all the way down to 5 10−13). The theoretical best accuracy for most commercially available non-laser-based instruments is in the range near 1 AU. The path length or concentration should then, when possible, be adjusted to achieve readings near this range.
glass, are rated by shade number, which is 7/3 times the absorbance plus one:
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
, the absorbance A (also called optical density) is defined as:
 ,
,where
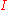 is the intensity of light at a specified wavelength
is the intensity of light at a specified wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
λ that has passed through a sample (transmitted light intensity) and
 is the intensity of the light before it enters the sample or incident light intensity
is the intensity of the light before it enters the sample or incident light intensityIntensity (physics)
In physics, intensity is a measure of the energy flux, averaged over the period of the wave. The word "intensity" here is not synonymous with "strength", "amplitude", or "level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech...
(or power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
). Absorbance measurements are often carried out in analytical chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, since the absorbance of a sample is proportional to the thickness of the sample and the concentration of the absorbing species in the sample, in contrast to the transmittance
Transmittance
In optics and spectroscopy, transmittance is the fraction of incident light at a specified wavelength that passes through a sample. A related term is absorptance, or absorption factor, which is the fraction of radiation absorbed by a sample at a specified wavelength...
 of a sample, which varies exponentially with thickness and concentration.
of a sample, which varies exponentially with thickness and concentration.
The ratio of the radiant flux absorbed by a body to that incident upon it. Also called [absorption] factor. Compare absorptivity
Absorptivity
The term absorptivity has two meanings:*In chemistry, it usually refers to Molar absorptivity : the constant \epsilon used in the Beer-Lambert law, A=\epsilon c l, where A is the absorbance, c is the concentration of the solution, and l is the path length....
. Total absorptance refers to absorptance measured over all wavelengths. Spectral absorptance refers to absorptance measured at a specified wavelength.
Absorptance is explained, as it relates to absorbance, on the Color and Vision Research Laboratories, Institute of Ophthalmology, UCL, in this way:
Absorbance spectra are typically used to define photopigment spectra because their shape, when normalized (i.e., plotted as a fraction of the maximum absorbance), is independent of pigment optical density (pigment concentration). In contrast, the absorptance spectra, like the spectral sensitivity of the human subject, broadens as the optical density increases.
Outside the field of analytical chemistry, e.g. when used with the Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS) technique, the absorbance is often defined using the natural logarithm
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
instead of the common logarithm
Common logarithm
The common logarithm is the logarithm with base 10. It is also known as the decadic logarithm, named after its base. It is indicated by log10, or sometimes Log with a capital L...
, i.e. as
 ,
,See the Beer-Lambert law
Beer-Lambert law
In optics, the Beer–Lambert law, also known as Beer's law or the Lambert–Beer law or the Beer–Lambert–Bouguer law relates the absorption of light to the properties of the material through which the light is travelling.-Equations:The law states that there is a logarithmic dependence between the...
for a more complete discussion.
Explanation
The term absorptionAbsorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance refers to the mathematical quantity. Also, absorbance does not always measure absorption: if a given sample is, for example, a dispersion, part of the incident light will in fact be scattered by the dispersed particles, and not really absorbed. However, in such cases, it is recommended that the term "attenuance" (formerly called "extinction") be used, which accounts for losses due to scattering and luminescence.
Although absorbance does not have true units, it is quite often reported in "Absorbance Units" or AU (not to be confused with the Astronomical unit
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
).
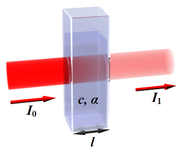
Absorbance vs transmittance
| Absorbance | Transmittance (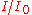 ) ) |
Percent transmittance (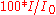 ) ) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 100 |
| 0.1 | 0.79 | 79 |
| 0.25 | 0.56 | 56 |
| 0.5 | 0.32 | 32 |
| 0.75 | 0.18 | 18 |
| 0.9 | 0.13 | 13 |
| 1 | 0.1 | 10 |
| 2 | 0.01 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.1 |
Instrument measurement range
Any real measuring instrument has a limited range over which it can accurately measure absorbance. An instrument must be calibrated and checked against known standards if the readings are to be trusted. Many instruments will become non-linear (fail to follow the Beer-Lambert law) starting at approximately 2 AU (~1% Transmission). It is also difficult to accurately measure very small absorbance values (below 10−4) with commercially available instruments for chemical analysis. In such cases,laser-based absorption techniques
Laser absorption spectrometry
Laser absorption spectrometry refers to techniques that use lasers to assess the concentration or amount of a species in gas phase by absorption spectrometry ....
can be used, since they have demonstrated detection limits that supersede those obtained by conventional non-laser-based instruments by many orders of magnitude (detections have been demonstrated all the way down to 5 10−13). The theoretical best accuracy for most commercially available non-laser-based instruments is in the range near 1 AU. The path length or concentration should then, when possible, be adjusted to achieve readings near this range.
Shade number
Some filters, notably weldingWelding
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes...
glass, are rated by shade number, which is 7/3 times the absorbance plus one:
- shade number =

See also
- Optical depthOptical depthOptical depth, or optical thickness, is a measure of transparency. Optical depth is defined by the negative logarithm of the fraction of radiation that is not scattered or absorbed on a path...
- Beer-Lambert lawBeer-Lambert lawIn optics, the Beer–Lambert law, also known as Beer's law or the Lambert–Beer law or the Beer–Lambert–Bouguer law relates the absorption of light to the properties of the material through which the light is travelling.-Equations:The law states that there is a logarithmic dependence between the...
- ReflectivityReflectivityIn optics and photometry, reflectivity is the fraction of incident radiation reflected by a surface. In general it must be treated as a directional property that is a function of the reflected direction, the incident direction, and the incident wavelength...
- Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS)
- DensitometryDensitometryDensitometry is the quantitative measurement of optical density in light-sensitive materials, such as photographic paper or film, due to exposure to light...
- Neutral density filterNeutral density filterIn photography and optics, a neutral density filter or ND filter can be a colorless or grey filter. An ideal neutral density filter reduces and/or modifies intensity of all wavelengths or colors of light equally, giving no changes in hue of color rendition.The purpose of standard photographic...

