
Chen model
Encyclopedia
In finance
, the Chen model is a mathematical model
describing the evolution of interest rate
s. It is a type of "three-factor model" (short rate model
) as it describes interest rate movements as driven by three sources of market risk. It was the first stochastic
mean and stochastic volatility
model and it was published in 1994 by the economist Lin Chen, a Harvard doctorate, former US Fed economist and professor of Yonsei University of Korea.
The dynamics of the instantaneous interest rate are specified by the stochastic differential equations:
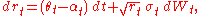
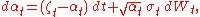
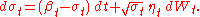
In an authoritative review of modern finance (Continuous-Time Methods in Finance: A Review and an Assessment), Chen model is listed along with the models of Robert C. Merton
, Oldrich Vasicek
, John C. Cox, Stephen A. Ross, Darrell Duffie
, John Hull
, Robert A. Jarrow, and Emanuel Derman
as a major term structure model.
Different variants of Chen model are still being used in financial institutions worldwide. James and Webber devote a section to discuss Chen model in their book; Gibson et al. devote a section to cover Chen model in their review article. Andersen et al. devote a paper to study and extend Chen model. Gallant et al. devote a paper to test Chen model and other models; Wibowo and Cai devote their PhD dissertations to testing Chen model and other competing interest rate models.
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, the Chen model is a mathematical model
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
describing the evolution of interest rate
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
s. It is a type of "three-factor model" (short rate model
Short rate model
In the context of interest rate derivatives, a short-rate model is a mathematical model that describes the future evolution of interest rates by describing the future evolution of the short rate, usually written r_t \,.-The short rate:...
) as it describes interest rate movements as driven by three sources of market risk. It was the first stochastic
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
mean and stochastic volatility
Stochastic volatility
Stochastic volatility models are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities, such as options. The name derives from the models' treatment of the underlying security's volatility as a random process, governed by state variables such as the price level of the...
model and it was published in 1994 by the economist Lin Chen, a Harvard doctorate, former US Fed economist and professor of Yonsei University of Korea.
The dynamics of the instantaneous interest rate are specified by the stochastic differential equations:
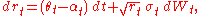
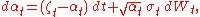
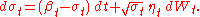
In an authoritative review of modern finance (Continuous-Time Methods in Finance: A Review and an Assessment), Chen model is listed along with the models of Robert C. Merton
Robert C. Merton
Robert Carhart Merton is an American economist, Nobel laureate in Economics, and professor at the MIT Sloan School of Management.-Biography:...
, Oldrich Vasicek
Oldrich Vasicek
Oldrich Alfons Vasicek a Czech mathematician, received his master's degree in math from the Czech Technical University, 1964, and a doctorate in probability theory from Charles University four years later....
, John C. Cox, Stephen A. Ross, Darrell Duffie
Darrell Duffie
James Darrell Duffie is a Canadian economist. He is the Dean Witter Distinguished Professor of Finance at Stanford Graduate School of Business, and has been on the finance faculty at Stanford since receiving his Ph.D. from Stanford in 1984...
, John Hull
John Hull
John C. Hull is a Professor of Derivatives and Risk Management at the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto.He is both a very well respected researcher in the academic field of quantitative finance , and also the author of two books on financial derivatives that have become...
, Robert A. Jarrow, and Emanuel Derman
Emanuel Derman
Emanuel Derman is a South African-born academic, businessman and writer. He is best known as a quantitative analyst, and author of the book My Life as A Quant: Reflections on Physics and Finance....
as a major term structure model.
Different variants of Chen model are still being used in financial institutions worldwide. James and Webber devote a section to discuss Chen model in their book; Gibson et al. devote a section to cover Chen model in their review article. Andersen et al. devote a paper to study and extend Chen model. Gallant et al. devote a paper to test Chen model and other models; Wibowo and Cai devote their PhD dissertations to testing Chen model and other competing interest rate models.

