
Cherenkov detector
Encyclopedia
A Cherenkov detector is a particle detector
using the mass-dependent threshold energy of Cherenkov radiation
. This allows a discrimination between a lighter particle (which does radiate) and a heavier particle (which does not radiate).
It is a more advanced form of scintillation counter
. A particle passing through a material at a velocity greater than that at which light can travel through the material emits light. This is similar to the production of a sonic boom
when an airplane is traveling through the air faster than sound waves can move through the air. This light is emitted in a cone about the direction in which the particle is moving. The angle of the cone,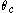 , is a direct measure of the particle's velocity through the formula
, is a direct measure of the particle's velocity through the formula
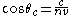 ,
,
where is the speed of light
is the speed of light
, and is the refractive index
is the refractive index
of the medium. Alternatively, if the momentum of the particle is known (from magnetic bending) the Cherenkov's information on the particle's velocity enables the mass to be deduced so that the particle can be identified.
Particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify high-energy particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a...
using the mass-dependent threshold energy of Cherenkov radiation
Cherenkov radiation
Cherenkov radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle passes through a dielectric medium at a speed greater than the phase velocity of light in that medium...
. This allows a discrimination between a lighter particle (which does radiate) and a heavier particle (which does not radiate).
It is a more advanced form of scintillation counter
Scintillation counter
A scintillation counter measures ionizing radiation. The sensor, called a scintillator, consists of a transparent crystal, usually phosphor, plastic , or organic liquid that fluoresces when struck by ionizing radiation. A sensitive photomultiplier tube measures the light from the crystal...
. A particle passing through a material at a velocity greater than that at which light can travel through the material emits light. This is similar to the production of a sonic boom
Sonic boom
A sonic boom is the sound associated with the shock waves created by an object traveling through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding much like an explosion...
when an airplane is traveling through the air faster than sound waves can move through the air. This light is emitted in a cone about the direction in which the particle is moving. The angle of the cone,
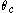 , is a direct measure of the particle's velocity through the formula
, is a direct measure of the particle's velocity through the formula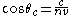 ,
,where
 is the speed of light
is the speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, and
 is the refractive index
is the refractive indexRefractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
of the medium. Alternatively, if the momentum of the particle is known (from magnetic bending) the Cherenkov's information on the particle's velocity enables the mass to be deduced so that the particle can be identified.
See also
- Ring imaging Cherenkov detectorRing imaging Cherenkov detectorA Ring Imaging Cherenkov detector is a particle detector that can determine the velocity, v , of a charged particle. This is done by an indirect measurement of the Cherenkov angle, \theta_c , i.e. the angle between the emitted Čerenkov radiation and the particle path...
- Super-KamiokandeSuper-KamiokandeSuper-Kamiokande is a neutrino observatory which is under Mount Kamioka near the city of Hida, Gifu Prefecture, Japan...
- Cherenkov radiationCherenkov radiationCherenkov radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle passes through a dielectric medium at a speed greater than the phase velocity of light in that medium...

