Chichibabin reaction
Encyclopedia
The Chichibabin reaction -chē-bā-bēn) is a method for producing 2-aminopyridine
derivatives by the reaction of pyridine with sodium amide
. It was reported by Aleksei Chichibabin
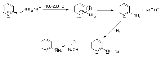
in 1914. The following is the overall form of the general reaction:
The direct amination of pyridine
with sodium amide
takes place in liquid ammonia
. Following the addition elimination mechanism first a nucleophilic
NH2- is added while a hydride (H-) is leaving.
Before the Chichibabin reaction, only electrophilic substitution
on the pyridine ring was possible, which is difficult because pyridine is an electron-poor aromatic compound and additionally forms positive charged pyridinum ions, which further decrease the probability of an electrophile attack. The positions in the pyridine system attacked by the electrophiles are the 3rd and the 5th position.
The Chichibabin reaction is a nucleophilic substitution on the pyridine ring; the 2nd and 6th positions are therefore favoured over the other positions.
The amino nucleophile attacks the carbon
Aminopyridine
Aminopyridine may refer to any of several chemical compounds:* 2-Aminopyridine* 3-Aminopyridine* 4-Aminopyridine...
derivatives by the reaction of pyridine with sodium amide
Sodium amide
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide, is the chemical compound with the formula NaNH2. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is white when pure, but commercial samples are typically gray due to the presence of small quantities of metallic iron from the manufacturing process...
. It was reported by Aleksei Chichibabin
Aleksei Chichibabin
For the poet, see Boris Chichibabin.Alekséy Yevgényevich Chichibábin was a Soviet/Russian organic chemist. His name is also written Alexei Yevgenievich Chichibabin and Alexei Euguenievich Tchitchibabine.- Life :...
in 1914. The following is the overall form of the general reaction:
The direct amination of pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
with sodium amide
Sodium amide
Sodium amide, commonly called sodamide, is the chemical compound with the formula NaNH2. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is white when pure, but commercial samples are typically gray due to the presence of small quantities of metallic iron from the manufacturing process...
takes place in liquid ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
. Following the addition elimination mechanism first a nucleophilic
Nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where in a chemical compound a π bond is removed by the creation of two new covalent bonds by the addition of a nucleophile....
NH2- is added while a hydride (H-) is leaving.
Before the Chichibabin reaction, only electrophilic substitution
Electrophilic substitution
Electrophilic substitution reactions are chemical reactions in which an electrophile displaces a group in a compound, typically but not always hydrogen. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is characteristic of aromatic compounds and is an important way of introducing functional groups onto benzene...
on the pyridine ring was possible, which is difficult because pyridine is an electron-poor aromatic compound and additionally forms positive charged pyridinum ions, which further decrease the probability of an electrophile attack. The positions in the pyridine system attacked by the electrophiles are the 3rd and the 5th position.
The Chichibabin reaction is a nucleophilic substitution on the pyridine ring; the 2nd and 6th positions are therefore favoured over the other positions.
The amino nucleophile attacks the carbon

