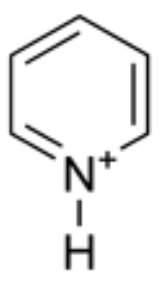
Pyridine
Overview
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic
organic compound
with the chemical formula
C5
H5
N
. It is structurally related to benzene
, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen
atom. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including azine
s and the vitamins niacin
and pyridoxal
.
Pyridine was discovered in 1849 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson
as one of the constituents of bone oil
. Two years later, Anderson isolated pure pyridine through fractional distillation
of the oil.
Heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound which has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring. The counterparts of heterocyclic compounds are homocyclic compounds, the rings of which are made of a single element....
organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C5
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
H5
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
N
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
. It is structurally related to benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including azine
Azine
Azines are a functional class of organic compounds, formed from the condensation reaction of two equivalents of an aldehyde or ketone with one equivalent of hydrazine...
s and the vitamins niacin
Niacin
"Niacin" redirects here. For the neo-fusion band, see Niacin .Niacin is an organic compound with the formula and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients.Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic deficiency disease: niacin deficiency...
and pyridoxal
Pyridoxal
Pyridoxal is one of the three natural forms of vitamin B6, along with pyridoxamine and pyridoxine . All of these forms are converted in the human body into a single biologically active form, pyridoxal 5-phosphate. All three forms of vitamin B6 are heterocyclic organic compounds...
.
Pyridine was discovered in 1849 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson
Thomas Anderson (chemist)
thumb|280pxThomas Anderson was a noted 19th century chemist. In 1853 his work on alkaloids led him to discover the correct structure for codeine...
as one of the constituents of bone oil
Dippel's oil
Dippel's Oil is a nitrogenous by-product of the destructive distillation manufacture of bone char . This liquid is dark colored and highly viscous with an unpleasant smell. The oil contains the organic base pyrrole. It is named after its inventor, Johann Conrad Dippel,Dippel's oil had a number...
. Two years later, Anderson isolated pure pyridine through fractional distillation
Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions, such as in separating chemical compounds by their boiling point by heating them to a temperature at which several fractions of the compound will evaporate. It is a special type of distillation...
of the oil.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

