
Niacin
Encyclopedia
"Niacin" redirects here. For the neo-fusion band, see Niacin (band)
.
Niacin (also known as vitamin B3, nicotinic acid and vitamin PP) is an organic compound
with the formula
and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients
.
Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic
deficiency disease: niacin deficiency (pellagra
), vitamin C
deficiency (scurvy
), thiamin deficiency (beriberi
), vitamin D
deficiency (rickets
), vitamin A deficiency
(night blindness and other symptoms).
Niacin has been used to increase levels of HDL cholesterol in the blood and has been found to modestly decrease the risk of cardiovascular events in a number of controlled human trials. However, in a recent trial AIM-HIGH, a slow-release form of niacin was found to have no effect on cardiovascular event and stroke risk in a group of patients with LDL levels already well-controlled by a statin drug, and the trial was halted prematurely on evidence that niacin addition actually increased stroke risk in this group. The role of niacin in treating cardiovascular risk remains under debate.
This colorless, water-soluble solid is a derivative of pyridine
, with a carboxyl group (COOH) at the 3-position. Other forms of vitamin B3 include the corresponding amide
, nicotinamide
("niacinamide"), where the carboxyl group has been replaced by a carboxamide group , as well as more complex amides and a variety of esters. The terms niacin, nicotinamide, and vitamin B3 are often used interchangeably to refer to any member of this family of compounds, since they have similar biochemical activity.
Niacin cannot be directly converted to nicotinamide, but both compounds could be converted to NAD
and NADP in vivo
. Although the two are identical in their vitamin activity, nicotinamide does not have the same pharmacological effects (lipid modifying effects) as niacin; these effects occur as side effects of niacin's conversion. Nicotinamide does not reduce cholesterol or cause flushing
. Nicotinamide may be toxic to the liver at doses exceeding 3 g/day for adults. Niacin is a precursor to NAD+/NADH
and NADP+/NADPH, which play essential metabolic
roles in living cells. Niacin is involved in both DNA repair, and the production of steroid hormone
s in the adrenal gland
.
as the critical adverse effect.
In general, niacin status is tested through urinary biomarkers, which are believed to be more reliable than plasma levels.
(corn, the only grain low in digestible niacin) as a staple food. A special cooking technique called nixtamalization
is needed to increase the bioavailability of niacin during maize meal/flour production.
Mild niacin deficiency has been shown to slow metabolism, causing decreased tolerance to cold.
Severe deficiency of niacin in the diet causes the disease pellagra
, which is characterized by diarrhea, dermatitis, and dementia, as well as “necklace” lesions on the lower neck, hyperpigmentation, thickening of the skin, inflammation of the mouth and tongue, digestive disturbances, amnesia, delirium, and eventually death, if left untreated. Common psychiatric symptoms of niacin deficiency include irritability, poor concentration, anxiety, fatigue, restlessness, apathy, and depression. Studies have indicated that, in patients with alcoholic pellagra, niacin deficiency may be an important factor influencing both the onset and severity of this condition. Alcoholic patients typically experience increased intestinal permeability, leading to negative health outcomes.
Hartnup’s disease is a hereditary nutritional disorder resulting in niacin deficiency. This condition was first identified in the 1950s by the Hartnup family in London. It is due to a deficit in the intestines and kidneys, making it difficult for the body to break down and absorb dietary tryptophan
. The resulting condition is similar to pellagra, including symptoms of red, scaly rash, and sensitivity to sunlight. Oral niacin is given as a treatment for this condition in doses ranging from 40–200 mg, with a good prognosis if identified and treated early. Niacin synthesis is also deficient in carcinoid syndrome
, because of metabolic diversion of its precursor tryptophan
to form serotonin
.
s in adipose tissue
. These fats are used to build very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) in the liver, which are precursors of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad" cholesterol. Because niacin blocks the breakdown of fats, it causes a decrease in free fatty acids in the blood and, as a consequence, decreases the secretion of VLDL and cholesterol by the liver.
By lowering VLDL levels, niacin also increases the level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or "good" cholesterol in blood, and therefore it is sometimes prescribed for people with low HDL, who are also at high risk of a heart attack.
The ARBITER 6-HALTS study, reported at the 2009 annual meeting of the American Heart Association
and in the New England Journal of Medicine
concluded that, when added to statins, 2000 mg/day of slow-release niacin was more effective than ezetimibe
(Zetia) in reducing carotid intima-media thickness, a marker of atherosclerosis. Additionally, a recent meta-analysis covering 11 randomized controlled clinical trials found positive effects of niacin alone or in combination on all cardiovascular events and on atherosclerosis evolution.
However, a 2011 study (AIM-HIGH) was halted early because patients showed no decrease in cardiovascular events, but did experience an increase in the risk of stroke. These patients already had LDL levels well-controlled by a statin
drug, and the aim of the study was to evaluate slow-release niacin (2000 mg per day) to see if raising HDL levels had an additional positive effect on risk. In this study, it did not have such an effect, and appeared to increase stroke risk. The role of niacin in patients whose LDL is not well-controlled (as in the majority of previous studies with niacin) is still under study and debate. However, it does not seem to offer benefits via raising HDL, in patients already lowering LDL by taking a statin.
and itching, dry skin, and skin rashes including eczema
exacerbation and acanthosis nigricans
. These symptoms are generally related to niacin's role as the rate limiting cofactor in the histidine decarboxylase enzyme which converts l-histidine into histamine. H1 and H2 receptor mediated histamine is metabolized via a sequence of mono (or di-) amine oxidase and COMT into methylhistamine which is then conjugated through the liver's CYP450 pathways. Persistent flushing and other symptoms may indicate deficiencies in one or more of the cofactors responsible for this enzymatic cascade. Gastrointestinal complaints, such as dyspepsia
(indigestion), nausea and liver toxicity fulminant hepatic failure, have also been reported. Side effects of hyperglycemia
, cardiac arrhythmias and "birth defects in experimental animals" have also been reported. The flush lasts for about 15 to 30 minutes, and is sometimes accompanied by a prickly or itching sensation, in particular, in areas covered by clothing. This effect is mediated by prostaglandin
and can be blocked by taking 300 mg of aspirin
half an hour before taking niacin, or by taking one tablet of ibuprofen
per day. Taking the niacin with meals also helps reduce this side effect. After several weeks of a consistent dose, most patients no longer flush. Slow- or "sustained"-release forms of niacin have been developed to lessen these side effects. One study showed the incidence of flushing was significantly lower with a sustained release
formulation though doses above 2 g per day have been associated with liver damage
, in particular, with slow-release formulations. Flushing is often thought to involve histamine, but histamine has been shown not to be involved in the reaction. Prostaglandin (PGD2) is the primary cause of the flushing reaction, with serotonin
appearing to have a secondary role in this reaction.
Although high doses of niacin may elevate blood sugar
, thereby worsening diabetes mellitus
, recent studies show the actual effect on blood sugar to be only 5–10%. Patients with diabetes who continued to take anti-diabetes drugs containing niacin did not experience major blood glucose changes. Thus looking at the big picture, niacin continues to be recommended as a drug for preventing CVD in patients with diabetes.
Hyperuricemia
is another side effect of taking high-dose niacin, and may exacerbate gout
.
Niacin in doses used to lower cholesterol levels has been associated with birth defects in laboratory animals, with possible consequences for infant development in pregnant
women.
Niacin, particularly the time-release variety, at extremely high doses can cause acute toxic reactions. Extremely high doses of niacin can also cause niacin maculopathy
, a thickening of the macula
and retina
, which leads to blurred vision and blindness. This maculopathy is reversible after niacin intake ceases.
that has been ester
ified with niacin on all six of inositol's alcohol groups. IHN is usually sold as "flush-free" or "no-flush" niacin in units of 250, 500, or 1000 mg/tablets or capsules. It is sold as an over-the-counter formulation, and often is marketed and labeled as niacin, thus misleading consumers into thinking they are getting the active form of the medication. While this form of niacin does not cause the flushing associated with the immediate-release products, the evidence that it has lipid-modifying functions is contradictory, at best. As the clinical trials date from the early 1960s (Dorner, Welsh) or the late 1970s (Ziliotto, Kruse, Agusti), it is difficult to assess them by today's standards. One of the last of those studies affirmed the superiority of inositol and xantinol esters of nicotinic acid for reducing serum free fatty acid, but other studies conducted during the same period found no benefit. Studies explain that this is primarily because "flush-free" preparations do not contain any free nicotinic acid. A more recent placebo-controlled trial was small (n=11/group), but results after three months at 1500 mg/day showed no trend for improvements in total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C or triglycerides. Thus, so far there is not enough evidence to recommend IHN to treat dyslipidemia
. Furthermore, the American Heart Association and the National Cholesterol Education Program both take the position that only prescription niacin should be used to treat dyslipidemias, and only under the management of a physician. The reason given is that niacin at effective intakes of 1500–3000 mg/day can also potentially have severe adverse effects. Thus liver function tests
to monitor liver enzymes are necessary when taking therapeutic doses of niacin, including alkaline phosphatase
(ALP), aspartate transaminase
(AST), and alanine transaminase
(ALT).
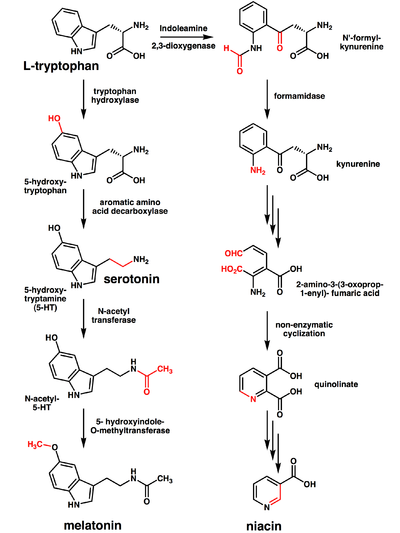 The liver
The liver
can synthesize niacin from the essential amino acid
tryptophan
, requiring 60 mg of tryptophan to make one mg of niacin. The 5-membered aromatic heterocycle
of tryptophan is cleaved and rearranged with the alpha amino group
of tryptophan into the 6-membered aromatic heterocycle of niacin. Riboflavin, Vitamin B6 and iron are required in some of the reactions involved in the conversion of tryptophan to NAD.
Several million kilograms of niacin are manufactured each year, starting from 3-methylpyridine
.
called HM74A. It couples to the Gi alpha subunit
.
, which is found in meat, dairy and eggs.
Animal products:
Fruits and vegetables:
Seeds:
Fungi:
Other:
in 1873 in his studies of nicotine
. The original preparation remains useful: The oxidation of nicotine
using nitric acid
. Niacin was extracted from livers by Conrad Elvehjem
, who later identified the active ingredient, then referred to as the "pellagra-preventing factor" and the "anti-blacktongue factor." When the biological significance of nicotinic acid was realized, it was thought appropriate to choose a name to dissociate it from nicotine, to avoid the perception that vitamins or niacin-rich food contains nicotine, or that cigarettes contain vitamins. The resulting name 'niacin' was derived from nicotinic acid + vitamin.
Carpenter found in 1951 that niacin in corn is biologically unavailable, and can be released only in very alkaline lime water of pH
11.
This process, known as nixtamalization
, was discovered by the prehistoric civilizations of Mesoamerica.
Niacin is referred to as vitamin B3 because it was the third of the B vitamins
to be discovered. It has historically been referred to as "vitamin PP" or "vitamin P-P".
is being tested in a clinical trial. Laropiprant reduces facial flushes induced by niacin.
Niacin (band)
Niacin is a neo-fusion instrumental trio featuring Billy Sheehan, Dennis Chambers and John Novello. Founded in 1996, the band's name comes from the timbral foundation of the Hammond B3 organ; vitamin B3 is also known as niacin....
.
Niacin (also known as vitamin B3, nicotinic acid and vitamin PP) is an organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients
Essential nutrient
An essential nutrient is a nutrient required for normal body functioning that either cannot be synthesized by the body at all, or cannot be synthesized in amounts adequate for good health , and thus must be obtained from a dietary source...
.
Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic
Pandemic
A pandemic is an epidemic of infectious disease that is spreading through human populations across a large region; for instance multiple continents, or even worldwide. A widespread endemic disease that is stable in terms of how many people are getting sick from it is not a pandemic...
deficiency disease: niacin deficiency (pellagra
Pellagra
Pellagra is a vitamin deficiency disease most commonly caused by a chronic lack of niacin in the diet. It can be caused by decreased intake of niacin or tryptophan, and possibly by excessive intake of leucine. It may also result from alterations in protein metabolism in disorders such as carcinoid...
), vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
deficiency (scurvy
Scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic...
), thiamin deficiency (beriberi
Beriberi
Beriberi is a nervous system ailment caused by a thiamine deficiency in the diet. Thiamine is involved in the breakdown of energy molecules such as glucose and is also found on the membranes of neurons...
), vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
deficiency (rickets
Rickets
Rickets is a softening of bones in children due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D, magnesium , phosphorus or calcium, potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries...
), vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency is a lack of vitamin A in humans. It is common in developing countries but rarely seen in developed countries. Night blindness is one of the first signs of vitamin A deficiency. Xerophthalmia and complete blindness can also occur since Vitamin A has a major role in...
(night blindness and other symptoms).
Niacin has been used to increase levels of HDL cholesterol in the blood and has been found to modestly decrease the risk of cardiovascular events in a number of controlled human trials. However, in a recent trial AIM-HIGH, a slow-release form of niacin was found to have no effect on cardiovascular event and stroke risk in a group of patients with LDL levels already well-controlled by a statin drug, and the trial was halted prematurely on evidence that niacin addition actually increased stroke risk in this group. The role of niacin in treating cardiovascular risk remains under debate.
This colorless, water-soluble solid is a derivative of pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
, with a carboxyl group (COOH) at the 3-position. Other forms of vitamin B3 include the corresponding amide
Amide
In chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an...
, nicotinamide
Nicotinamide
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide and nicotinic acid amide, is the amide of nicotinic acid . Nicotinamide is a water-soluble vitamin and is part of the vitamin B group...
("niacinamide"), where the carboxyl group has been replaced by a carboxamide group , as well as more complex amides and a variety of esters. The terms niacin, nicotinamide, and vitamin B3 are often used interchangeably to refer to any member of this family of compounds, since they have similar biochemical activity.
Niacin cannot be directly converted to nicotinamide, but both compounds could be converted to NAD
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
and NADP in vivo
In vivo
In vivo is experimentation using a whole, living organism as opposed to a partial or dead organism, or an in vitro controlled environment. Animal testing and clinical trials are two forms of in vivo research...
. Although the two are identical in their vitamin activity, nicotinamide does not have the same pharmacological effects (lipid modifying effects) as niacin; these effects occur as side effects of niacin's conversion. Nicotinamide does not reduce cholesterol or cause flushing
Flushing (physiology)
For a person to flush is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or...
. Nicotinamide may be toxic to the liver at doses exceeding 3 g/day for adults. Niacin is a precursor to NAD+/NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
and NADP+/NADPH, which play essential metabolic
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
roles in living cells. Niacin is involved in both DNA repair, and the production of steroid hormone
Steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into five groups by the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens, and progestogens...
s in the adrenal gland
Adrenal gland
In mammals, the adrenal glands are endocrine glands that sit atop the kidneys; in humans, the right suprarenal gland is triangular shaped, while the left suprarenal gland is semilunar shaped...
.
Dietary needs
One recommended daily allowance of niacin is 2–12 mg/day for children, 14 mg/day for women, 16 mg/day for men, and 18 mg/day for pregnant or breast-feeding women. The upper limit for adult men and women is 35 mg/day, which is based on flushingFlushing (physiology)
For a person to flush is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or...
as the critical adverse effect.
In general, niacin status is tested through urinary biomarkers, which are believed to be more reliable than plasma levels.
Deficiency
At present, niacin deficiency is sometimes seen in developed countries, and it is usually apparent in conditions of poverty, malnutrition, and chronic alcoholism. It also tends to occur in areas where people eat maizeMaize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
(corn, the only grain low in digestible niacin) as a staple food. A special cooking technique called nixtamalization
Nixtamalization
Nixtamalization typically refers to a process for the preparation of maize , or other grain, in which the grain is soaked and cooked in an alkaline solution, usually limewater, and hulled. The term can also refer to the removal via an alkali process of the pericarp from other grains such as sorghum...
is needed to increase the bioavailability of niacin during maize meal/flour production.
Mild niacin deficiency has been shown to slow metabolism, causing decreased tolerance to cold.
Severe deficiency of niacin in the diet causes the disease pellagra
Pellagra
Pellagra is a vitamin deficiency disease most commonly caused by a chronic lack of niacin in the diet. It can be caused by decreased intake of niacin or tryptophan, and possibly by excessive intake of leucine. It may also result from alterations in protein metabolism in disorders such as carcinoid...
, which is characterized by diarrhea, dermatitis, and dementia, as well as “necklace” lesions on the lower neck, hyperpigmentation, thickening of the skin, inflammation of the mouth and tongue, digestive disturbances, amnesia, delirium, and eventually death, if left untreated. Common psychiatric symptoms of niacin deficiency include irritability, poor concentration, anxiety, fatigue, restlessness, apathy, and depression. Studies have indicated that, in patients with alcoholic pellagra, niacin deficiency may be an important factor influencing both the onset and severity of this condition. Alcoholic patients typically experience increased intestinal permeability, leading to negative health outcomes.
Hartnup’s disease is a hereditary nutritional disorder resulting in niacin deficiency. This condition was first identified in the 1950s by the Hartnup family in London. It is due to a deficit in the intestines and kidneys, making it difficult for the body to break down and absorb dietary tryptophan
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is one of the 20 standard amino acids, as well as an essential amino acid in the human diet. It is encoded in the standard genetic code as the codon UGG...
. The resulting condition is similar to pellagra, including symptoms of red, scaly rash, and sensitivity to sunlight. Oral niacin is given as a treatment for this condition in doses ranging from 40–200 mg, with a good prognosis if identified and treated early. Niacin synthesis is also deficient in carcinoid syndrome
Carcinoid syndrome
Carcinoid syndrome refers to the array of symptoms that occur secondary to carcinoid tumors. The syndrome includes flushing and diarrhea, and, less frequently, heart failure and bronchoconstriction...
, because of metabolic diversion of its precursor tryptophan
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is one of the 20 standard amino acids, as well as an essential amino acid in the human diet. It is encoded in the standard genetic code as the codon UGG...
to form serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
.
Lipid-modifying effects
Niacin blocks the breakdown of fatFat
Fats consist of a wide group of compounds that are generally soluble in organic solvents and generally insoluble in water. Chemically, fats are triglycerides, triesters of glycerol and any of several fatty acids. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure...
s in adipose tissue
Adipose tissue
In histology, adipose tissue or body fat or fat depot or just fat is loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes. It is technically composed of roughly only 80% fat; fat in its solitary state exists in the liver and muscles. Adipose tissue is derived from lipoblasts...
. These fats are used to build very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) in the liver, which are precursors of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad" cholesterol. Because niacin blocks the breakdown of fats, it causes a decrease in free fatty acids in the blood and, as a consequence, decreases the secretion of VLDL and cholesterol by the liver.
By lowering VLDL levels, niacin also increases the level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or "good" cholesterol in blood, and therefore it is sometimes prescribed for people with low HDL, who are also at high risk of a heart attack.
The ARBITER 6-HALTS study, reported at the 2009 annual meeting of the American Heart Association
American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a non-profit organization in the United States that fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and deaths caused by cardiovascular disease and stroke. It is headquartered in Dallas, Texas...
and in the New England Journal of Medicine
New England Journal of Medicine
The New England Journal of Medicine is an English-language peer-reviewed medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It describes itself as the oldest continuously published medical journal in the world.-History:...
concluded that, when added to statins, 2000 mg/day of slow-release niacin was more effective than ezetimibe
Ezetimibe
Ezetimibe is a drug that lowers cholesterol. It acts by decreasing cholesterol absorption in the intestine. It may be used alone , when other cholesterol-lowering medications are not tolerated, or together with statins when statins alone do not control cholesterol.Even though ezetimibe decreases...
(Zetia) in reducing carotid intima-media thickness, a marker of atherosclerosis. Additionally, a recent meta-analysis covering 11 randomized controlled clinical trials found positive effects of niacin alone or in combination on all cardiovascular events and on atherosclerosis evolution.
However, a 2011 study (AIM-HIGH) was halted early because patients showed no decrease in cardiovascular events, but did experience an increase in the risk of stroke. These patients already had LDL levels well-controlled by a statin
Statin
Statins are a class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol in the liver. Increased cholesterol levels have been associated with cardiovascular diseases, and statins are therefore used in the...
drug, and the aim of the study was to evaluate slow-release niacin (2000 mg per day) to see if raising HDL levels had an additional positive effect on risk. In this study, it did not have such an effect, and appeared to increase stroke risk. The role of niacin in patients whose LDL is not well-controlled (as in the majority of previous studies with niacin) is still under study and debate. However, it does not seem to offer benefits via raising HDL, in patients already lowering LDL by taking a statin.
Toxicity
Pharmacological doses of niacin (1.5 - 6 g per day) occasionally lead to side effects that can include dermatological conditions such as skin flushingFlushing (physiology)
For a person to flush is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or...
and itching, dry skin, and skin rashes including eczema
Eczema
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the epidermis . In England, an estimated 5.7 million or about one in every nine people have been diagnosed with the disease by a clinician at some point in their lives.The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions...
exacerbation and acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is a brown to black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin. It is usually found in body folds, such as the posterior and lateral folds of the neck, the axilla, groin, umbilicus, forehead, and other areas.-Causes:...
. These symptoms are generally related to niacin's role as the rate limiting cofactor in the histidine decarboxylase enzyme which converts l-histidine into histamine. H1 and H2 receptor mediated histamine is metabolized via a sequence of mono (or di-) amine oxidase and COMT into methylhistamine which is then conjugated through the liver's CYP450 pathways. Persistent flushing and other symptoms may indicate deficiencies in one or more of the cofactors responsible for this enzymatic cascade. Gastrointestinal complaints, such as dyspepsia
Dyspepsia
Dyspepsia , also known as upset stomach or indigestion, refers to a condition of impaired digestion. It is a medical condition characterized by chronic or recurrent pain in the upper abdomen, upper abdominal fullness and feeling full earlier than expected when eating...
(indigestion), nausea and liver toxicity fulminant hepatic failure, have also been reported. Side effects of hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia or Hyperglycæmia, or high blood sugar, is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a glucose level higher than 13.5mmol/l , but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 15-20 mmol/l...
, cardiac arrhythmias and "birth defects in experimental animals" have also been reported. The flush lasts for about 15 to 30 minutes, and is sometimes accompanied by a prickly or itching sensation, in particular, in areas covered by clothing. This effect is mediated by prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
and can be blocked by taking 300 mg of aspirin
Aspirin
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
half an hour before taking niacin, or by taking one tablet of ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
per day. Taking the niacin with meals also helps reduce this side effect. After several weeks of a consistent dose, most patients no longer flush. Slow- or "sustained"-release forms of niacin have been developed to lessen these side effects. One study showed the incidence of flushing was significantly lower with a sustained release
Sustained release
Time release technology, also known as sustained-release , sustained-action , extended-release , time-release or timed-release, controlled-release , modified release , or continuous-release , is a mechanism used in pill tablets or capsules to...
formulation though doses above 2 g per day have been associated with liver damage
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage.The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges, may injure...
, in particular, with slow-release formulations. Flushing is often thought to involve histamine, but histamine has been shown not to be involved in the reaction. Prostaglandin (PGD2) is the primary cause of the flushing reaction, with serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
appearing to have a secondary role in this reaction.
Although high doses of niacin may elevate blood sugar
Blood sugar
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal. Normally in mammals, the body maintains the blood glucose level at a reference range between about 3.6 and 5.8 mM , or 64.8 and 104.4 mg/dL...
, thereby worsening diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
, recent studies show the actual effect on blood sugar to be only 5–10%. Patients with diabetes who continued to take anti-diabetes drugs containing niacin did not experience major blood glucose changes. Thus looking at the big picture, niacin continues to be recommended as a drug for preventing CVD in patients with diabetes.
Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricemia is a level of uric acid in the blood that is abnormally high. In humans, the upper end of the normal range is 360 µmol/L for women and 400 µmol/L for men.-Causes:...
is another side effect of taking high-dose niacin, and may exacerbate gout
Gout
Gout is a medical condition usually characterized by recurrent attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis—a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected . However, it may also present as tophi, kidney stones, or urate...
.
Niacin in doses used to lower cholesterol levels has been associated with birth defects in laboratory animals, with possible consequences for infant development in pregnant
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
women.
Niacin, particularly the time-release variety, at extremely high doses can cause acute toxic reactions. Extremely high doses of niacin can also cause niacin maculopathy
Maculopathy
A maculopathy is any pathological condition of the macula, an area at the centre of the retina that is associated with highly sensitive, accurate vision.-Examples Of Maculopathies:...
, a thickening of the macula
Macula
The macula or macula lutea is an oval-shaped highly pigmented yellow spot near the center of the retina of the human eye. It has a diameter of around 5 mm and is often histologically defined as having two or more layers of ganglion cells...
and retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
, which leads to blurred vision and blindness. This maculopathy is reversible after niacin intake ceases.
Inositol hexanicotinate
One form of dietary supplement is inositol hexanicotinate (IHN), which is inositolInositol
Inositol or cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol is a chemical compound with formula 6126 or 6, a sixfold alcohol of cyclohexane. It exists in nine possible stereoisomers, of which the most prominent form, widely occurring in nature, is cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-cyclohexanehexol, or myo-inositol...
that has been ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
ified with niacin on all six of inositol's alcohol groups. IHN is usually sold as "flush-free" or "no-flush" niacin in units of 250, 500, or 1000 mg/tablets or capsules. It is sold as an over-the-counter formulation, and often is marketed and labeled as niacin, thus misleading consumers into thinking they are getting the active form of the medication. While this form of niacin does not cause the flushing associated with the immediate-release products, the evidence that it has lipid-modifying functions is contradictory, at best. As the clinical trials date from the early 1960s (Dorner, Welsh) or the late 1970s (Ziliotto, Kruse, Agusti), it is difficult to assess them by today's standards. One of the last of those studies affirmed the superiority of inositol and xantinol esters of nicotinic acid for reducing serum free fatty acid, but other studies conducted during the same period found no benefit. Studies explain that this is primarily because "flush-free" preparations do not contain any free nicotinic acid. A more recent placebo-controlled trial was small (n=11/group), but results after three months at 1500 mg/day showed no trend for improvements in total cholesterol, LDL-C, HDL-C or triglycerides. Thus, so far there is not enough evidence to recommend IHN to treat dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia or dyslipidaemia is an abnormal amount of lipids in the blood. In developed countries, most dyslipidemias are hyperlipidemias; that is, an elevation of lipids in the blood, often due to diet and lifestyle. The prolonged elevation of insulin levels can lead to dyslipidemia...
. Furthermore, the American Heart Association and the National Cholesterol Education Program both take the position that only prescription niacin should be used to treat dyslipidemias, and only under the management of a physician. The reason given is that niacin at effective intakes of 1500–3000 mg/day can also potentially have severe adverse effects. Thus liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests , are groups of clinical biochemistry laboratory blood assays designed to give information about the state of a patient's liver. The parameters measured include PT/INR, aPTT, albumin, billirubin and others...
to monitor liver enzymes are necessary when taking therapeutic doses of niacin, including alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation...
(ALP), aspartate transaminase
Aspartate transaminase
Aspartate transaminase , also called aspartate aminotransferase or serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase , is a pyridoxal phosphate -dependent transaminase enzyme . AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in...
(AST), and alanine transaminase
Alanine transaminase
Alanine transaminase or ALT is a transaminase enzyme . It is also called serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase or alanine aminotransferase ....
(ALT).
Biosynthesis and chemical synthesis

Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
can synthesize niacin from the essential amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
tryptophan
Tryptophan
Tryptophan is one of the 20 standard amino acids, as well as an essential amino acid in the human diet. It is encoded in the standard genetic code as the codon UGG...
, requiring 60 mg of tryptophan to make one mg of niacin. The 5-membered aromatic heterocycle
Heterocyclic compound
A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound which has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring. The counterparts of heterocyclic compounds are homocyclic compounds, the rings of which are made of a single element....
of tryptophan is cleaved and rearranged with the alpha amino group
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
of tryptophan into the 6-membered aromatic heterocycle of niacin. Riboflavin, Vitamin B6 and iron are required in some of the reactions involved in the conversion of tryptophan to NAD.
Several million kilograms of niacin are manufactured each year, starting from 3-methylpyridine
3-Methylpyridine
3-Methylpyridine, or 3-picoline, is the organic compound with formula 3-CH3C5H4N. It is one of the three isomers of methylpyridine. This colorless liquid is a precursor to pyridine derivatives that have applications in the pharmaceutical and agricultural industries. Like pyridine, 3-methylpyridine...
.
Receptor
In addition to its effects as NAD and NADP, niacin may have additional effects by receptor activation. The receptor for niacin is a G protein-coupled receptorG protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors , also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein-linked receptors , comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal...
called HM74A. It couples to the Gi alpha subunit
Gi alpha subunit
Gi alpha subunit is a heterotrimeric G protein subunit that inhibits the production of cAMP from ATP.- Receptors :The following G protein-coupled receptors couple to the Gi subunit:* Acetylcholine M2 & M4 receptors...
.
Food sources
Niacin is found in variety of foods, including liver, chicken, beef, fish, cereal, peanuts and legumes, and is also synthesized from tryptophanTryptophan
Tryptophan is one of the 20 standard amino acids, as well as an essential amino acid in the human diet. It is encoded in the standard genetic code as the codon UGG...
, which is found in meat, dairy and eggs.
Animal products:
- liverLiverThe liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, heartHeartThe heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
and kidneyKidneyThe kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and... - chickenChicken (food)Chicken is the most common type of poultry in the world, and is prepared as food in a wide variety of ways, varying by region and culture.- History :...
- beefBeefBeef is the culinary name for meat from bovines, especially domestic cattle. Beef can be harvested from cows, bulls, heifers or steers. It is one of the principal meats used in the cuisine of the Middle East , Australia, Argentina, Brazil, Europe and the United States, and is also important in...
- fishFish (food)Fish is a food consumed by many species, including humans. The word "fish" refers to both the animal and to the food prepared from it. Fish has been an important source of protein for humans throughout recorded history.-Terminology:...
: tunaTunaTuna is a salt water fish from the family Scombridae, mostly in the genus Thunnus. Tuna are fast swimmers, and some species are capable of speeds of . Unlike most fish, which have white flesh, the muscle tissue of tuna ranges from pink to dark red. The red coloration derives from myoglobin, an...
, salmonSalmonSalmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true... - eggsEgg (food)Eggs are laid by females of many different species, including birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, and have probably been eaten by mankind for millennia. Bird and reptile eggs consist of a protective eggshell, albumen , and vitellus , contained within various thin membranes...
Fruits and vegetables:
- avocadoAvocadoThe avocado is a tree native to Central Mexico, classified in the flowering plant family Lauraceae along with cinnamon, camphor and bay laurel...
s - dateDate PalmThe date palm is a palm in the genus Phoenix, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit. Although its place of origin is unknown because of long cultivation, it probably originated from lands around the Persian Gulf. It is a medium-sized plant, 15–25 m tall, growing singly or forming a clump with...
s - tomatoTomatoThe word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler...
es - leaf vegetableLeaf vegetableLeaf vegetables, also called potherbs, green vegetables, greens, leafy greens or salad greens, are plant leaves eaten as a vegetable, sometimes accompanied by tender petioles and shoots...
s - broccoliBroccoliBroccoli is a plant in the cabbage family, whose large flower head is used as a vegetable.-General:The word broccoli, from the Italian plural of , refers to "the flowering top of a cabbage"....
- carrotCarrotThe carrot is a root vegetable, usually orange in colour, though purple, red, white, and yellow varieties exist. It has a crisp texture when fresh...
s - sweet potatoSweet potatoThe sweet potato is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the family Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting, tuberous roots are an important root vegetable. The young leaves and shoots are sometimes eaten as greens. Of the approximately 50 genera and more than 1,000 species of...
es - asparagusAsparagusAsparagus officinalis is a spring vegetable, a flowering perennialplant species in the genus Asparagus. It was once classified in the lily family, like its Allium cousins, onions and garlic, but the Liliaceae have been split and the onion-like plants are now in the family Amaryllidaceae and...
Seeds:
- nutNut (fruit)A nut is a hard-shelled fruit of some plants having an indehiscent seed. While a wide variety of dried seeds and fruits are called nuts in English, only a certain number of them are considered by biologists to be true nuts...
s - whole grainWhole grainWhole grains are cereal grains that contain cereal germ, endosperm, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm. Whole grains can generally be sprouted while refined grains generally will not sprout. Whole-meal products are made by grinding whole grains in order to make...
productProduct (business)In general, the product is defined as a "thing produced by labor or effort" or the "result of an act or a process", and stems from the verb produce, from the Latin prōdūce ' lead or bring forth'. Since 1575, the word "product" has referred to anything produced...
s - legumes
- saltbush seedsSEEDSSEEDS is a voluntary organisation registered under the Societies Act of India....
Fungi:
- mushroomMushroomA mushroom is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or on its food source. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that...
s - brewer's yeast
Other:
- VegemiteVegemiteVegemite is a dark brown Australian food paste made from yeast extract. It is a spread for sandwiches, toast, crumpets and cracker biscuits, and filling for pastries...
(from spent brewer's yeast)
History
Niacin was first described by Hugo WeidelHugo Weidel
Hugo Weidel 13 November 1849 – 7 June 1899) was an Austrian chemist known for inventing Weidel's reaction and describing the structure of organic compound niacin. For his achievements, Weidel received the Lieben Prize in 1880.-Life and work:...
in 1873 in his studies of nicotine
Nicotine
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants that constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco, with biosynthesis taking place in the roots and accumulation occurring in the leaves...
. The original preparation remains useful: The oxidation of nicotine
Nicotine
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants that constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco, with biosynthesis taking place in the roots and accumulation occurring in the leaves...
using nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
. Niacin was extracted from livers by Conrad Elvehjem
Conrad Elvehjem
Conrad A. Elvehjem, , was internationally known as a biochemist in nutrition. In 1937 he identified a molecule found in fresh meat and yeast as a new vitamin, nicotinic acid, now called niacin...
, who later identified the active ingredient, then referred to as the "pellagra-preventing factor" and the "anti-blacktongue factor." When the biological significance of nicotinic acid was realized, it was thought appropriate to choose a name to dissociate it from nicotine, to avoid the perception that vitamins or niacin-rich food contains nicotine, or that cigarettes contain vitamins. The resulting name 'niacin' was derived from nicotinic acid + vitamin.
Carpenter found in 1951 that niacin in corn is biologically unavailable, and can be released only in very alkaline lime water of pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
11.
This process, known as nixtamalization
Nixtamalization
Nixtamalization typically refers to a process for the preparation of maize , or other grain, in which the grain is soaked and cooked in an alkaline solution, usually limewater, and hulled. The term can also refer to the removal via an alkali process of the pericarp from other grains such as sorghum...
, was discovered by the prehistoric civilizations of Mesoamerica.
Niacin is referred to as vitamin B3 because it was the third of the B vitamins
B vitamins
B vitamins are a group of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism. The B vitamins were once thought to be a single vitamin, referred to as vitamin B . Later research showed that they are chemically distinct vitamins that often coexist in the same foods...
to be discovered. It has historically been referred to as "vitamin PP" or "vitamin P-P".
Research
, a combination of niacin with laropiprantLaropiprant
Laropiprant is used in combination with niacin to reduce blood cholesterol . Merck & Co. planned to market this combination under the trade names Cordaptive and Tredaptive. On April 28, 2008, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued a "not approved" letter for Cordaptive...
is being tested in a clinical trial. Laropiprant reduces facial flushes induced by niacin.

