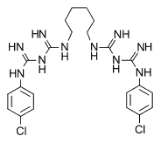
Chlorhexidine gluconate
Overview
Chlorhexidine is a chemical antiseptic
. It is effective on both Gram-positive
and Gram-negative
bacteria
, although it is less effective with some Gram-negative bacteria. It has both bactericidal and bacteriostatic mechanisms of action, the mechanism of action being membrane disruption, not ATPase
inactivation as previously thought. It is also useful against fungi and enveloped viruses, though this has not been extensively investigated.
Antiseptic
Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction...
. It is effective on both Gram-positive
Gram-positive
Gram-positive bacteria are those that are stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining. This is in contrast to Gram-negative bacteria, which cannot retain the crystal violet stain, instead taking up the counterstain and appearing red or pink...
and Gram-negative
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counterstain is added after the crystal violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red or pink color...
bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, although it is less effective with some Gram-negative bacteria. It has both bactericidal and bacteriostatic mechanisms of action, the mechanism of action being membrane disruption, not ATPase
ATPase
ATPases are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of adenosine triphosphate into adenosine diphosphate and a free phosphate ion. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur...
inactivation as previously thought. It is also useful against fungi and enveloped viruses, though this has not been extensively investigated.

