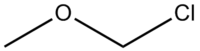
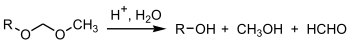Chloromethyl methyl ether
Encyclopedia
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s with the general structure R-O-(CH2)n-Cl, characterized as an ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
connected to a chloromethyl group via a alkane
Alkane
Alkanes are chemical compounds that consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and are bonded exclusively by single bonds without any cycles...
chain.
Chloromethyl methyl ether
Chloromethyl methyl ether
Chloroalkyl ethers are a class of organic compounds with the general structure R-O-n-Cl, characterized as an ether connected to a chloromethyl group via a alkane chain.Chloromethyl methyl ether is an ether with the formula...
(CMME) is an ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
with the formula . It is used as an alkylating agent and industrial solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
to manufacture dodecylbenzyl chloride, water repellents, ion-exchange resins, polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
s, and as a chloromethylation reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
. It is a known human carcinogen
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that is an agent directly involved in causing cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes...
. In organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
the compound is used for the introduction of the methoxymethyl (MOM) protecting group
Protecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group in order to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction...
.
Closely related compounds of industrial importance are bis(chloromethyl ether) (BCME) (closely related to chemical weapon sulfur mustard
Sulfur mustard
The sulfur mustards, or sulphur mustards, commonly known as mustard gas, are a class of related cytotoxic, vesicant chemical warfare agents with the ability to form large blisters on exposed skin. Pure sulfur mustards are colorless, viscous liquids at room temperature...
) and benzyl chloromethyl ether (BOMCl).
| Chloromethyl ether | |R | |Molar mass Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... |
CAS number | Boiling point Boiling point The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid.... °C |
|
| Benzyl chloromethyl ether | Benzyl Benzyl In organic chemistry, benzyl is the term used to describe the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure C6H5CH2-. Benzyl features a benzene ring attached to a CH2 group.-Nomenclature:... |
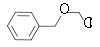 |
156.61 | 3587-60-8 | 102°C @ 14 mmHg (1,866.5 Pa) |
| Chloromethyl methyl ether Chloromethyl methyl ether Chloroalkyl ethers are a class of organic compounds with the general structure R-O-n-Cl, characterized as an ether connected to a chloromethyl group via a alkane chain.Chloromethyl methyl ether is an ether with the formula... |
Methyl | 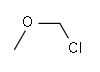 |
80.51 | 107-30-2 | 55-57 |
| Bischloromethyl ether | 2.svg.png) |
114.96 | 542-88-1 | 106 | |
| tert-Butyl chloromethyl ether | Butyl Butyl In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula -C4H9, derived from either of the two isomers of butane.... |
 |
124.5 | ||
| Methoxyethyl chloromethyl ether | 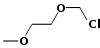 |
124.57 | 3970-21-6 | 50-52°C @ 13 mmHg (1,733.2 Pa) | |
| Dichloromethyl methyl ether Dichloromethyl methyl ether Dichloromethyl methyl ether is an organic compound that belongs to the class of ethers with a dichloromethyl group and a methyl group... |
114.96 | 4885-02-3 | 82 - 85.5°C | ||
| Representative chloroalkyl ethers | |||||
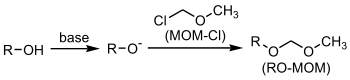
MOM ethers
Methyl chloromethyl ether (often abbreviated MOMCl) is used as a protecting groupProtecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group in order to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction...
for alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s. The product formed is a MOM ether. A base such as N,N-diisopropylethylamine is a requirement.
The MOM group can be removed by application of dilute acid.
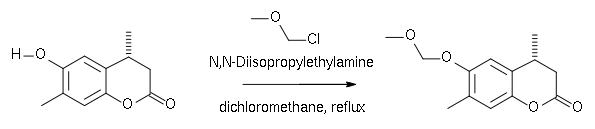
An example is the protection of a phenol group:
With a benzyl group the protective group becomes a BOM-ether. See also the closely related methylthiomethyl ether
Methylthiomethyl ether
In organic chemistry a methylthiomethyl ether is a protective group for hydroxyl groups. Hydroxyl groups are present in many chemical compounds and they must be protected during oxidation, acylation, halogenation, dehydration and other reactions to which they are susceptible.Many kinds of...
s.
A t-butyl group can also be used. The chloride is prepaired from Methyl tert-butyl ether
Methyl tert-butyl ether
Methyl tert-butyl ether, also known as methyl tertiary butyl ether and MTBE, is an organic compound with molecular formula 3COCH3. MTBE is a volatile, flammable, and colorless liquid that is immiscible with water. It has a minty odor vaguely reminiscent of diethyl ether, leading to unpleasant taste...
using a photochemical chlorination.
With a methoxyethoxyl group the protective group becomes a MEM-ether. This ether is much more stable than the MOM ether to hydrolysis.