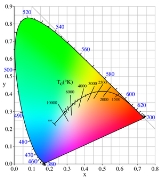
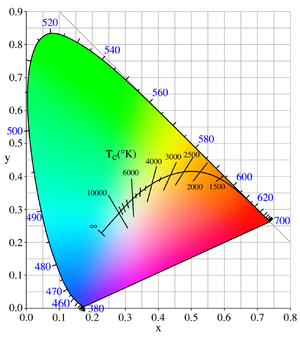
Chromaticity
Encyclopedia
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
regardless of its luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
, that is, as determined by its hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
and colorfulness (or saturation, chroma, intensity, or excitation purity).
In color science, the white point
White point
A white point is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results...
of an illuminant or of a display is a neutral reference characterized by a chromaticity; for example, the white point of an sRGB display is an x,y chromaticity of [0.3127,0.3290]. All other chromaticities may be defined in relation to this reference using polar coordinates. The hue is the angular component, and the purity is the radial component, normalized by the maximum radius for that hue.
In color science
Purity is roughly equivalent to the term "saturationSaturation (color theory)
In colorimetry and color theory, colorfulness, chroma, and saturation are related but distinct concepts referring to the perceived intensity of a specific color. Colorfulness is the degree of difference between a color and gray. Chroma is the colorfulness relative to the brightness of another color...
" in the HSV color model. The property "hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
" is as used in general color theory and in specific color models such as HSV or HSL
HSL color space
HSL and HSV are the two most common cylindrical-coordinate representations of points in an RGB color model, which rearrange the geometry of RGB in an attempt to be more intuitive and perceptually relevant than the cartesian representation...
, though it is more perceptually uniform in color models such as Munsell, CIELAB or CIECAM02
CIECAM02
Published in 2002 by the CIE Technical Committee 8-01 , as of 2008 CIECAM02 is the most recent color appearance model ratified by the CIE, and the successor of CIECAM97s.| quote=The CIECAM97s model was adopted by the CIE in 1997 for color imaging applications. It includes forward and reverse modes...
.
Some color space
Color space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
s separate the three dimensions of color into one luminance dimension and a pair of chromaticity dimensions. For example, the chromaticity coordinates are a* and b* in CIELAB, u and v in CIELUV, x and y in xyY space, etc. These pairs define chromaticity vectors in a rectangular 2-space, unlike the polar coordinates of hue angle and saturation that are used in HSV color space.
On the other hand, some color spaces such as RGB
RGB color space
An RGB color space is any additive color space based on the RGB color model. A particular RGB color space is defined by the three chromaticities of the red, green, and blue additive primaries, and can produce any chromaticity that is the triangle defined by those primary colors...
and XYZ do not separate out chromaticity; chromaticity coordinates such as r and g or x and y can be calculated by an operation that normalizes out intensity.
The xyY space is a cross between the CIEXYZ
CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
and its normalized chromaticity coordinates xyz, such that the luminance Y is preserved and augmented with just the required two chromaticity dimensions.
External links
- Stanford University CS 178 interactive Flash demo explaining chromaticity diagrams.

