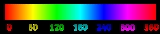
Hue
Encyclopedia



Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
, defined technically (in the CIECAM02
CIECAM02
Published in 2002 by the CIE Technical Committee 8-01 , as of 2008 CIECAM02 is the most recent color appearance model ratified by the CIE, and the successor of CIECAM97s.| quote=The CIECAM97s model was adopted by the CIE in 1997 for color imaging applications. It includes forward and reverse modes...
model), as "the degree to which a stimulus can be described
as similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
, green
Green
Green is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 520–570 nanometres. In the subtractive color system, it is not a primary color, but is created out of a mixture of yellow and blue, or yellow and cyan; it is considered...
, blue
Blue
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal...
, and yellow
Yellow
Yellow is the color evoked by light that stimulates both the L and M cone cells of the retina about equally, with no significant stimulation of the S cone cells. Light with a wavelength of 570–590 nm is yellow, as is light with a suitable mixture of red and green...
," (the unique hues
Unique hues
In the opponent process theory of color, there are four unique hues – red, yellow, green, and blue – relative to which other hues are defined. Unique red is a red which appears to have no yellow or blue in it; unique yellow is a yellow which appears to have no red or green in it; etc.Color names...
). The other main correlatives of color appearance are colorfulness, chroma, saturation
Saturation (color theory)
In colorimetry and color theory, colorfulness, chroma, and saturation are related but distinct concepts referring to the perceived intensity of a specific color. Colorfulness is the degree of difference between a color and gray. Chroma is the colorfulness relative to the brightness of another color...
, lightness
Lightness (color)
Lightness is a property of a color, or a dimension of a color space, that is defined in a way to reflect the subjective brightness perception of a color for humans along a lightness–darkness axis. A color's lightness also corresponds to its amplitude.Various color models have an explicit term for...
, and brightness
Brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target...
.
Usually, colors with the same hue are distinguished with adjectives referring to their lightness and/or chroma, such as with "light blue", "pastel blue", "vivid blue". Exceptions include brown
Brown
Brown is a color term, denoting a range of composite colors produced by a mixture of orange, red, rose, or yellow with black or gray. The term is from Old English brún, in origin for any dusky or dark shade of color....
, which is a dark orange
Orange (colour)
The colour orange occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum at a wavelength of about 585–620 nm, and has a hue of 30° in HSV colour space. It is numerically halfway between red and yellow in a gamma-compressed RGB colour space, the expression of which is the RGB colour wheel. The...
, and pink
Pink
Pink is a mixture of red and white. Commonly used for Valentine's Day and Easter, pink is sometimes referred to as "the color of love." The use of the word for the color known today as pink was first recorded in the late 17th century....
, a light red with reduced chroma.
In painting
Painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a surface . The application of the medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush but other objects can be used. In art, the term painting describes both the act and the result of the action. However, painting is...
color theory
Color theory
In the visual arts, color theory is a body of practical guidance to color mixing and the visual impacts of specific color combinations. Although color theory principles first appeared in the writings of Leone Battista Alberti and the notebooks of Leonardo da Vinci , a tradition of "colory theory"...
, a hue refers to a pure color—one without tint or shade
Tints and shades
In color theory, a tint is the mixture of a color with white, which increases lightness, and a shade is the mixture of a color with black, which reduces lightness...
(added white or black pigment
Pigment
A pigment is a material that changes the color of reflected or transmitted light as the result of wavelength-selective absorption. This physical process differs from fluorescence, phosphorescence, and other forms of luminescence, in which a material emits light.Many materials selectively absorb...
, respectively). A hue is an element of the color wheel
Color wheel
A color wheel or color circle is an abstract illustrative organization of color hues around a circle that shows relationships between primary colors, secondary colors, complementary colors, etc....
. Hues are first processed in the brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
in areas in the extended V4 called glob
Glob (visual system)
Globs are millimeter-sized color modules found beyond the visual area V2 in the brain's color processing ventral pathway. They are scattered throughout the posterior inferior temporal cortex in an area called the V4 complex. They are clustered by color preference, and organized as color columns...
s.
Computing hue
In opponent color spacesOpponent process
The color opponent process is a color theory that states that the human visual system interprets information about color by processing signals from cones and rods in an antagonistic manner...
in which two of the axes are perceptually orthogonal to lightness, such as the CIE 1976 (L*, a*, b*) (CIELAB) and 1976 (L*, u*, v*) (CIELUV) color spaces, hue may be computed together with chroma by converting these coordinates from rectangular form to polar form. Hue is the angular component of the polar representation, while chroma is the radial component.
Specifically, in CIELAB:

while, analogously, in CIELUV:
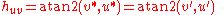
Where, atan2
Atan2
In trigonometry, the two-argument function atan2 is a variation of the arctangent function. For any real arguments and not both equal to zero, is the angle in radians between the positive -axis of a plane and the point given by the coordinates on it...
is a two-argument inverse tangent.
Computing hue from RGB
Preucil describes a color hexagon, similar to a trilinear plot described by Evans, Hanson, and Brewer, which may be used to compute hue from RGB. To place redRed
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
at 0°, green
Green
Green is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 520–570 nanometres. In the subtractive color system, it is not a primary color, but is created out of a mixture of yellow and blue, or yellow and cyan; it is considered...
at 120°, and blue
Blue
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal...
at 240°.
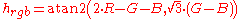
Note: This is equation assumes the form atan2
Atan2
In trigonometry, the two-argument function atan2 is a variation of the arctangent function. For any real arguments and not both equal to zero, is the angle in radians between the positive -axis of a plane and the point given by the coordinates on it...
(x,y), many programs and spreadsheets use atan2
Atan2
In trigonometry, the two-argument function atan2 is a variation of the arctangent function. For any real arguments and not both equal to zero, is the angle in radians between the positive -axis of a plane and the point given by the coordinates on it...
(y,x).
Equivalently, one may solve:
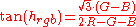
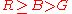
Preucil used a polar plot, which he termed a color circle. Using R, G, and B, one may compute hue angle using the following scheme: determine which of the six possible orderings of R, G, and B prevail, then apply the formula given in the table below.


| Ordering | Hue Region | Formula |
|---|---|---|
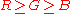 |
Red-Yellow |  |
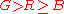 |
Yellow-Green | 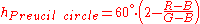 |
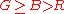 |
Green-Cyan | 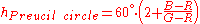 |
 |
Cyan-Blue | 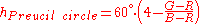 |
 |
Blue-Magenta | 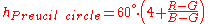 |
 |
Magenta-Red | 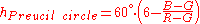 |
Note that in each case the formula contains the fraction
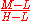 , where H is the highest of R, G, and B; L is the lowest, and M is the mid one between the other two. This is referred to as the Preucil Hue Error, and was used in the computation of mask strength in photomechanical color reproduction.
, where H is the highest of R, G, and B; L is the lowest, and M is the mid one between the other two. This is referred to as the Preucil Hue Error, and was used in the computation of mask strength in photomechanical color reproduction.Hue angles computed for the Preucil circle agree with the hue angle computed for the Preucil Hexagon at integer multiples of 30 degrees (red, yellow, green, cyan, blue, magenta, and the colors mid-way between contiguous pairs) and differ by approximately 1.2 degrees at odd integer multiples of 15 degrees (based on the circle formula), the maximum divergence between the two.
The process of converting an RGB color into an HSL color space
HSL color space
HSL and HSV are the two most common cylindrical-coordinate representations of points in an RGB color model, which rearrange the geometry of RGB in an attempt to be more intuitive and perceptually relevant than the cartesian representation...
or HSV color space is usually based on a 6-piece piecewise mapping, treating the HSV cone as a hexacone, or the HSL double cone as a double hexacone. The formulae used are those in the table above.
Specialized hues
The hues exhibited by caramel colorings and beerBeer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
s are fairly limited in range. The Linner hue index
Linner hue index
The Linner hue index, H_L, is used to describe the hues which a given caramel coloring may produce. In conjunction with tinctorial strength, or the depth of a caramel coloring's color, it describes the spectra which a solution of the coloring may produce at different dilutions and thicknesses...
is used to quantify the hue of such products.
Hue as a qualification in the names of artist's colors
Manufacturers of pigments use the word hue e.g. 'Cadmium Yellow (hue)' to indicate that the original pigmentation ingredient, often toxic, has been replaced by safer (or cheaper) alternatives whilst retaining the hue of the original. Replacements are often used for chromiumChromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
, cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
and alizarin
Alizarin
Alizarin or 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a prominent dye, originally derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.Alizarin was used as a red dye for the English parliamentary "new model" army...
.
Hue vs. dominant wavelength
Dominant wavelengthDominant wavelength
In color science, the dominant wavelength and complementary wavelength are ways of describing non-spectral light mixtures in terms of the spectral light that evokes an identical perception of hue....
(or sometimes equivalent wavelength) is a physical analog to the perceptual attribute hue. On a chromaticity diagram, a line is drawn from a white point
White point
A white point is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results...
through the coordinates of the color in question, until it intersects the spectral locus. The wavelength at which the line intersects the spectrum locus is identified as the color's dominant wavelength
Dominant wavelength
In color science, the dominant wavelength and complementary wavelength are ways of describing non-spectral light mixtures in terms of the spectral light that evokes an identical perception of hue....
if the point is on the same side of the white point as the spectral locus, and as the color's complementary wavelength if the point is on the opposite side.
Hue difference: 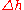 or
or 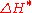 ?
?
There are two main ways in which hue difference is quantified. The first is the simple difference between the two hue angles. The symbol for this expression of hue difference is 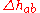 in CIELAB and
in CIELAB and 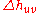 in CIELUV. The other is computed as the residual total color difference after Lightness and Chroma differences have been accounted for; its symbol is
in CIELUV. The other is computed as the residual total color difference after Lightness and Chroma differences have been accounted for; its symbol is 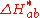 in CIELAB and
in CIELAB and 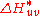 in CIELUV.
in CIELUV.See also
- Lightness (color)Lightness (color)Lightness is a property of a color, or a dimension of a color space, that is defined in a way to reflect the subjective brightness perception of a color for humans along a lightness–darkness axis. A color's lightness also corresponds to its amplitude.Various color models have an explicit term for...
- Colorfulness
- ChromaticityChromaticityChromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance, that is, as determined by its hue and colorfulness ....
- Munsell color systemMunsell color systemIn colorimetry, the Munsell color system is a color space that specifies colors based on three color dimensions: hue, value , and chroma . It was created by Professor Albert H...
- Bezold-Brücke shiftBezold-Brücke shiftThe Bezold–Brücke shift is a change in hue perception as intensity changes. As intensity increases, spectral colors shift more towards blue or yellow . At lower intensities, the red/green axis dominates....

