
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
Encyclopedia
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also called the Church of the Resurrection by Eastern Christian
s, is a church within the walled Old City of Jerusalem. It is a few steps away from the Muristan
.
The site is venerated as Golgotha
(the Hill of Calvary), where Jesus
was crucified
, and is said also to contain the place where Jesus was buried (the sepulchre
). The church has been an important Christian pilgrimage
destination since at least the 4th century
, as the purported site of the resurrection of Jesus
. Today it also serves as the headquarters of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
, while control of the building is shared between several Christian churches
and secular entities in complicated arrangements essentially unchanged for centuries. Today, the church is home to Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy
and Roman Catholicism. Anglican
and Protestant
Christian
s have no permanent presence in the church.
The latest trend among visitors to the spot (standing outside the Church) is to applaud loudly during bells' ringing. This is to recognize the unique beauty of the Church and its unique history. The origin of this practice is in dispute; one source describes a similar act in the Peter Greenaway
movie The Belly of an Architect
.
 In the early 2nd century, the site of the present Church had been a temple of Aphrodite
In the early 2nd century, the site of the present Church had been a temple of Aphrodite
; several ancient writers alternatively describe it as a temple to Venus
, the Roman equivalent to Aphrodite. Eusebius
claims, in his Life of Constantine, that the site of the Church had originally been a Christian place of veneration, but that Hadrian
had deliberately covered these Christian sites with earth, and built his own temple on top, due to his hatred for Christianity (the authenticity/inaccuracy of this claim is discussed below). Although Eusebius does not say as much, the temple of Aphrodite was probably built as part of Hadrian
's reconstruction of Jerusalem as Aelia Capitolina
in 135, following the destruction of the Jewish Revolt
of 70 and Bar Kokhba's revolt
of 132–135.
Emperor Constantine I
ordered in about 325/326 that the temple be demolished and the soil - which had provided a flat surface for the temple - be removed, instructing Macarius of Jerusalem
, the local Bishop, to build a church on the site. The Pilgrim of Bordeaux
reports in 333: There, at present, by the command of the Emperor Constantine, has been built a basilica, that is to say, a church of wondrous beauty. Constantine directed his mother, Helena
, to build churches upon sites which commemorated the life of Jesus Christ; she was present in 326 at the construction of the church on the site, and involved herself in the excavations and construction.
During the excavation, Helena is alleged to have rediscovered the True Cross
, and a tomb, though Eusebius' account makes no mention of Helena's presence at the excavation, nor of the finding of the cross but only the tomb. According to Eusebius, the tomb exhibited a clear and visible proof that it was the tomb of Jesus
; several scholars have criticised Eusebius' account for an uncritical use of sources, and for being dishonest with Edward Gibbon
, for example, pointing out that Eusebius' chapter headings claim that fictions are lawful and fitting for him to use. Socrates Scholasticus
(born c. 380), in his Ecclesiastical History, gives a full description of the discovery (that was repeated later by Sozomen
and by Theodoret
) which emphasizes the role played in the excavations and construction by Helena; just as the Church of the Nativity
in Bethlehem
(also founded by Constantine and Helena) commemorated the birth of Jesus, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre would commemorate his death and resurrection.
Constantine's church was built as two connected churches over the two different holy sites, including a great basilica
(the Martyrium visited by Egeria in the 380s), an enclosed colonnade
d atrium
(the Triportico) with the traditional site of Golgotha in one corner, and a rotunda
, called the Anastasis ("Resurrection"), which contained the remains of a rock-cut room that Helena and Macarius identified as the burial site of Jesus. The rockface at the west end of the building was cut away, although it is unclear how much remained in Constantine's time, as archaeological investigation has revealed that the temple of Aphrodite reached far into the current rotunda area, and the temple enclosure would therefore have reached even further to the west.
According to tradition, Constantine arranged for the rockface to be removed from around the tomb, without harming it, in order to isolate the tomb; in the centre of the rotunda is a small building called the Kouvouklion (Kουβούκλιον; Modern Greek for small compartment) or Aedicule (from Latin: aediculum, small building), which supposedly encloses this tomb, although it is not currently possible to verify the claim, as the remains are completely enveloped by a marble sheath. The discovery of the kokhim
tombs just beyond the west end of the Church, and more recent archaeological investigation of the rotunda floor, suggest that a narrow spur
of at least ten yards length would have had to jut out from the rock face if the contents of the Aedicule were once inside it. The dome
of the rotunda was completed by the end of the 4th century.
Each year, the Eastern Orthodox Church
celebrates the anniversary of the consecration
of the Church of the Resurrection (Holy Sepulchre) on September 13 (for those churches which follow the traditional Julian Calendar
, September 13 currently falls on September 26 of the modern Gregorian Calendar
).
 This building was damaged by fire in 614 when the Persians
This building was damaged by fire in 614 when the Persians
under Khosrau II invaded Jerusalem and captured the Cross. In 630, Emperor Heraclius
marched triumphantly into Jerusalem and restored the True Cross
to the rebuilt Church of the Holy Sepulchre. Under the Muslims it remained a Christian church. The early Muslim rulers protected the city's Christian sites, prohibiting their destruction and their use as living quarters. In 966 the doors and roof were burnt during a riot.
On October 18, 1009, under Fatimid
caliph
Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
, orders for the complete destruction of the Church were carried out. It is believed that Al-Hakim "was aggrieved by the scale of the Easter
pilgrimage to Jerusalem, which was caused specially by the annual miracle of the Holy Fire
within the Sepulchre. The measures against the church were part of a more general campaign against Christian places of worship in Palestine and Egypt, which involved a great deal of other damage: Adhemar of Chabannes recorded that the church of St George at Lydda
'with many other churches of the saints' had been attacked, and the 'basilica of the Lord's Sepulchre destroyed down to the ground'. ...The Christian writer Yahya ibn Sa'id reported that everything was razed 'except those parts which were impossible to destroy or would have been too difficult to carry away'." The Church's foundations were hacked down to bedrock. The Edicule and the east and west walls and the roof of the cut-rock tomb it encased were destroyed or damaged (contemporary accounts vary), but the north and south walls were likely protected by rubble from further damage. The "mighty pillars resisted destruction up to the height of the gallery pavement, and are now effectively the only remnant of the fourth-century buildings." Some minor repairs were done to the section believed to be the tomb of Jesus almost immediately after 1009, but a true attempt at restoration would have to wait for decades.
European reaction was of shock and dismay, with far-reaching and intense consequences. For example, Clunaic monk
Raoul Glaber blamed the Jews, with the result that Jews were expelled from Limoges
and other French
towns. Ultimately, this destruction provided an impetus to the later Crusades.
in 1027-8 an agreement was reached whereby the new Caliph Ali az-Zahir
(Al-Hakim's son) agreed to allowing the rebuilding and redecoration of the Church. The rebuilding was finally completed with the financing of the huge expense by Emperor Constantine IX Monomachos
and Patriarch Nicephorus of Constantinople in 1048. As a concession, the mosque in Constantinople
was re-opened and sermons were to be pronounced in az-Zahir's name. Muslim sources say a by-product of the agreement was the recanting of Islam by many Christians who had been forced to convert under Al-Hakim's persecutions. In addition the Byzantines, while releasing 5,000 Muslim prisoners, made demands for the restoration of other churches destroyed by Al-Hakim and the re-establishment of a Patriarch
in Jerusalem. Contemporary sources credit the emperor with spending vast sums in an effort to restore the Church of the Holy Sepulchre after this agreement was made. Despite the Byzantines spending vast sums on the project, "a total replacement was far beyond available resources. The new construction was concentrated on the rotunda and its surrounding buildings: the great basilica remained in ruins." The rebuilt church site consisted of "a court open to the sky, with five small chapels attached to it." The chapels were "to the east of the court of resurrection, where the wall of the great church had been. They commemorated scenes from the passion, such as the location of the prison of Christ and of his flagellation, and presumably were so placed because of the difficulties for free movement among shrines in the streets of the city. The dedication of these chapels indicates the importance of the pilgrims' devotion to the suffering of Christ. They have been described as 'a sort of Via Dolorosa
in miniature'... since little or no rebuilding took place on the site of the great basilica. Western pilgrims to Jerusalem during the eleventh century found much of the sacred site in ruins." Control of Jerusalem, and thereby the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, continued to change hands several times between the Fatimids and the Seljuk Turks
(loyal to the Abbasid
caliph in Baghdad
) until the arrival of the Crusaders in 1099.
, was the threat to Constantinople from the Turkish invasion of Asia Minor in response to the appeal of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos
. Still, historians agree that the fate of Jerusalem and thereby the Church of the Holy Sepulchre was of concern if not the immediate goal of papal policy in 1095. The idea of taking Jerusalem gained more focus as the Crusade was underway. The rebuilt church site was taken from the Fatimids (who had recently taken it from the Abassids) by the knight
s of the First Crusade
on 15 July 1099.
The First Crusade was envisioned as an armed pilgrimage, and no crusader could consider his journey complete unless he had prayed as a pilgrim at the Holy Sepulchre. Crusader Prince Godfrey of Bouillon
, who became the first crusader monarch of Jerusalem
, decided not to use the title "king" during his lifetime, and declared himself Advocatus Sancti Sepulchri (Protector (or Defender) of the Holy Sepulchre). By the crusader period, a cistern
under the former basilica was rumoured to have been the location that Helena had found the True Cross, and began to be venerated as such; although the cistern later became the Chapel of the Invention of the Cross, there is no evidence for the rumour prior to the 11th century, and modern archaeological investigation has now dated the cistern to the 11th century repairs by Monomachos.
The chronicler William of Tyre
reports on the renovation of the Church in the mid-12th century. The crusaders investigated the eastern ruins on the site, occasionally excavating through the rubble, and while attempting to reach the cistern, they discovered part of the original ground level of Hadrian's temple enclosure; they decided to transform this space into a chapel dedicated to Helena (the Chapel of Saint Helena
), widening their original excavation tunnel into a proper staircase. The crusaders began to refurnish the church in a Romanesque
style and added a bell tower. These renovations unified the small chapels on the site and were completed during the reign of Queen Melisende
in 1149, placing all the Holy places under one roof for the first time. The church became the seat of the first Latin Patriarchs
, and was also the site of the kingdom's scriptorium
. The church was lost to Saladin
, along with the rest of the city, in 1187, although the treaty established after the Third Crusade
allowed for Christian pilgrims to visit the site. Emperor Frederick II
regained the city and the church by treaty in the 13th century, while he himself was under a ban of excommunication, leading to the curious result of the holiest church in Christianity being laid under interdict
. Both city and church were captured by the Khwarezm
ians in 1244.
 The Franciscan
The Franciscan
friars renovated it further in 1555, as it had been neglected despite increased numbers of pilgrims. The Franciscans rebuilt the Aedicule, extending the structure to create an ante-chamber. After the renovation of 1555, control of the church oscillated between the Franciscans and the Orthodox, depending on which community could obtain a favorable firman from the Sublime Porte at a particular time, often through outright bribery, and violent clashes were not uncommon. There was no agreement about this question, although it was talked about it at the negotiations to the Treaty of Karlowitz
in 1699. In 1767, weary of the squabbling, the Porte issued a firman that divided the church among the claimants.
A fire severely damaged the structure again in 1808, causing the dome of the Rotunda to collapse and smashing the Edicule's exterior decoration. The Rotunda and the Edicule's exterior were rebuilt in 1809–1810 by architect Komminos of Mytilene
in the then current Ottoman Baroque
style. The fire did not reach the interior of the Aedicule, and the marble decoration of the Tomb dates mainly to the 1555 restoration, although the interior of the ante-chamber, now known as the Chapel of the Angel, was partly re-built to a square ground-plan, in place of the previously semi-circular western end. Another decree in 1853 from the sultan solidified the existing territorial division among the communities and set a status quo
for arrangements to "remain forever", caused differences of opinion about upkeep and even minor changes, including disagreement on the removal of an exterior ladder under one of the windows; this ladder has remained in the same position since then.
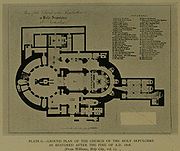 The cladding of red marble applied to the Aedicule by Komminos has deteriorated badly and is detaching from the underlying structure; since 1947 it has been held in place with an exterior scaffolding of iron girders installed by the British Mandate. No plans have been agreed upon for its renovation.
The cladding of red marble applied to the Aedicule by Komminos has deteriorated badly and is detaching from the underlying structure; since 1947 it has been held in place with an exterior scaffolding of iron girders installed by the British Mandate. No plans have been agreed upon for its renovation.
The current dome dates from 1870, although it was restored during 1994–1997, as part of extensive modern renovations to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, which have been ongoing since 1959. During 1973–1978 restoration works and excavations inside the building, and under the nearby Muristan, it was found that the area was originally a quarry, from which white meleke
limestone
was struck. To the east of the Chapel of St. Helena, the excavators discovered a void containing a 2nd century drawing of a roman ship, two low walls which supported the platform of Hadrian's 2nd century temple, and a higher 4th century wall built to support Constantine's basilica; the Armenian authorities have recently converted this archaeological space into the Chapel of Saint Vartan, and created an artificial walkway over the quarry on the north of the chapel, so that the new Chapel could be accessed (by permission) from the Chapel of St. Helena.
There was some controversy in 2010, when the Jerusalem City Council threatened to cut off water to the site due to disputed water bills.
. This narrow way of access to such a large structure has proven to be hazardous at times. For example, when a fire broke out in 1840, dozens of pilgrims were trampled to death. In 1999 the communities agreed to install a new exit door in the church, but there was never any report of this door being completed.
(an aisle surrounding the end of the choir or chancel of a church) is a stairway climbing to Calvary (Golgotha), traditionally regarded as the site of Jesus' crucifixion and the most lavishly decorated part of the church. The main altar there belongs to the Greek Orthodox, which contains The Rock of Calvary (12th Station of the Cross). The rock can be seen under glass on both sides of the altar, and beneath the altar there is a hole said to be the place where the cross was raised. The Roman Catholics (Franciscan
s) have an altar to the side, The Chapel of the Nailing of the Cross (11th Station of the Cross). On the left of the altar, towards the Eastern Orthodox chapel, there is a statue of Mary, believed to be working wonders (the 13th Station of the Cross, where Jesus' body was removed from the cross and given to his family).
Beneath the Calvary and the two chapels there, on the main floor, there is The Chapel of Adam. According to tradition, Jesus was crucified over the place where Adam's skull was buried. The Rock of Calvary is seen cracked through a window on the altar wall, the crack traditionally being said to be caused by the earthquake that occurred when Jesus died on the cross, and being said by more critical scholars to be the result of quarrying against a natural flaw in the rock.
 Just inside the entrance is The Stone of Anointing, also known as The Stone of Unction, which tradition claims to be the spot where Jesus' body was prepared for burial by Joseph of Arimathea
Just inside the entrance is The Stone of Anointing, also known as The Stone of Unction, which tradition claims to be the spot where Jesus' body was prepared for burial by Joseph of Arimathea
. However, this tradition is only attested since the crusader era, and the present stone was only added in the 1810 reconstruction. The wall behind the stone was a temporary addition to support the arch above it, which had been weakened after the damage in the 1808 fire; the wall blocks the view of the rotunda, sits on top of the graves of four 12th century kings, and is no longer structurally necessary. There is a difference of opinion as to whether it is the 13th Station of the Cross
, which others identify as the lowering of Jesus from the cross and locate between the 11th and 12th station up on Calvary. The lamps that hang over the stone are contributed by Armenians, Copts, Greeks and Latins.
is located in the centre of the Anastasis, beneath the larger of the church's two domes. In the centre of the Rotunda is the chapel called The Edicule, which contains the Holy Sepulchre itself. The Edicule has two rooms. The first one holds The Angel's Stone, a fragment of the stone believed to have sealed the tomb after Jesus' burial. The second one is the tomb itself.
the Eastern Orthodox
, Roman Catholic, and Armenian Apostolic
Churches all have rights to the interior of the tomb, and all three communities celebrate the Divine Liturgy
or Holy Mass
there daily. It is also used for other ceremonies on special occasions, such as the Holy Saturday
ceremony of the Holy Fire
celebrated by the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
. To its rear, within a chapel constructed of iron latticework
upon a stone base semicircular in plan, lies the altar used by the Coptic Orthodox
.
Beyond that to the rear of the Rotunda is a very rough hewn chapel, containing an opening to a rock-cut chamber, from which several kokh
-tombs radiate. Although this space was discovered comparatively recently, and contains no identifying marks, many Christians believe it to be the tomb of Joseph of Arimathea
in which the Syriac Orthodox
celebrate their Liturgy on Sundays. To the right of the sepulchre on the southeastern side of the Rotunda is the Chapel of the Apparition which is reserved for Roman Catholic use.

Further to the east in the ambulatory are three chapels (from south to north):

, south of the rotunda and on the west side of the front courtyard originally formed the baptistery
complex of the Constantinean church, the southern most chapel being the vestibule, the middle chapel being the actual baptistery
and the north chapel being the chamber in which the patriarch chrism
ated the newly baptized before leading them into the rotunda north of this complex.
.
 The primary custodians are the Eastern Orthodox
The primary custodians are the Eastern Orthodox
, Armenian Apostolic
, and Roman Catholic Churches, with the Greek Orthodox Church having the lion's share. In the 19th century, the Coptic Orthodox, the Ethiopian Orthodox and the Syriac Orthodox
acquired lesser responsibilities, which include shrines and other structures within and around the building. Times and places of worship for each community are strictly regulated in common areas.
Establishment of the 1853 status quo did not halt the violence, which continues to break out every so often even in modern times. On a hot summer day in 2002, a Coptic monk moved his chair from its agreed spot into the shade. This was interpreted as a hostile move by the Ethiopians, and eleven were hospitalized after the resulting fracas.
In another incident in 2004 during Orthodox celebrations of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross
, a door to the Franciscan chapel was left open. This was taken as a sign of disrespect by the Orthodox and a fistfight broke out. Some people were arrested, but no one was seriously injured.
On Palm Sunday
, in April 2008, a brawl broke out when a Greek monk
was ejected from the building by a rival faction. Police were called to the scene but were also attacked by the enraged brawlers. On Sunday, November 9, 2008, a clash erupted between Armenian and Greek monks during celebrations for the Feast of the Holy Cross.
Under the status quo, no part of what is designated as common territory may be so much as rearranged without consent from all communities. This often leads to the neglect of badly needed repairs when the communities cannot come to an agreement among themselves about the final shape of a project. Just such a disagreement has delayed the renovation of the edicule, where the need is now dire, but also where any change in the structure might result in a change to the status quo disagreeable to one or more of the communities.
A less grave sign of this state of affairs is located on a window ledge over the church's entrance. Someone placed a wooden ladder there sometime before 1852, when the status quo defined both the doors and the window ledges as common ground. The ladder remains there to this day, in almost exactly the same position it can be seen to occupy in century-old photographs and engravings.
No one controls the main entrance. In 1192, Saladin
assigned responsibility for it to the Muslim Nuseibeh
family. The Joudeh Al-Goudia family were entrusted as custodian to the keys of the Holy Sepulchre by the Ottomans few hundred years later, and both families now share the responsibility. This arrangement has persisted into modern times.
 As noted above, the site had been a temple of Aphrodite prior to Constantine's aedifice being built, a detail that Christian tradition puts down to Hadrian deliberately siting the temple over Jesus' tomb as a slight against Christianity. However, Hadrian's temple had actually been located there simply because it was the junction of the main north-south road
As noted above, the site had been a temple of Aphrodite prior to Constantine's aedifice being built, a detail that Christian tradition puts down to Hadrian deliberately siting the temple over Jesus' tomb as a slight against Christianity. However, Hadrian's temple had actually been located there simply because it was the junction of the main north-south road
(which is now the Suq Khan-ez-Zeit) with one of the two main east-west roads
(which is now the Via Dolorosa
), and directly adjacent to the forum
(which is now the location of the (smaller) Muristan
); the forum itself had been placed, as is traditional in Roman towns, at the junction of the main north-south road with the (other) main east-west road (which is now El-Bazar/David Street). The temple and forum together took up the entire space between the two main east-west roads (a few above-ground remains of the east end of the temple precinct still survive in the Russia
n Mission in Exile).
From the archaeological excavations in the 1970s, it is clear that construction took over most of the site of the earlier temple enclosure and that the Triportico and Rotunda roughly overlapped with the temple building itself; the excavations indicate that the temple extended at least as far back as the Aedicule, and the temple enclosure would have reached back slightly further. Virgilio Canio Corbo
, a Franciscan priest and archaeologist, who was present at the excavations, estimated from the archaeological evidence that the western retaining wall, of the temple itself, would have passed extremely close to the east side of the supposed tomb; if the wall had been any further west any tomb would have been crushed under the weight of the wall (which would be immediately above it) if it had not already been destroyed when foundations for the wall were made.
Other archaeologists have criticised Corbo's reconstructions. Dan Bahat, the former official City Archaeologist of Jerusalem, regards them as unsatisfactory, as there is no known Temple of Aphrodite matching Corbo's design, and no archaeological evidence for Corbo's suggestion that the Temple Building was on a platform raised high enough to avoid including anything sited where the Aedicule is now; indeed Bahat notes that many temples to Aphrodite have a rotunda-like design, and argues that there is no archaeological reason to assume that the present rotunda wasn't based on a rotunda in the temple previously on the site.
, which were built by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent
in 1538. Some have claimed that the city had been much narrower in Jesus' time, with the site then having been outside the walls; since Herod Agrippa (41–44) is recorded by history as extending the city to the north (beyond the present northern walls), the required repositioning of the western wall is traditionally attributed to him as well.
However, a wall would imply the existence of a defensive ditch outside it, so an earlier wall could not be immediately adjacent to site of the tomb, which combined with the presence of the Temple Mount
would make the city inside the wall quite thin; essentially for the traditional site to have been outside the wall, the city would have had to be limited to the lower parts of the Tyropoeon Valley
, rather than including the defensively advantageous western hill. Since these geographic considerations imply that, not including the hill within, the walls would be willfully making the city prone to attack from it, some scholars, including the late 19th century surveyors of the Palestine Exploration Fund
, consider it unlikely that a wall would ever have been built that would cut the hill off from the city in the valley; archaeological evidence for the existence of an earlier city wall in such a location has never been found. The area immediately to the south and east of the sepulchre was a quarry and outside the city during the early 1st century as excavations under the Lutheran Church of the Redeemer across the street demonstrated. This obviated the need for a defensive ditch or fosse since the line of the city wall would follow the south lip of the quarry. The quarry and tombs associated with it are north, not west of the main city and west only of the merchant area in the Tyropoeon Valley, which was enclosed by the Second Wall.
Although, in 2007, Dan Bahat stated that Six graves from the first century were found on the area of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. That means, this place [was] outside of the city, without any doubt, ...., the dating of the tombs is based on the fact that they are in the kokh
style, which was common in 1st century; however, the kokh style of tomb was also common in the first to 3rd centuries BC.
The likelihood of a 1st century tomb being built to the west of the city is questionable, as according to the late 1st century Rabbinic leader, Akiba ben Joseph, quoted in the Mishnah
, tombs should not built to the west of the city, as the wind in Jerusalem generally blows from the west, and would blow the smell of the corpses and their impurity over the city, and the Temple Mount. Additionally, the Aedicule would be quite close to the city even the west wall of the city had been to its east; yet Akiba remarks that Jewish law insists that tombs should not be built within 50 cubits of a city. The archaeological record indicates that the instructions reported by Akiba, for choosing a burial location, were rigidly adhered to; almost all of the tombs from classical Jerusalem are to the east of the city, on the Mount of Olives
, except for a few located over a kilometre to the west, and those in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
One might note, however, that what is assumed to be a niche for the Torah scroll in the building probably originally built as a Judeo-Christian synagogue between AD 70 and AD 135 on the traditional site of the Cenacle
or upper room of the Last Supper
and now identified as the site of the King David's Tomb is oriented not towards the Temple Mount
, but towards the site of the Holy Sepulchre, which would seem to indicate that the Christian community that had built it had already began to transfer many of the religious traditions originally associated with the Temple to the sites they associated with Christ's death and resurrection (such as the burial place of Adam and the centre of the world)
After time spent in Palestine in 1882–83, General Charles George Gordon
found a location outside the old city walls that he suggested to have been the real location of Golgotha. Although the Church of the Holy Sepulchre has its tomb just a few yards away from its Golgotha, there is no particular reason to regard this close juxtaposition as a necessity; however, Gordon followed this principle, concluding that his site for Golgotha must also be the approximate location for Jesus' burial, identifying a nearby tomb, now called the Garden Tomb
, as the location for the event. Pottery and archaeological findings in the area have subsequently been dated to the 7th century BC so, in the opinion of archaeologists the Garden Tomb site would have been abandoned by the 1st century. Biblically this does not match three of the Gospel accounts (Matthew, Luke, and John) which specifically state the tomb was new and no one had ever been laid inside. Despite the archaeological discoveries, the Garden Tomb has become a popular place of pilgrimage among Protestants. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints leaders have been more hesitant to formally commit to the identification even though many Mormon
s regard the Garden Tomb as the correct location of Jesus' tomb.
Currently, no other potential site for the tomb has received much attention or academic support.
_-_planimetria.svg.png) From the 9th century, the construction of churches inspired in the Anastasis was extended across Europe.
From the 9th century, the construction of churches inspired in the Anastasis was extended across Europe.
One example is Santo Stefano
in Bologna
, Italy, an agglomeration of seven churches recreating shrines of Jerusalem.
Several churches and monasteries in Europe, for instance Germany
and Russia
have been modeled on the Church of the Resurrection, some even reproducing other Holy Places
for the benefit of pilgrims who could not travel to the Holy Land. They includes New Jerusalem monastery
in the Moscow region constructed by Patriarch Nikon
constructed from 1656 to 1666, Heiliges Grab of Görlitz constructed between 1481 and 1504.
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises the Christian traditions and churches that developed in the Balkans, Eastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Middle East, Northeastern Africa, India and parts of the Far East over several centuries of religious antiquity. The term is generally used in Western Christianity to...
s, is a church within the walled Old City of Jerusalem. It is a few steps away from the Muristan
Muristan
The Muristan is a complex of streets and shops in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem...
.
The site is venerated as Golgotha
Calvary
Calvary or Golgotha was the site, outside of ancient Jerusalem’s early first century walls, at which the crucifixion of Jesus is said to have occurred. Calvary and Golgotha are the English names for the site used in Western Christianity...
(the Hill of Calvary), where Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
was crucified
Crucifixion
Crucifixion is an ancient method of painful execution in which the condemned person is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross and left to hang until dead...
, and is said also to contain the place where Jesus was buried (the sepulchre
Sepulchre
The rock-cut tombs in ancient Israel are a group of hundreds of rock-cut tombs constructed in Israel in ancient times. They were cut into the rock, sometimes with elaborate facades and multiple burial chambers. Some are free-standing, but most are caves. Each tomb typically belonged to a...
). The church has been an important Christian pilgrimage
Christian pilgrimage
Christian pilgrimage was first made to sites connected with the ministry of Jesus. Surviving descriptions of Christian pilgrimages to the Holy Land and Jerusalem date from the 4th century, when pilgrimage was encouraged by church fathers like Saint Jerome and established by Helena, the mother of...
destination since at least the 4th century
Christianity in the 4th century
Christianity in the 4th century was dominated by Constantine the Great, and the First Council of Nicea of 325, which was the beginning of the period of the First seven Ecumenical Councils and the attempt to reach an orthodox consensus and to establish a unified Christendom as the State church of...
, as the purported site of the resurrection of Jesus
Resurrection of Jesus
The Christian belief in the resurrection of Jesus states that Jesus returned to bodily life on the third day following his death by crucifixion. It is a key element of Christian faith and theology and part of the Nicene Creed: "On the third day he rose again in fulfillment of the Scriptures"...
. Today it also serves as the headquarters of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem is the head bishop of the Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, ranking fourth of nine Patriarchs in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 2005, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem has been Theophilos III...
, while control of the building is shared between several Christian churches
Simultaneum
A shared church, or Simultankirche, Simultaneum or, more fully, simultaneum mixtum, a term first coined in 16th century Germany, is a church in which public worship is conducted by adherents of two or more religious groups. Such churches became common in Europe in the wake of the Reformation...
and secular entities in complicated arrangements essentially unchanged for centuries. Today, the church is home to Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy
Oriental Orthodoxy
Oriental Orthodoxy is the faith of those Eastern Christian Churches that recognize only three ecumenical councils — the First Council of Nicaea, the First Council of Constantinople and the First Council of Ephesus. They rejected the dogmatic definitions of the Council of Chalcedon...
and Roman Catholicism. Anglican
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a tradition within Christianity comprising churches with historical connections to the Church of England or similar beliefs, worship and church structures. The word Anglican originates in ecclesia anglicana, a medieval Latin phrase dating to at least 1246 that means the English...
and Protestant
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
s have no permanent presence in the church.
The latest trend among visitors to the spot (standing outside the Church) is to applaud loudly during bells' ringing. This is to recognize the unique beauty of the Church and its unique history. The origin of this practice is in dispute; one source describes a similar act in the Peter Greenaway
Peter Greenaway
Peter Greenaway, CBE is a British film director. His films are noted for the distinct influence of Renaissance and Baroque painting, and Flemish painting in particular...
movie The Belly of an Architect
The Belly of an Architect
The Belly of an Architect is a 1987 film drama written and directed by Peter Greenaway, featuring original music by Glenn Branca and Wim Mertens....
.
Construction

Aphrodite
Aphrodite is the Greek goddess of love, beauty, pleasure, and procreation.Her Roman equivalent is the goddess .Historically, her cult in Greece was imported from, or influenced by, the cult of Astarte in Phoenicia....
; several ancient writers alternatively describe it as a temple to Venus
Venus (mythology)
Venus is a Roman goddess principally associated with love, beauty, sex,sexual seduction and fertility, who played a key role in many Roman religious festivals and myths...
, the Roman equivalent to Aphrodite. Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea also called Eusebius Pamphili, was a Roman historian, exegete and Christian polemicist. He became the Bishop of Caesarea in Palestine about the year 314. Together with Pamphilus, he was a scholar of the Biblical canon...
claims, in his Life of Constantine, that the site of the Church had originally been a Christian place of veneration, but that Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
had deliberately covered these Christian sites with earth, and built his own temple on top, due to his hatred for Christianity (the authenticity/inaccuracy of this claim is discussed below). Although Eusebius does not say as much, the temple of Aphrodite was probably built as part of Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
's reconstruction of Jerusalem as Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina was a city built by the emperor Hadrian, and occupied by a Roman colony, on the site of Jerusalem, which was in ruins since 70 AD, leading in part to the Bar Kokhba revolt of 132–136.-Politics:...
in 135, following the destruction of the Jewish Revolt
First Jewish-Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War , sometimes called The Great Revolt , was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews of Judaea Province , against the Roman Empire...
of 70 and Bar Kokhba's revolt
Bar Kokhba's revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt 132–136 CE; or mered bar kokhba) against the Roman Empire, was the third major rebellion by the Jews of Judaea Province being the last of the Jewish-Roman Wars. Simon bar Kokhba, the commander of the revolt, was acclaimed as a Messiah, a heroic figure who could restore Israel...
of 132–135.
Emperor Constantine I
Constantine I
Constantine the Great , also known as Constantine I or Saint Constantine, was Roman Emperor from 306 to 337. Well known for being the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity, Constantine and co-Emperor Licinius issued the Edict of Milan in 313, which proclaimed religious tolerance of all...
ordered in about 325/326 that the temple be demolished and the soil - which had provided a flat surface for the temple - be removed, instructing Macarius of Jerusalem
Macarius of Jerusalem
Saint Macarius of Jerusalem was Bishop of Jerusalem from 312 to shortly before 335, according to Sozomen.St. Athanasius, in one of his orations against Arianism, refers to St. Macarius as an example of "the honest and simple style of apostolical men." The date 312 for Macarius's accession to the...
, the local Bishop, to build a church on the site. The Pilgrim of Bordeaux
Itinerarium Burdigalense
The Itinerarium Burdigalense is the oldest known Christian itinerarium, written by an anonymous pilgrim from Burdigala...
reports in 333: There, at present, by the command of the Emperor Constantine, has been built a basilica, that is to say, a church of wondrous beauty. Constantine directed his mother, Helena
Helena of Constantinople
Saint Helena also known as Saint Helen, Helena Augusta or Helena of Constantinople was the consort of Emperor Constantius, and the mother of Emperor Constantine I...
, to build churches upon sites which commemorated the life of Jesus Christ; she was present in 326 at the construction of the church on the site, and involved herself in the excavations and construction.
During the excavation, Helena is alleged to have rediscovered the True Cross
True Cross
The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a Christian tradition, are believed to be from the cross upon which Jesus was crucified.According to post-Nicene historians, Socrates Scholasticus and others, the Empress Helena The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a...
, and a tomb, though Eusebius' account makes no mention of Helena's presence at the excavation, nor of the finding of the cross but only the tomb. According to Eusebius, the tomb exhibited a clear and visible proof that it was the tomb of Jesus
Tomb of Jesus
Several places have been proposed as the tomb of Jesus, the place where Jesus Christ was buried:*Church of the Holy Sepulchre, Jerusalem, accepted by many Christians and scholars as built on ground on which Jesus was crucified and buried...
; several scholars have criticised Eusebius' account for an uncritical use of sources, and for being dishonest with Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon was an English historian and Member of Parliament...
, for example, pointing out that Eusebius' chapter headings claim that fictions are lawful and fitting for him to use. Socrates Scholasticus
Socrates Scholasticus
Socrates of Constantinople, also known as Socrates Scholasticus, not to be confused with the Greek philosopher Socrates, was a Greek Christian church historian, a contemporary of Sozomen and Theodoret, who used his work; he was born at Constantinople c. 380: the date of his death is unknown...
(born c. 380), in his Ecclesiastical History, gives a full description of the discovery (that was repeated later by Sozomen
Sozomen
Salminius Hermias Sozomenus was a historian of the Christian church.-Family and Home:He was born around 400 in Bethelia, a small town near Gaza, into a wealthy Christian family of Palestine....
and by Theodoret
Theodoret
Theodoret of Cyrus or Cyrrhus was an influential author, theologian, and Christian bishop of Cyrrhus, Syria . He played a pivotal role in many early Byzantine church controversies that led to various ecumenical acts and schisms...
) which emphasizes the role played in the excavations and construction by Helena; just as the Church of the Nativity
Church of the Nativity
The Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem is one of the oldest continuously operating churches in the world. The structure is built over the cave that tradition marks as the birthplace of Jesus of Nazareth, and thus it is considered sacred by Christians...
in Bethlehem
Bethlehem
Bethlehem is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank of the Jordan River, near Israel and approximately south of Jerusalem, with a population of about 30,000 people. It is the capital of the Bethlehem Governorate of the Palestinian National Authority and a hub of Palestinian culture and tourism...
(also founded by Constantine and Helena) commemorated the birth of Jesus, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre would commemorate his death and resurrection.
Constantine's church was built as two connected churches over the two different holy sites, including a great basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
(the Martyrium visited by Egeria in the 380s), an enclosed colonnade
Colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade denotes a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building....
d atrium
Atrium (architecture)
In modern architecture, an atrium is a large open space, often several stories high and having a glazed roof and/or large windows, often situated within a larger multistory building and often located immediately beyond the main entrance doors...
(the Triportico) with the traditional site of Golgotha in one corner, and a rotunda
Rotunda (architecture)
A rotunda is any building with a circular ground plan, sometimes covered by a dome. It can also refer to a round room within a building . The Pantheon in Rome is a famous rotunda. A Band Rotunda is a circular bandstand, usually with a dome...
, called the Anastasis ("Resurrection"), which contained the remains of a rock-cut room that Helena and Macarius identified as the burial site of Jesus. The rockface at the west end of the building was cut away, although it is unclear how much remained in Constantine's time, as archaeological investigation has revealed that the temple of Aphrodite reached far into the current rotunda area, and the temple enclosure would therefore have reached even further to the west.
According to tradition, Constantine arranged for the rockface to be removed from around the tomb, without harming it, in order to isolate the tomb; in the centre of the rotunda is a small building called the Kouvouklion (Kουβούκλιον; Modern Greek for small compartment) or Aedicule (from Latin: aediculum, small building), which supposedly encloses this tomb, although it is not currently possible to verify the claim, as the remains are completely enveloped by a marble sheath. The discovery of the kokhim
Kokhim
Kokh is a type of tomb complex characterized by a series of long narrow shafts, in which the deceased were placed for burial, radiating from a central chamber...
tombs just beyond the west end of the Church, and more recent archaeological investigation of the rotunda floor, suggest that a narrow spur
Spur (mountain)
A spur is a subsidiary summit of a hill or mountain. By definition, spurs have low topographic prominence, as they are lower than their parent summit and are closely connected to them on the same ridgeline...
of at least ten yards length would have had to jut out from the rock face if the contents of the Aedicule were once inside it. The dome
Dome
A dome is a structural element of architecture that resembles the hollow upper half of a sphere. Dome structures made of various materials have a long architectural lineage extending into prehistory....
of the rotunda was completed by the end of the 4th century.
Each year, the Eastern Orthodox Church
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church, officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the second largest Christian denomination in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents mainly in the countries of Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece,...
celebrates the anniversary of the consecration
Consecration
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service, usually religious. The word "consecration" literally means "to associate with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different groups...
of the Church of the Resurrection (Holy Sepulchre) on September 13 (for those churches which follow the traditional Julian Calendar
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
, September 13 currently falls on September 26 of the modern Gregorian Calendar
Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar, also known as the Western calendar, or Christian calendar, is the internationally accepted civil calendar. It was introduced by Pope Gregory XIII, after whom the calendar was named, by a decree signed on 24 February 1582, a papal bull known by its opening words Inter...
).
Damage and destruction

Sassanid Empire
The Sassanid Empire , known to its inhabitants as Ērānshahr and Ērān in Middle Persian and resulting in the New Persian terms Iranshahr and Iran , was the last pre-Islamic Persian Empire, ruled by the Sasanian Dynasty from 224 to 651...
under Khosrau II invaded Jerusalem and captured the Cross. In 630, Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius
Heraclius was Byzantine Emperor from 610 to 641.He was responsible for introducing Greek as the empire's official language. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, successfully led a revolt against the unpopular usurper Phocas.Heraclius'...
marched triumphantly into Jerusalem and restored the True Cross
True Cross
The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a Christian tradition, are believed to be from the cross upon which Jesus was crucified.According to post-Nicene historians, Socrates Scholasticus and others, the Empress Helena The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a...
to the rebuilt Church of the Holy Sepulchre. Under the Muslims it remained a Christian church. The early Muslim rulers protected the city's Christian sites, prohibiting their destruction and their use as living quarters. In 966 the doors and roof were burnt during a riot.
On October 18, 1009, under Fatimid
Fatimid
The Fatimid Islamic Caliphate or al-Fāṭimiyyūn was a Berber Shia Muslim caliphate first centered in Tunisia and later in Egypt that ruled over varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and Hijaz from 5 January 909 to 1171.The caliphate was ruled by the Fatimids, who established the...
caliph
Caliph
The Caliph is the head of state in a Caliphate, and the title for the ruler of the Islamic Ummah, an Islamic community ruled by the Shari'ah. It is a transcribed version of the Arabic word which means "successor" or "representative"...
Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
Abu ‘Ali Mansur Tāriqu l-Ḥākim, called Al-Hakim bi Amr al-Lāh , was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili imam .- History :...
, orders for the complete destruction of the Church were carried out. It is believed that Al-Hakim "was aggrieved by the scale of the Easter
Easter
Easter is the central feast in the Christian liturgical year. According to the Canonical gospels, Jesus rose from the dead on the third day after his crucifixion. His resurrection is celebrated on Easter Day or Easter Sunday...
pilgrimage to Jerusalem, which was caused specially by the annual miracle of the Holy Fire
Holy Fire
The Holy Fire is described by Orthodox Christians as a miracle that occurs every year at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem on Holy Saturday, the day preceding Orthodox Easter. It is considered by many to be the longest-attested annual miracle in the Christian world...
within the Sepulchre. The measures against the church were part of a more general campaign against Christian places of worship in Palestine and Egypt, which involved a great deal of other damage: Adhemar of Chabannes recorded that the church of St George at Lydda
Lod
Lod is a city located on the Sharon Plain southeast of Tel Aviv in the Center District of Israel. At the end of 2010, it had a population of 70,000, roughly 75 percent Jewish and 25 percent Arab.The name is derived from the Biblical city of Lod...
'with many other churches of the saints' had been attacked, and the 'basilica of the Lord's Sepulchre destroyed down to the ground'. ...The Christian writer Yahya ibn Sa'id reported that everything was razed 'except those parts which were impossible to destroy or would have been too difficult to carry away'." The Church's foundations were hacked down to bedrock. The Edicule and the east and west walls and the roof of the cut-rock tomb it encased were destroyed or damaged (contemporary accounts vary), but the north and south walls were likely protected by rubble from further damage. The "mighty pillars resisted destruction up to the height of the gallery pavement, and are now effectively the only remnant of the fourth-century buildings." Some minor repairs were done to the section believed to be the tomb of Jesus almost immediately after 1009, but a true attempt at restoration would have to wait for decades.
European reaction was of shock and dismay, with far-reaching and intense consequences. For example, Clunaic monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
Raoul Glaber blamed the Jews, with the result that Jews were expelled from Limoges
Limoges
Limoges |Limousin]] dialect of Occitan) is a city and commune, the capital of the Haute-Vienne department and the administrative capital of the Limousin région in west-central France....
and other French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
towns. Ultimately, this destruction provided an impetus to the later Crusades.
Reconstruction
In wide ranging negotiations between the Fatimids and the Byzantine EmpireByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
in 1027-8 an agreement was reached whereby the new Caliph Ali az-Zahir
Ali az-Zahir
ʻAlī az-Zāhir was the Seventh Caliph of the Fātimids . Az-Zāhir assumed the Caliphate after the disappearance of his father Tāriqu l-Ḥakīm bi Amr al-Lāh...
(Al-Hakim's son) agreed to allowing the rebuilding and redecoration of the Church. The rebuilding was finally completed with the financing of the huge expense by Emperor Constantine IX Monomachos
Constantine IX Monomachos
Constantine IX Monomachos, Latinized as Constantine IX Monomachus , c. 1000 – January 11, 1055, reigned as Byzantine emperor from June 11, 1042 to January 11, 1055. He had been chosen by the Empress Zoe as a husband and co-emperor in 1042, although he had been exiled for conspiring...
and Patriarch Nicephorus of Constantinople in 1048. As a concession, the mosque in Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
was re-opened and sermons were to be pronounced in az-Zahir's name. Muslim sources say a by-product of the agreement was the recanting of Islam by many Christians who had been forced to convert under Al-Hakim's persecutions. In addition the Byzantines, while releasing 5,000 Muslim prisoners, made demands for the restoration of other churches destroyed by Al-Hakim and the re-establishment of a Patriarch
Patriarch
Originally a patriarch was a man who exercised autocratic authority as a pater familias over an extended family. The system of such rule of families by senior males is called patriarchy. This is a Greek word, a compound of πατριά , "lineage, descent", esp...
in Jerusalem. Contemporary sources credit the emperor with spending vast sums in an effort to restore the Church of the Holy Sepulchre after this agreement was made. Despite the Byzantines spending vast sums on the project, "a total replacement was far beyond available resources. The new construction was concentrated on the rotunda and its surrounding buildings: the great basilica remained in ruins." The rebuilt church site consisted of "a court open to the sky, with five small chapels attached to it." The chapels were "to the east of the court of resurrection, where the wall of the great church had been. They commemorated scenes from the passion, such as the location of the prison of Christ and of his flagellation, and presumably were so placed because of the difficulties for free movement among shrines in the streets of the city. The dedication of these chapels indicates the importance of the pilgrims' devotion to the suffering of Christ. They have been described as 'a sort of Via Dolorosa
Via Dolorosa
The Via Dolorosa is a street, in two parts, within the Old City of Jerusalem, held to be the path that Jesus walked, carrying his cross, on the way to his crucifixion. The current route has been established since the 18th century, replacing various earlier versions...
in miniature'... since little or no rebuilding took place on the site of the great basilica. Western pilgrims to Jerusalem during the eleventh century found much of the sacred site in ruins." Control of Jerusalem, and thereby the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, continued to change hands several times between the Fatimids and the Seljuk Turks
Seljuq dynasty
The Seljuq ; were a Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim dynasty that ruled parts of Central Asia and the Middle East from the 11th to 14th centuries...
(loyal to the Abbasid
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or, more simply, the Abbasids , was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphate from all but the al-Andalus region....
caliph in Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
) until the arrival of the Crusaders in 1099.
Crusader period
Many historians still maintain that the main concern of Pope Urban II, when calling for the First CrusadeFirst Crusade
The First Crusade was a military expedition by Western Christianity to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem...
, was the threat to Constantinople from the Turkish invasion of Asia Minor in response to the appeal of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos, Latinized as Alexius I Comnenus , was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118, and although he was not the founder of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during his reign that the Komnenos family came to full power. The title 'Nobilissimus' was given to senior army commanders,...
. Still, historians agree that the fate of Jerusalem and thereby the Church of the Holy Sepulchre was of concern if not the immediate goal of papal policy in 1095. The idea of taking Jerusalem gained more focus as the Crusade was underway. The rebuilt church site was taken from the Fatimids (who had recently taken it from the Abassids) by the knight
Knight
A knight was a member of a class of lower nobility in the High Middle Ages.By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior....
s of the First Crusade
First Crusade
The First Crusade was a military expedition by Western Christianity to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem...
on 15 July 1099.
The First Crusade was envisioned as an armed pilgrimage, and no crusader could consider his journey complete unless he had prayed as a pilgrim at the Holy Sepulchre. Crusader Prince Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon
Godfrey of Bouillon was a medieval Frankish knight who was one of the leaders of the First Crusade from 1096 until his death. He was the Lord of Bouillon, from which he took his byname, from 1076 and the Duke of Lower Lorraine from 1087...
, who became the first crusader monarch of Jerusalem
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem was a Catholic kingdom established in the Levant in 1099 after the First Crusade. The kingdom lasted nearly two hundred years, from 1099 until 1291 when the last remaining possession, Acre, was destroyed by the Mamluks, but its history is divided into two distinct periods....
, decided not to use the title "king" during his lifetime, and declared himself Advocatus Sancti Sepulchri (Protector (or Defender) of the Holy Sepulchre). By the crusader period, a cistern
Cistern
A cistern is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by their waterproof linings...
under the former basilica was rumoured to have been the location that Helena had found the True Cross, and began to be venerated as such; although the cistern later became the Chapel of the Invention of the Cross, there is no evidence for the rumour prior to the 11th century, and modern archaeological investigation has now dated the cistern to the 11th century repairs by Monomachos.
The chronicler William of Tyre
William of Tyre
William of Tyre was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from a predecessor, William of Malines...
reports on the renovation of the Church in the mid-12th century. The crusaders investigated the eastern ruins on the site, occasionally excavating through the rubble, and while attempting to reach the cistern, they discovered part of the original ground level of Hadrian's temple enclosure; they decided to transform this space into a chapel dedicated to Helena (the Chapel of Saint Helena
Chapel of Saint Helena, Jerusalem
The Chapel of Saint Helena is a 12th century Armenian church in the lower level of the Church of the Holy Sepulcher in Jerusalem.In the south east of the chapel there is a chair which was reputed to be a seat that was sat in by Saint Helena, the mother of the Emperor Constantine when she was...
), widening their original excavation tunnel into a proper staircase. The crusaders began to refurnish the church in a Romanesque
Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
style and added a bell tower. These renovations unified the small chapels on the site and were completed during the reign of Queen Melisende
Melisende of Jerusalem
Melisende was Queen of Jerusalem from 1131 to 1153, and regent for her son between 1153 and 1161 while he was on campaign. She was the eldest daughter of King Baldwin II of Jerusalem, and the Armenian princess Morphia of Melitene. She was named after her paternal grandmother, Melisende of...
in 1149, placing all the Holy places under one roof for the first time. The church became the seat of the first Latin Patriarchs
Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem
The Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem is the title possessed by the Latin Rite Catholic Archbishop of Jerusalem. The Archdiocese of Jerusalem has jurisdiction for all Latin Rite Catholics in Israel, the Palestinian Territories, Jordan and Cyprus...
, and was also the site of the kingdom's scriptorium
Scriptorium
Scriptorium, literally "a place for writing", is commonly used to refer to a room in medieval European monasteries devoted to the copying of manuscripts by monastic scribes...
. The church was lost to Saladin
Saladin
Ṣalāḥ ad-Dīn Yūsuf ibn Ayyūb , better known in the Western world as Saladin, was an Arabized Kurdish Muslim, who became the first Sultan of Egypt and Syria, and founded the Ayyubid dynasty. He led Muslim and Arab opposition to the Franks and other European Crusaders in the Levant...
, along with the rest of the city, in 1187, although the treaty established after the Third Crusade
Third Crusade
The Third Crusade , also known as the Kings' Crusade, was an attempt by European leaders to reconquer the Holy Land from Saladin...
allowed for Christian pilgrims to visit the site. Emperor Frederick II
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II , was one of the most powerful Holy Roman Emperors of the Middle Ages and head of the House of Hohenstaufen. His political and cultural ambitions, based in Sicily and stretching through Italy to Germany, and even to Jerusalem, were enormous...
regained the city and the church by treaty in the 13th century, while he himself was under a ban of excommunication, leading to the curious result of the holiest church in Christianity being laid under interdict
Interdict (Roman Catholic Church)
In Roman Catholic canon law, an interdict is an ecclesiastical censure that excludes from certain rites of the Church individuals or groups, who nonetheless do not cease to be members of the Church.-Distinctions in canon law:...
. Both city and church were captured by the Khwarezm
Khwarezm
Khwarezm, or Chorasmia, is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, which borders to the north the Aral Sea, to the east the Kyzylkum desert, to the south the Karakum desert and to the west the Ustyurt Plateau...
ians in 1244.
Later periods

Franciscan
Most Franciscans are members of Roman Catholic religious orders founded by Saint Francis of Assisi. Besides Roman Catholic communities, there are also Old Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, ecumenical and Non-denominational Franciscan communities....
friars renovated it further in 1555, as it had been neglected despite increased numbers of pilgrims. The Franciscans rebuilt the Aedicule, extending the structure to create an ante-chamber. After the renovation of 1555, control of the church oscillated between the Franciscans and the Orthodox, depending on which community could obtain a favorable firman from the Sublime Porte at a particular time, often through outright bribery, and violent clashes were not uncommon. There was no agreement about this question, although it was talked about it at the negotiations to the Treaty of Karlowitz
Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed on 26 January 1699 in Sremski Karlovci , concluding the Austro-Ottoman War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman side had been defeated at the Battle of Zenta...
in 1699. In 1767, weary of the squabbling, the Porte issued a firman that divided the church among the claimants.
A fire severely damaged the structure again in 1808, causing the dome of the Rotunda to collapse and smashing the Edicule's exterior decoration. The Rotunda and the Edicule's exterior were rebuilt in 1809–1810 by architect Komminos of Mytilene
Mytilene
Mytilene is a town and a former municipality on the island of Lesbos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lesbos, of which it is a municipal unit. It is the capital of the island of Lesbos. Mytilene, whose name is pre-Greek, is built on the...
in the then current Ottoman Baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
style. The fire did not reach the interior of the Aedicule, and the marble decoration of the Tomb dates mainly to the 1555 restoration, although the interior of the ante-chamber, now known as the Chapel of the Angel, was partly re-built to a square ground-plan, in place of the previously semi-circular western end. Another decree in 1853 from the sultan solidified the existing territorial division among the communities and set a status quo
Status quo
Statu quo, a commonly used form of the original Latin "statu quo" – literally "the state in which" – is a Latin term meaning the current or existing state of affairs. To maintain the status quo is to keep the things the way they presently are...
for arrangements to "remain forever", caused differences of opinion about upkeep and even minor changes, including disagreement on the removal of an exterior ladder under one of the windows; this ladder has remained in the same position since then.

The current dome dates from 1870, although it was restored during 1994–1997, as part of extensive modern renovations to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, which have been ongoing since 1959. During 1973–1978 restoration works and excavations inside the building, and under the nearby Muristan, it was found that the area was originally a quarry, from which white meleke
Meleke
Meleke — also transliterated melekeh or malaki — is a lithologic type of white, coarsely crystalline, thickly bedded limestone found in the Judean Hills in Israel and the West Bank. It has been used in the traditional architecture of Jerusalem since ancient times, especially in Herodian...
limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
was struck. To the east of the Chapel of St. Helena, the excavators discovered a void containing a 2nd century drawing of a roman ship, two low walls which supported the platform of Hadrian's 2nd century temple, and a higher 4th century wall built to support Constantine's basilica; the Armenian authorities have recently converted this archaeological space into the Chapel of Saint Vartan, and created an artificial walkway over the quarry on the north of the chapel, so that the new Chapel could be accessed (by permission) from the Chapel of St. Helena.
There was some controversy in 2010, when the Jerusalem City Council threatened to cut off water to the site due to disputed water bills.
Modern arrangement of the church
The entrance to the church is through a single door in the south transeptTransept
For the periodical go to The Transept.A transept is a transverse section, of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In Christian churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform building in Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architecture...
. This narrow way of access to such a large structure has proven to be hazardous at times. For example, when a fire broke out in 1840, dozens of pilgrims were trampled to death. In 1999 the communities agreed to install a new exit door in the church, but there was never any report of this door being completed.
Calvary (Golgotha)
On the south side of the altar via the ambulatoryAmbulatory
The ambulatory is the covered passage around a cloister. The term is sometimes applied to the procession way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar....
(an aisle surrounding the end of the choir or chancel of a church) is a stairway climbing to Calvary (Golgotha), traditionally regarded as the site of Jesus' crucifixion and the most lavishly decorated part of the church. The main altar there belongs to the Greek Orthodox, which contains The Rock of Calvary (12th Station of the Cross). The rock can be seen under glass on both sides of the altar, and beneath the altar there is a hole said to be the place where the cross was raised. The Roman Catholics (Franciscan
Franciscan
Most Franciscans are members of Roman Catholic religious orders founded by Saint Francis of Assisi. Besides Roman Catholic communities, there are also Old Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, ecumenical and Non-denominational Franciscan communities....
s) have an altar to the side, The Chapel of the Nailing of the Cross (11th Station of the Cross). On the left of the altar, towards the Eastern Orthodox chapel, there is a statue of Mary, believed to be working wonders (the 13th Station of the Cross, where Jesus' body was removed from the cross and given to his family).
Beneath the Calvary and the two chapels there, on the main floor, there is The Chapel of Adam. According to tradition, Jesus was crucified over the place where Adam's skull was buried. The Rock of Calvary is seen cracked through a window on the altar wall, the crack traditionally being said to be caused by the earthquake that occurred when Jesus died on the cross, and being said by more critical scholars to be the result of quarrying against a natural flaw in the rock.
The Stone of Anointing

Joseph of Arimathea
Joseph of Arimathea was, according to the Gospels, the man who donated his own prepared tomb for the burial of Jesus after Jesus' Crucifixion. He is mentioned in all four Gospels.-Gospel references:...
. However, this tradition is only attested since the crusader era, and the present stone was only added in the 1810 reconstruction. The wall behind the stone was a temporary addition to support the arch above it, which had been weakened after the damage in the 1808 fire; the wall blocks the view of the rotunda, sits on top of the graves of four 12th century kings, and is no longer structurally necessary. There is a difference of opinion as to whether it is the 13th Station of the Cross
Stations of the Cross
Stations of the Cross refers to the depiction of the final hours of Jesus, and the devotion commemorating the Passion. The tradition as chapel devotion began with St...
, which others identify as the lowering of Jesus from the cross and locate between the 11th and 12th station up on Calvary. The lamps that hang over the stone are contributed by Armenians, Copts, Greeks and Latins.
The Rotunda and the Aedicule
The RotundaRotunda (architecture)
A rotunda is any building with a circular ground plan, sometimes covered by a dome. It can also refer to a round room within a building . The Pantheon in Rome is a famous rotunda. A Band Rotunda is a circular bandstand, usually with a dome...
is located in the centre of the Anastasis, beneath the larger of the church's two domes. In the centre of the Rotunda is the chapel called The Edicule, which contains the Holy Sepulchre itself. The Edicule has two rooms. The first one holds The Angel's Stone, a fragment of the stone believed to have sealed the tomb after Jesus' burial. The second one is the tomb itself.
The Status Quo in the Rotunda
Under the status quoStatus quo
Statu quo, a commonly used form of the original Latin "statu quo" – literally "the state in which" – is a Latin term meaning the current or existing state of affairs. To maintain the status quo is to keep the things the way they presently are...
the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church, officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the second largest Christian denomination in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents mainly in the countries of Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece,...
, Roman Catholic, and Armenian Apostolic
Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church is the world's oldest National Church, is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, and is one of the most ancient Christian communities. Armenia was the first country to adopt Christianity as its official religion in 301 AD, in establishing this church...
Churches all have rights to the interior of the tomb, and all three communities celebrate the Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy
Divine Liturgy is the common term for the Eucharistic service of the Byzantine tradition of Christian liturgy. As such, it is used in the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches. Armenian Christians, both of the Armenian Apostolic Church and of the Armenian Catholic Church, use the same term...
or Holy Mass
Mass (liturgy)
"Mass" is one of the names by which the sacrament of the Eucharist is called in the Roman Catholic Church: others are "Eucharist", the "Lord's Supper", the "Breaking of Bread", the "Eucharistic assembly ", the "memorial of the Lord's Passion and Resurrection", the "Holy Sacrifice", the "Holy and...
there daily. It is also used for other ceremonies on special occasions, such as the Holy Saturday
Holy Saturday
Holy Saturday , sometimes known as Easter Eve or Black Saturday, is the day after Good Friday. It is the day before Easter and the last day of Holy Week in which Christians prepare for Easter...
ceremony of the Holy Fire
Holy Fire
The Holy Fire is described by Orthodox Christians as a miracle that occurs every year at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem on Holy Saturday, the day preceding Orthodox Easter. It is considered by many to be the longest-attested annual miracle in the Christian world...
celebrated by the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem is the head bishop of the Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, ranking fourth of nine Patriarchs in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 2005, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem has been Theophilos III...
. To its rear, within a chapel constructed of iron latticework
Latticework
Latticework is a framework consisting of a criss-crossed pattern of strips of building material, typically wood or metal. The design is created by crossing the strips to form a network...
upon a stone base semicircular in plan, lies the altar used by the Coptic Orthodox
Coptic Christianity
The Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria is the official name for the largest Christian church in Egypt and the Middle East. The Church belongs to the Oriental Orthodox family of churches, which has been a distinct church body since the Council of Chalcedon in AD 451, when it took a different...
.
Beyond that to the rear of the Rotunda is a very rough hewn chapel, containing an opening to a rock-cut chamber, from which several kokh
Kokhim
Kokh is a type of tomb complex characterized by a series of long narrow shafts, in which the deceased were placed for burial, radiating from a central chamber...
-tombs radiate. Although this space was discovered comparatively recently, and contains no identifying marks, many Christians believe it to be the tomb of Joseph of Arimathea
Joseph of Arimathea
Joseph of Arimathea was, according to the Gospels, the man who donated his own prepared tomb for the burial of Jesus after Jesus' Crucifixion. He is mentioned in all four Gospels.-Gospel references:...
in which the Syriac Orthodox
Syriac Orthodox Church
The Syriac Orthodox Church; is an autocephalous Oriental Orthodox church based in the Eastern Mediterranean, with members spread throughout the world. The Syriac Orthodox Church claims to derive its origin from one of the first Christian communities, established in Antioch by the Apostle St....
celebrate their Liturgy on Sundays. To the right of the sepulchre on the southeastern side of the Rotunda is the Chapel of the Apparition which is reserved for Roman Catholic use.
The Catholicon and the Ambulatory
- The Catholicon - On the east side opposite the Rotunda is the Crusader structure housing the main altar of the Church, today the Greek Orthodox catholiconCatholiconCatholicon may refer to:* Catholicon, the conventual church at the centre of an abbey* Katholikon, the primary church in an Orthodox or Eastern Catholic monastery* Catholicon , part of the Holy Liturgy of Mor Yakub of the Syriac Orthodox Church...
. The second, smaller dome sits directly over the centre of the transept crossingCrossing (architecture)A crossing, in ecclesiastical architecture, is the junction of the four arms of a cruciform church.In a typically oriented church , the crossing gives access to the nave on the west, the transept arms on the north and south, and the choir on the east.The crossing is sometimes surmounted by a tower...
of the choirQuire (architecture)Architecturally, the choir is the area of a church or cathedral, usually in the western part of the chancel between the nave and the sanctuary . The choir is occasionally located in the eastern part of the nave...
where the compas, an omphalosOmphalosAn omphalos is an ancient religious stone artifact, or baetylus. In Greek, the word omphalos means "navel" . According to the ancient Greeks, Zeus sent out two eagles to fly across the world to meet at its center, the "navel" of the world...
once thought to be the centre of the world (associated to the site of the Crucifixion and the Resurrection), is situated. East of this is a large iconostasisIconostasisIn Eastern Christianity an iconostasis is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a church. Iconostasis also refers to a portable icon stand that can be placed anywhere within a church...
demarcating the Orthodox sanctuary before which is set the throne of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of JerusalemGreek Orthodox Patriarch of JerusalemThe Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem is the head bishop of the Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, ranking fourth of nine Patriarchs in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 2005, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem has been Theophilos III...
on the south side facing the throne of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of AntiochPatriarch of AntiochPatriarch of Antioch is a traditional title held by the Bishop of Antioch. As the traditional "overseer" of the first gentile Christian community, the position has been of prime importance in the church from its earliest period...
on the north side.

- Prison of Christ - In the north-east side of the complex there is The Prison of Christ, alleged by the Franciscans to be where Jesus was held. The Greek Orthodox allege that the real place that Jesus was held was the similarly named Prison of Christ, within their Monastery of the Praetorium, located near the Church of Ecce HomoEcce Homo (church)Ecce Homo Church is a Roman Catholic church on Via Dolorosa in Jerusalem, along the path that according to tradition Jesus walked, carrying his cross, on the way to his crucifixion. The church is now part of the Convent of the Sisters of Zion....
, at the first station on the Via DolorosaVia DolorosaThe Via Dolorosa is a street, in two parts, within the Old City of Jerusalem, held to be the path that Jesus walked, carrying his cross, on the way to his crucifixion. The current route has been established since the 18th century, replacing various earlier versions...
. The Armenians regard a recess in the Monastery of the Flagellation, a building near the second station on the Via Dolorosa, as the Prison of Christ. A cistern among the ruins near the Church of St. Peter in GallicantuChurch of St. Peter in GallicantuThe Church of Saint Peter in Gallicantu is a Roman Catholic church located on the eastern slope of Mount Zion, just outside the Old City of Jerusalem in Israel.-History:...
is also alleged to have been the Prison of Christ.
Further to the east in the ambulatory are three chapels (from south to north):
- Greek Chapel of St. Longinus - The Orthodox Greek chapel is dedicated to St. Longinus, a Roman soldier who according the New TestamentNew TestamentThe New Testament is the second major division of the Christian biblical canon, the first such division being the much longer Old Testament....
pierced Jesus with a spear. - Armenian Chapel of Division of Robes -
- Greek Chapel of the Derision - the southernmost chapel in the ambulatory.
Armenian compound

- The Chapel of St. Helena - between the first two chapels are stairs descending to The Chapel of St. HelenaChapel of Saint Helena, JerusalemThe Chapel of Saint Helena is a 12th century Armenian church in the lower level of the Church of the Holy Sepulcher in Jerusalem.In the south east of the chapel there is a chair which was reputed to be a seat that was sat in by Saint Helena, the mother of the Emperor Constantine when she was...
, belonging to the Armenians. - Chapel of St. Vartan - on the north side of the Chapel of St. Helena is an ornate wrought ironWrought ironthumb|The [[Eiffel tower]] is constructed from [[puddle iron]], a form of wrought ironWrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon...
door, beyond which a raised artificial platform affords views of the QuarryQuarryA quarry is a type of open-pit mine from which rock or minerals are extracted. Quarries are generally used for extracting building materials, such as dimension stone, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, and gravel. They are often collocated with concrete and asphalt plants due to the requirement...
, and which leads to the Chapel of St. Vartan. The latter Chapel contains archaeological remains from Hadrian's temple and Constantine's basilica. These areas are usually closed. - Chapel of the Invention of the Holy Cross - another set of 22 stairs from the Chapel of St. Helena leads down to the Roman Catholic Chapel of the Invention of the Holy Cross believed to be the place where the True CrossTrue CrossThe True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a Christian tradition, are believed to be from the cross upon which Jesus was crucified.According to post-Nicene historians, Socrates Scholasticus and others, the Empress Helena The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a...
was found.
North of the Aedicule
- Chapel of Mary Magdalene - The chapel indicates the place where Mary MagdaleneMary MagdaleneMary Magdalene was one of Jesus' most celebrated disciples, and the most important woman disciple in the movement of Jesus. Jesus cleansed her of "seven demons", conventionally interpreted as referring to complex illnesses...
met Jesus after his resurrection. - The Franciscan Church -
South of the Aedicule
The three Greek Orthodox chapels of St. James the Just, St. John the Baptist and of the Forty Martyrs of SebasteForty Martyrs of Sebaste
The Forty Martyrs of Sebaste or the Holy Forty were a group of Roman soldiers in the Legio XII Fulminata whose martyrdom in 320 for the Christian faith is recounted in traditional martyrologies.They were killed near Sebaste, in Lesser Armenia, victims of the persecutions of Licinius,...
, south of the rotunda and on the west side of the front courtyard originally formed the baptistery
Baptistery
In Christian architecture the baptistry or baptistery is the separate centrally-planned structure surrounding the baptismal font. The baptistry may be incorporated within the body of a church or cathedral and be provided with an altar as a chapel...
complex of the Constantinean church, the southern most chapel being the vestibule, the middle chapel being the actual baptistery
Baptistery
In Christian architecture the baptistry or baptistery is the separate centrally-planned structure surrounding the baptismal font. The baptistry may be incorporated within the body of a church or cathedral and be provided with an altar as a chapel...
and the north chapel being the chamber in which the patriarch chrism
Chrism
Chrism , also called "Myrrh" , Holy anointing oil, or "Consecrated Oil", is a consecrated oil used in the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Eastern Rite Catholic, Oriental Orthodox, in the Assyrian Church of the East, and in Old-Catholic churches, as well as Anglican churches in the administration...
ated the newly baptized before leading them into the rotunda north of this complex.
The roof of the church
One can access the roof of the church from the courtyard of the Greek Orthodox PatriarchateGreek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem is the head bishop of the Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, ranking fourth of nine Patriarchs in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 2005, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem has been Theophilos III...
.
Status quo

Eastern Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church, officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the second largest Christian denomination in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents mainly in the countries of Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece,...
, Armenian Apostolic
Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church is the world's oldest National Church, is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, and is one of the most ancient Christian communities. Armenia was the first country to adopt Christianity as its official religion in 301 AD, in establishing this church...
, and Roman Catholic Churches, with the Greek Orthodox Church having the lion's share. In the 19th century, the Coptic Orthodox, the Ethiopian Orthodox and the Syriac Orthodox
Syriac Orthodox Church
The Syriac Orthodox Church; is an autocephalous Oriental Orthodox church based in the Eastern Mediterranean, with members spread throughout the world. The Syriac Orthodox Church claims to derive its origin from one of the first Christian communities, established in Antioch by the Apostle St....
acquired lesser responsibilities, which include shrines and other structures within and around the building. Times and places of worship for each community are strictly regulated in common areas.
Establishment of the 1853 status quo did not halt the violence, which continues to break out every so often even in modern times. On a hot summer day in 2002, a Coptic monk moved his chair from its agreed spot into the shade. This was interpreted as a hostile move by the Ethiopians, and eleven were hospitalized after the resulting fracas.
In another incident in 2004 during Orthodox celebrations of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross
Feast of the Cross
In the Christian liturgical calendar, there are several different Feasts of the Cross, all of which commemorate the cross used in the crucifixion of Jesus....
, a door to the Franciscan chapel was left open. This was taken as a sign of disrespect by the Orthodox and a fistfight broke out. Some people were arrested, but no one was seriously injured.
On Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday is a Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Jesus' triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in all four Canonical Gospels. ....
, in April 2008, a brawl broke out when a Greek monk
Monk
A monk is a person who practices religious asceticism, living either alone or with any number of monks, while always maintaining some degree of physical separation from those not sharing the same purpose...
was ejected from the building by a rival faction. Police were called to the scene but were also attacked by the enraged brawlers. On Sunday, November 9, 2008, a clash erupted between Armenian and Greek monks during celebrations for the Feast of the Holy Cross.
Under the status quo, no part of what is designated as common territory may be so much as rearranged without consent from all communities. This often leads to the neglect of badly needed repairs when the communities cannot come to an agreement among themselves about the final shape of a project. Just such a disagreement has delayed the renovation of the edicule, where the need is now dire, but also where any change in the structure might result in a change to the status quo disagreeable to one or more of the communities.
A less grave sign of this state of affairs is located on a window ledge over the church's entrance. Someone placed a wooden ladder there sometime before 1852, when the status quo defined both the doors and the window ledges as common ground. The ladder remains there to this day, in almost exactly the same position it can be seen to occupy in century-old photographs and engravings.
No one controls the main entrance. In 1192, Saladin
Saladin
Ṣalāḥ ad-Dīn Yūsuf ibn Ayyūb , better known in the Western world as Saladin, was an Arabized Kurdish Muslim, who became the first Sultan of Egypt and Syria, and founded the Ayyubid dynasty. He led Muslim and Arab opposition to the Franks and other European Crusaders in the Levant...
assigned responsibility for it to the Muslim Nuseibeh
Nusaybah clan
The Nusaybah Clan alternatively spelt Nusseibeh is the name of the oldest Arab family in Jerusalem, The Nusaybah family has long history and tight bonds with the Holy Land, Jerusalem, since the days their first forefathers arrived into Jerusalem in the 7th century.According to tradition, the...
family. The Joudeh Al-Goudia family were entrusted as custodian to the keys of the Holy Sepulchre by the Ottomans few hundred years later, and both families now share the responsibility. This arrangement has persisted into modern times.
Relationship to the Temple of Aphrodite

Cardo
The cardo was a north-south oriented street in Roman cities, military camps, and coloniae. The cardo, an integral component of city planning, was lined with shops and vendors, and served as a hub of economic life. The main cardo was called cardo maximus.Most Roman cities also had a Decumanus...
(which is now the Suq Khan-ez-Zeit) with one of the two main east-west roads
Decumanus Maximus
In Roman city planning, a decumanus was an east-west-oriented road in a Roman city, castra , or colonia. The main decumanus was the Decumanus Maximus, which normally connected the Porta Praetoria to the Porta Decumana .This name comes from the fact that the via decumana or decimana In Roman city...
(which is now the Via Dolorosa
Via Dolorosa
The Via Dolorosa is a street, in two parts, within the Old City of Jerusalem, held to be the path that Jesus walked, carrying his cross, on the way to his crucifixion. The current route has been established since the 18th century, replacing various earlier versions...
), and directly adjacent to the forum
Forum (Roman)
A forum was a public square in a Roman municipium, or any civitas, reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, along with the buildings used for shops and the stoas used for open stalls...
(which is now the location of the (smaller) Muristan
Muristan
The Muristan is a complex of streets and shops in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem...
); the forum itself had been placed, as is traditional in Roman towns, at the junction of the main north-south road with the (other) main east-west road (which is now El-Bazar/David Street). The temple and forum together took up the entire space between the two main east-west roads (a few above-ground remains of the east end of the temple precinct still survive in the Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n Mission in Exile).
From the archaeological excavations in the 1970s, it is clear that construction took over most of the site of the earlier temple enclosure and that the Triportico and Rotunda roughly overlapped with the temple building itself; the excavations indicate that the temple extended at least as far back as the Aedicule, and the temple enclosure would have reached back slightly further. Virgilio Canio Corbo
Virgilio Canio Corbo
Born: 1918Dead: December 6, 1991,A Franciscan Friar and professor of archaeology at the Studium Biblicum Franciscanum in Jerusalem. Remembered for the excavations of many religious sites:* the Shepherds' field near Bethlehem...
, a Franciscan priest and archaeologist, who was present at the excavations, estimated from the archaeological evidence that the western retaining wall, of the temple itself, would have passed extremely close to the east side of the supposed tomb; if the wall had been any further west any tomb would have been crushed under the weight of the wall (which would be immediately above it) if it had not already been destroyed when foundations for the wall were made.
Other archaeologists have criticised Corbo's reconstructions. Dan Bahat, the former official City Archaeologist of Jerusalem, regards them as unsatisfactory, as there is no known Temple of Aphrodite matching Corbo's design, and no archaeological evidence for Corbo's suggestion that the Temple Building was on a platform raised high enough to avoid including anything sited where the Aedicule is now; indeed Bahat notes that many temples to Aphrodite have a rotunda-like design, and argues that there is no archaeological reason to assume that the present rotunda wasn't based on a rotunda in the temple previously on the site.
Relationship of the site to the city
The Bible describes Jesus' tomb as being outside the city wall, as was normal for burials across the ancient world, which were regarded as unclean, but the Church of the Holy Sepulchre is in the heart of Hadrian's city, well within the Old City wallsJerusalem's Old City walls
The Old City is a walled area within the modern city of Jerusalem. Until 1860, when the Jewish neighborhood, Mishkenot Sha'ananim, was established, this area constituted the entire city of Jerusalem...
, which were built by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I was the tenth and longest-reigning Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1520 to his death in 1566. He is known in the West as Suleiman the Magnificent and in the East, as "The Lawgiver" , for his complete reconstruction of the Ottoman legal system...
in 1538. Some have claimed that the city had been much narrower in Jesus' time, with the site then having been outside the walls; since Herod Agrippa (41–44) is recorded by history as extending the city to the north (beyond the present northern walls), the required repositioning of the western wall is traditionally attributed to him as well.
However, a wall would imply the existence of a defensive ditch outside it, so an earlier wall could not be immediately adjacent to site of the tomb, which combined with the presence of the Temple Mount
Temple Mount
The Temple Mount, known in Hebrew as , and in Arabic as the Haram Ash-Sharif , is one of the most important religious sites in the Old City of Jerusalem. It has been used as a religious site for thousands of years...
would make the city inside the wall quite thin; essentially for the traditional site to have been outside the wall, the city would have had to be limited to the lower parts of the Tyropoeon Valley
Tyropoeon Valley
Tyropoeon Valley is the name given by Josephus the historian to the valley or rugged ravine, in the Old City of Jerusalem, which in ancient times separated Mount Moriah from Mount Zion and emptied into the valley of Hinnom...
, rather than including the defensively advantageous western hill. Since these geographic considerations imply that, not including the hill within, the walls would be willfully making the city prone to attack from it, some scholars, including the late 19th century surveyors of the Palestine Exploration Fund
Palestine Exploration Fund
The Palestine Exploration Fund is a British society often simply known as the PEF. It was founded in 1865 and is still functioning today. Its initial object was to carry out surveys of the topography and ethnography of Ottoman Palestine with a remit that fell somewhere between an expeditionary...
, consider it unlikely that a wall would ever have been built that would cut the hill off from the city in the valley; archaeological evidence for the existence of an earlier city wall in such a location has never been found. The area immediately to the south and east of the sepulchre was a quarry and outside the city during the early 1st century as excavations under the Lutheran Church of the Redeemer across the street demonstrated. This obviated the need for a defensive ditch or fosse since the line of the city wall would follow the south lip of the quarry. The quarry and tombs associated with it are north, not west of the main city and west only of the merchant area in the Tyropoeon Valley, which was enclosed by the Second Wall.
Although, in 2007, Dan Bahat stated that Six graves from the first century were found on the area of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. That means, this place [was] outside of the city, without any doubt, ...., the dating of the tombs is based on the fact that they are in the kokh
Kokhim
Kokh is a type of tomb complex characterized by a series of long narrow shafts, in which the deceased were placed for burial, radiating from a central chamber...
style, which was common in 1st century; however, the kokh style of tomb was also common in the first to 3rd centuries BC.
The likelihood of a 1st century tomb being built to the west of the city is questionable, as according to the late 1st century Rabbinic leader, Akiba ben Joseph, quoted in the Mishnah
Mishnah
The Mishnah or Mishna is the first major written redaction of the Jewish oral traditions called the "Oral Torah". It is also the first major work of Rabbinic Judaism. It was redacted c...
, tombs should not built to the west of the city, as the wind in Jerusalem generally blows from the west, and would blow the smell of the corpses and their impurity over the city, and the Temple Mount. Additionally, the Aedicule would be quite close to the city even the west wall of the city had been to its east; yet Akiba remarks that Jewish law insists that tombs should not be built within 50 cubits of a city. The archaeological record indicates that the instructions reported by Akiba, for choosing a burial location, were rigidly adhered to; almost all of the tombs from classical Jerusalem are to the east of the city, on the Mount of Olives
Mount of Olives
The Mount of Olives is a mountain ridge in East Jerusalem with three peaks running from north to south. The highest, at-Tur, rises to 818 meters . It is named for the olive groves that once covered its slopes...
, except for a few located over a kilometre to the west, and those in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
One might note, however, that what is assumed to be a niche for the Torah scroll in the building probably originally built as a Judeo-Christian synagogue between AD 70 and AD 135 on the traditional site of the Cenacle
Cenacle
The Cenacle , also known as the "Upper Room", is the term used for the site of The Last Supper. The word is a derivative of the Latin word cena, which means dinner....
or upper room of the Last Supper
Last Supper
The Last Supper is the final meal that, according to Christian belief, Jesus shared with his Twelve Apostles in Jerusalem before his crucifixion. The Last Supper provides the scriptural basis for the Eucharist, also known as "communion" or "the Lord's Supper".The First Epistle to the Corinthians is...
and now identified as the site of the King David's Tomb is oriented not towards the Temple Mount
Temple Mount
The Temple Mount, known in Hebrew as , and in Arabic as the Haram Ash-Sharif , is one of the most important religious sites in the Old City of Jerusalem. It has been used as a religious site for thousands of years...
, but towards the site of the Holy Sepulchre, which would seem to indicate that the Christian community that had built it had already began to transfer many of the religious traditions originally associated with the Temple to the sites they associated with Christ's death and resurrection (such as the burial place of Adam and the centre of the world)
Other possible sites
Although the identification of the Aedicule as the site of Jesus' tomb is not a tenet of faith for any major Christian denomination, many Catholic and Orthodox Christians hold fast to this traditional location. However, due to the many issues the site raises, several scholars have rejected its validity. Additionally many Protestants have often opposed the traditional location because it has previously received support from Catholics.After time spent in Palestine in 1882–83, General Charles George Gordon
Charles George Gordon
Major-General Charles George Gordon, CB , known as "Chinese" Gordon, Gordon Pasha, and Gordon of Khartoum, was a British army officer and administrator....
found a location outside the old city walls that he suggested to have been the real location of Golgotha. Although the Church of the Holy Sepulchre has its tomb just a few yards away from its Golgotha, there is no particular reason to regard this close juxtaposition as a necessity; however, Gordon followed this principle, concluding that his site for Golgotha must also be the approximate location for Jesus' burial, identifying a nearby tomb, now called the Garden Tomb
Garden Tomb
The Garden Tomb , located in Jerusalem, outside the city walls and close to the Damascus Gate, is a rock-cut tomb considered by some to be the site of the burial and resurrection of Jesus, and to be adjacent to Golgotha, in contradistinction to the traditional site for these—the Church of the Holy...
, as the location for the event. Pottery and archaeological findings in the area have subsequently been dated to the 7th century BC so, in the opinion of archaeologists the Garden Tomb site would have been abandoned by the 1st century. Biblically this does not match three of the Gospel accounts (Matthew, Luke, and John) which specifically state the tomb was new and no one had ever been laid inside. Despite the archaeological discoveries, the Garden Tomb has become a popular place of pilgrimage among Protestants. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints leaders have been more hesitant to formally commit to the identification even though many Mormon
Mormon
The term Mormon most commonly denotes an adherent, practitioner, follower, or constituent of Mormonism, which is the largest branch of the Latter Day Saint movement in restorationist Christianity...
s regard the Garden Tomb as the correct location of Jesus' tomb.
Currently, no other potential site for the tomb has received much attention or academic support.
Influence
_-_planimetria.svg.png)
One example is Santo Stefano
Santo Stefano (Bologna)
Santo Stefano's Basilica is a complex of religious edifices in the city of Bologna, Italy. Located in the eponymous square, it is locally known as Sette Chiese ....
in Bologna
Bologna
Bologna is the capital city of Emilia-Romagna, in the Po Valley of Northern Italy. The city lies between the Po River and the Apennine Mountains, more specifically, between the Reno River and the Savena River. Bologna is a lively and cosmopolitan Italian college city, with spectacular history,...
, Italy, an agglomeration of seven churches recreating shrines of Jerusalem.
Several churches and monasteries in Europe, for instance Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
have been modeled on the Church of the Resurrection, some even reproducing other Holy Places
Holy places
Holy places, generally refers to the sites that a religion considers to be of special religious significance. They are usually places visited by pilgrims.-Baha'i:...
for the benefit of pilgrims who could not travel to the Holy Land. They includes New Jerusalem monastery
New Jerusalem Monastery
The New Jerusalem Monastery or Novoiyerusalimsky Monastery , also known as the Voskresensky Monastery, is a male monastery, located in the town of Istra in Moscow Oblast, Russia....
in the Moscow region constructed by Patriarch Nikon
Nikon
, also known as just Nikon, is a multinational corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, specializing in optics and imaging. Its products include cameras, binoculars, microscopes, measurement instruments, and the steppers used in the photolithography steps of semiconductor fabrication, of which...
constructed from 1656 to 1666, Heiliges Grab of Görlitz constructed between 1481 and 1504.
See also
- Holy FireHoly FireThe Holy Fire is described by Orthodox Christians as a miracle that occurs every year at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem on Holy Saturday, the day preceding Orthodox Easter. It is considered by many to be the longest-attested annual miracle in the Christian world...
- Brotherhood of the Holy SepulchreBrotherhood of the Holy SepulchreThe Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre, or The Holy Community of the All-Holy Sepulchre, is the Orthodox monastic fraternity that for centuries has guarded and protected the Christian Holy places in the Holy Land...
- Order of the Holy SepulchreOrder of the Holy SepulchreThe Equestrian Order of the Holy Sepulchre of Jerusalem is a Roman Catholic order of knighthood under the protection of the pope. It traces its roots to Duke Godfrey of Bouillon, principal leader of the First Crusade...
, initiated by Godfrey of BouillonGodfrey of BouillonGodfrey of Bouillon was a medieval Frankish knight who was one of the leaders of the First Crusade from 1096 until his death. He was the Lord of Bouillon, from which he took his byname, from 1076 and the Duke of Lower Lorraine from 1087... - Orthodox Patriarch of JerusalemOrthodox Patriarch of JerusalemThe Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem is the head bishop of the Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, ranking fourth of nine Patriarchs in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 2005, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem has been Theophilos III...
- History of the Eastern Orthodox ChurchHistory of the Eastern Orthodox ChurchThe Eastern Orthodox Churches trace their roots back to the Apostles and Jesus Christ. Apostolic succession established the seats of Patriarchy...
- Early Christian art and architectureEarly Christian art and architectureEarly Christian art and architecture is the art produced by Christians or under Christian patronage from about the year 100 to about the year 500. Prior to 100 there is no surviving art that can be called Christian with absolute certainty...
- Oldest churches in the worldOldest churches in the worldThis article lists the oldest church buildings.The oldest extant buildings identified as early sites of Christian worship date to the 3rd century....
- Constantine I and ChristianityConstantine I and ChristianityDuring the reign of the Emperor Constantine the Great, Christianity became the dominant religion of the Roman Empire. Constantine, also known as Constantine I, had a significant religious experience following his victory at the Battle of Milvian Bridge in 312...
- Art of the CrusadesArt of the CrusadesThe art of the Crusades, meaning primarily the art produced in Middle Eastern areas under Crusader control, spanned two artistic periods in Europe, the Romanesque and the Gothic, but in the Crusader kingdoms of the Levant the Gothic style barely appeared...
- Monza ampullaeMonza ampullaeThe Monza ampullae form the largest collection of a specific type of Early Medieval pilgrimage ampullae or small flasks designed to hold holy oil from pilgrimage sites in the Holy Land related to the life of Jesus, that were made in Palestine, probably in the fifth to early seventh centuries...
- Temple ChurchTemple ChurchThe Temple Church is a late-12th-century church in London located between Fleet Street and the River Thames, built for and by the Knights Templar as their English headquarters. In modern times, two Inns of Court both use the church. It is famous for its effigy tombs and for being a round church...
in London - Talpiot TombTalpiot TombThe Talpiot Tomb is a rock-cut tomb discovered in 1980 in the East Talpiot neighborhood, five kilometers south of the Old City in East Jerusalem. It contained ten ossuaries, six of them with epigraphs, including one with the inscription that has been interpreted as "Jesus, son of Joseph", though...
- Rock-cut tombs in ancient Israel
- Church of the NativityChurch of the NativityThe Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem is one of the oldest continuously operating churches in the world. The structure is built over the cave that tradition marks as the birthplace of Jesus of Nazareth, and thus it is considered sacred by Christians...
- Third Temple
- Burial places of founders of world religionsBurial places of founders of world religions-Bahá'í Faith:Located in Bahji near Acre, Israel, the Shrine of Bahá'u'lláh is the most holy place for Bahá'ís and their Qiblih, or direction of prayer...
- Palestinian ChristiansPalestinian ChristiansPalestinian Christians are Arabic-speaking Christians descended from the people of the geographical area of Palestine. Within Palestine, there are churches and believers from many Christian denominations, including Oriental Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodoxy, Catholic , Protestant, and others...
Further reading
- Roese, Gerhard, Die Rekonstruktion des Turmes der Grabeskirche in Jerusalem (Darmstadt, Roese-Design, 2002), isbn=3000097759.
- Glenn Bowman, '“In Dubious Battle on the Plains of Heav'n”: The Politics of Possession in Jerusalem's Holy Sepulchre,' History and Anthropology, 22,3 (2011), 371-399.
External links
General sites
- Article with Photos (article, interactive plan, photo gallery)
- OrthodoxWiki (article)
- Sacred Destinations (article, interactive plan, photo gallery)
- The Reconstruction of the Tower of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem (article)
- The Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem (article, photos & video)
Custodians
- Franciscan Custody of the Holy Land (Roman Catholic custodians)
- Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre (Greek Orthodox custodians)
- Joudeh family (Muslim custodian)
- Nuseibeh family (Muslim custodian)
- Homily of John Paul II in the church of the Holy Sepulchre
Primary sources and scholarly articles
- Egeria's description in the 380s
- The Church of the Resurrection (EHR 7:417‑436, 669‑684)
Photo galleries
- Photos Gallery of the Church - allaboutJerusalem.com
- Inside Photos of the Church
- Jerusalem Shots
- Photo Gallery of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in 2007
- Virtual tour Full HD December 2007
- VR Panoramic Images of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
- Unique 360 degrees panoramic tour
Miscellaneous
- The Wall Street Journal on factional disputes over the Church
- Miracle of the Holy Fire
- Commemoration of the Founding of the Church of the Resurrection (Holy Sepulchre) at Jerusalem Orthodox iconIconAn icon is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, from Eastern Christianity and in certain Eastern Catholic churches...
and synaxarion for September 13 - "Divvying up the Most Sacred Place by Chris Armstrong, Christianity Today, Week of July 29, 2002, retrieved February 28, 2006.

