Circular motion
Overview
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
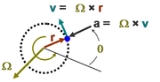
, circular motion is rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
along a circular path
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
or a circular orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
. It can be uniform
Uniform circular motion
In physics, uniform circular motion describes the motion of a body traversing a circular path at constant speed. The distance of the body from the axis of rotation remains constant at all times. Though the body's speed is constant, its velocity is not constant: velocity, a vector quantity, depends...
, that is, with constant angular rate of rotation (and thus constant speed), or non-uniform
Non-uniform circular motion
Non-uniform circular motion is any case in which an object moving in a circular path has a varying speed. Some examples of non-uniform circular motion include a roller coaster, a vertical pendulum, and a car riding over a hill. All of these situations include an object traveling at different...
, that is, with a changing rate of rotation. The rotation around a fixed axis
Rotation around a fixed axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed axis hypothesis exclude the possibility of a moving axis, and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation around more than one axis at the same...
of a three-dimensional body involves circular motion of its parts. The equations describing circular motion of an object do not take size or geometry into account, rather, the motion of a point mass in a plane is assumed.
Unanswered Questions

