
Cluny Abbey
Encyclopedia

Cluny
Cluny or Clungy is a commune in the Saône-et-Loire department in the region of Bourgogne in eastern France. It is 20 km northwest of Mâcon.The town grew up around the Benedictine Cluny Abbey, founded by Duke William I of Aquitaine in 910...
, Saône-et-Loire
Saône-et-Loire
Saône-et-Loire is a French department, named after the Saône and the Loire rivers between which it lies.-History:When it was formed during the French Revolution, as of March 4, 1790 in fulfillment of the law of December 22, 1789, the new department combined parts of the provinces of southern...
, France. It was built in the Romanesque
Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
style, with three churches built in succession from the 10th to the early 12th centuries.
Cluny was founded by William I, Duke of Aquitaine in 910. He nominated Berno as the first Abbot
Abbot
The word abbot, meaning father, is a title given to the head of a monastery in various traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not actually the head of a monastery...
of Cluny, subject only to Pope Sergius III
Pope Sergius III
Pope Sergius III was a pope of the Roman Catholic Church from 29 January 904 to 14 April 911. Because Sergius III was possibly the only pope known to have ordered the murder of another pope and the only pope to have fathered an illegitimate son who later became pope , his reign has been described...
. The Abbey was notable for its stricter adherence to the Rule of St. Benedict and the place where the Benedictine Order was formed, whereby Cluny became acknowledged as the leader of western monasticism
Monasticism
Monasticism is a religious way of life characterized by the practice of renouncing worldly pursuits to fully devote one's self to spiritual work...
. The establishment of the Benedictine order was a keystone to the stability of European society that was achieved in the 11th century. In 1790 during the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, the abbey was sacked and mostly destroyed. Only a small part of the original remains.
Dating around 1334, the abbots of Cluny had a townhouse in Paris known as the Hôtel de Cluny
Musée de Cluny
The Musée de Cluny , officially known as Musée National du Moyen Âge , is a museum in Paris, France...
, what is now a public museum since 1833. Apart from the name, it no longer possesses anything originally connected with Cluny.

Foundation
In 910, William I, Duke of Aquitaine "the Pious", and Count of AuvergneRulers of Auvergne
-History:In the 7th century Auvergne was disputed between the Franks and Aquitanians. It was later conquered by the Carolingians, and was integrated for a time into the kingdom of Aquitaine...
, founded the Benedictine abbey of Cluny on a modest scale, as the mother house of the Congregation of Cluny. In donating his hunting preserve in the forests of Burgundy, William released the Cluny abbey from all future obligation to him and his family other than prayer. Contemporary patrons normally retained a proprietary interest and expected to install their kinsmen as abbots. William appears to have made this arrangement with Berno, the first abbot
Abbot
The word abbot, meaning father, is a title given to the head of a monastery in various traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not actually the head of a monastery...
, to free the new monastery from such secular entanglements and initiate the Cluniac Reforms
Cluniac Reforms
The Cluniac Reforms were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of West focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. The movement is named for the Abbey of Cluny in Burgundy, where it started within the Benedictine order. The reforms were...
. The abbots of Cluny were statesmen on the international stage and the monastery of Cluny was considered the grandest, most prestigious and best-endowed monastic institution in Europe. The height of Cluniac influence was from the second half of the 10th century through the early 12th. The first female members were admitted to the order during the eleventh century.
Organization

- organizational structure;
- prohibition on holding land by feudal service; and
- execution of the liturgyLiturgyLiturgy is either the customary public worship done by a specific religious group, according to its particular traditions or a more precise term that distinguishes between those religious groups who believe their ritual requires the "people" to do the "work" of responding to the priest, and those...
as its main form of work.
While most Benedictine monasteries remained autonomous and associated with each other only informally, Cluny created a large, federated order in which the administrators of subsidiary houses served as deputies of the abbot of Cluny and answered to him. The Cluniac houses, being directly under the supervision of the abbot of Cluny, the autocrat of the Order, were styled priories
Priory
A priory is a house of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or religious sisters , or monasteries of monks or nuns .The Benedictines and their offshoots , the Premonstratensians, and the...
, not abbeys. The priors, or chiefs of priories, met at Cluny once a year to deal with administrative issues and to make reports. Many other Benedictine houses, even those of earlier formation, came to regard Cluny as their guide. When in 1016 Pope Benedict VIII
Pope Benedict VIII
Pope Benedict VIII , born Theophylactus, Pope from 1012 to 1024, of the noble family of the counts of Tusculum , descended from Theophylact, Count of Tusculum like his predecessor Pope Benedict VI .Benedict VIII was opposed by an antipope, Gregory...
decreed that the privileges of Cluny be extended to subordinate houses, there was further incentive for Benedictine communities to insinuate themselves in the Cluniac order.
Partly due to the order's opulence, the Cluniac nunneries were not seen as being particularly cost-effective. The order did not have interest in founding many new houses for women.
The customs of Cluny represented a shift from the earlier ideal of a Benedictine monastery as an agriculturally self-sufficient unit. This was similar to the contemporary villa
Villa
A villa was originally an ancient Roman upper-class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity,...
of the more Romanized parts of Europe and the manor
Manorialism
Manorialism, an essential element of feudal society, was the organizing principle of rural economy that originated in the villa system of the Late Roman Empire, was widely practiced in medieval western and parts of central Europe, and was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market...
of the more feudal parts, in which each member did physical labor as well as offering prayer. In 817 St Benedict of Aniane
Benedict of Aniane
Saint Benedict of Aniane , born Witiza and called the Second Benedict, was a Benedictine monk and monastic reformer, who left a large imprint on the religious practice of the Carolingian Empire...
, the "second Benedict", developed monastic constitutions at the urging of Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious , also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was the King of Aquitaine from 781. He was also King of the Franks and co-Emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813...
to govern all the Carolingian monasteries. He acknowledged that the Black Monks no longer supported themselves by physical labor. Cluny's agreement to offer perpetual prayer (laus perennis (literally "perpetual praise") meant that it had increased a specialization in roles.
As perhaps the wealthiest monastic house of the Western world, Cluny hired managers and workers to do the labor of monks in other orders. The monks devoted themselves to almost constant prayer, thus elevating their position into a profession. Despite the monastic ideal of a frugal life, the abbey in Cluny commissioned candelabras of solid silver and gold chalices made with precious gems for use at the abbey Masses. Instead of being limited to the traditional fare of broth and porridge, the monks ate very well, enjoying roasted chickens (a luxury in France then) and wines from their vineyards and cheeses made by their employees. The monks wore the finest linen habits and silk vestment
Vestment
Vestments are liturgical garments and articles associated primarily with the Christian religion, especially among Latin Rite and other Catholics, Eastern Orthodox, Anglicans, and Lutherans...
s at Mass. Artifacts exemplifying the wealth of Cluny Abbey are today on display at the Musée de Cluny
Musée de Cluny
The Musée de Cluny , officially known as Musée National du Moyen Âge , is a museum in Paris, France...
in Paris.
Cluniac Houses in Britain
All of the English and Scottish Cluniac houses which were larger than cells were known as priories
Priory
A priory is a house of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. Priories may be houses of mendicant friars or religious sisters , or monasteries of monks or nuns .The Benedictines and their offshoots , the Premonstratensians, and the...
, symbolising their subordination to Cluny. Cluny's influence spread into the British Isles in the eleventh century, first at Lewes
Lewes
Lewes is the county town of East Sussex, England and historically of all of Sussex. It is a civil parish and is the centre of the Lewes local government district. The settlement has a history as a bridging point and as a market town, and today as a communications hub and tourist-oriented town...
, and then elsewhere. The head of their order was the Abbot at Cluny. All English and Scottish Cluniacs were bound to cross to France to Cluny to consult or be consulted unless the Abbot chose to come to Britain, which he did five times in the 13th century, and only twice in the 14th.
Arts
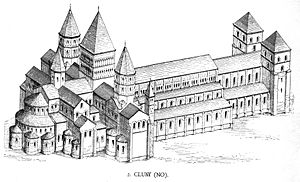
At Cluny, the central activity was the liturgy; it was extensive and beautifully presented in inspiring surroundings, reflecting the new personally-felt wave of piety of the 11th century. Monastic intercession was believed indispensable to achieving a state of grace, and lay rulers competed to be remembered in Cluny's endless prayers; this inspired the endowments in land and benefices that made other arts possible.The fast-growing community at Cluny required buildings on a large scale. The examples at Cluny profoundly affected architectural practice in Western Europe from the tenth through the twelfth centuries. The three successive churches are conventionally called Cluny I, II and III. In building the third and final church at Cluny, the monastery constructed what was the largest building in Europe before the 16th century, when St. Peter's
St. Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter , officially known in Italian as ' and commonly known as Saint Peter's Basilica, is a Late Renaissance church located within the Vatican City. Saint Peter's Basilica has the largest interior of any Christian church in the world...
in Rome was rebuilt. The construction of Cluny II, ca. 955-981, begun after the destructive Hungarian
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
raids of 953, led the tendency for Burgundian churches to be stone-vaulted.
Ferdinand I of León
Ferdinand I , called the Great , was the Count of Castile from his uncle's death in 1029 and the King of León after defeating his brother-in-law in 1037. According to tradition, he was the first to have himself crowned Emperor of Spain , and his heirs carried on the tradition...
, ruler of a united León-Castile, some time between 1053 and 1065. (Alfonso VI re-established it in 1077, and confirmed it in 1090.) Ferdinand fixed the sum at 1,000 gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
en aurei, an amount which Alfonso VI doubled in 1090. This was the biggest annuity that the Order ever received from king or layman, and it was never surpassed. Henry I of England's annual grant from 1131 of 100 mark
Mark (money)
Mark was a measure of weight mainly for gold and silver, commonly used throughout western Europe and often equivalent to 8 ounces. Considerable variations, however, occurred throughout the Middle Ages Mark (from a merging of three Teutonic/Germanic languages words, Latinized in 9th century...
s of silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, not gold, seemed little by comparison. The Alfonsine census enabled Abbot Hugh (who died in 1109) to undertake construction of the huge third abbey church. When payments in the Islamic gold coin later lapsed, the Cluniac order suffered a financial crisis that crippled them during the abbacies of Pons of Melgueil
Pons of Melgueil
Pons of Melgueil was the seventh Abbot of Cluny from 1109 to 1122. He was descended from a noble lineage of Languedoc which had long supported the Gregorian reform. He himself was a godson of Pope Paschal II....
(1109 – 1125) and Peter the Venerable
Peter the Venerable
Peter the Venerable , also known as Peter of Montboissier, abbot of the Benedictine abbey of Cluny, born to Blessed Raingarde in Auvergne, France. He has been honored as a saint but has never been formally canonized.-Life:Peter was "Dedicated to God" at birth and given to the monastery at...
(1122 – 1156). The Spanish wealth donated to Cluny publicized the rise of the Spanish Christians, and drew central Spain for the first time into the larger European orbit.
The library
The Cluny library was one of the richest and most important in France and Europe. It was a storehouse of numerous very valuable manuscripts. During the religious conflicts of 1562, the HuguenotHuguenot
The Huguenots were members of the Protestant Reformed Church of France during the 16th and 17th centuries. Since the 17th century, people who formerly would have been called Huguenots have instead simply been called French Protestants, a title suggested by their German co-religionists, the...
s sacked the abbey, destroying or dispersing many of the manuscripts. Of those that were left, some were burned in 1790 by a rioting mob related to the excesses of the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
. Others still were stored away in the Cluny town hall.
The French Government worked to relocate such treasures, including those that ended up in private hands. They are now held by the Bibliothèque nationale de France
Bibliothèque nationale de France
The is the National Library of France, located in Paris. It is intended to be the repository of all that is published in France. The current president of the library is Bruno Racine.-History:...
at Paris. The British Museum
British Museum
The British Museum is a museum of human history and culture in London. Its collections, which number more than seven million objects, are amongst the largest and most comprehensive in the world and originate from all continents, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its...
holds some sixty or so charters originating from Cluny.
Cluny's influence

Fleury
Fleury can refer to:* Abbo of Fleury abbot of the monastery of Fleury* Andrew of Fleury, historian from the monstery of Fleury* Cardinal André-Hercule de Fleury, Bishop of Fréjus , chief minister of Louis XV of France...
and inspiring St Dunstan
Dunstan
Dunstan was an Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey, a Bishop of Worcester, a Bishop of London, and an Archbishop of Canterbury, later canonised as a saint. His work restored monastic life in England and reformed the English Church...
in England. There were no official English Cluniac priories until that of Lewes
Lewes Priory
The Priory of St Pancras was the first Cluniac house in England and had one of the largest monastic churches in the country. It was set within an extensive walled and gated precinct laid out in a commanding location fronting the tidal shore-line at the head of the Ouse valley to the south of Lewes...
in Sussex, founded by the Anglo-Norman earl William de Warenne
William de Warenne
William de Warenne may refer to:*William de Warenne, 1st Earl of Surrey *William de Warenne, 2nd Earl of Surrey *William de Warenne, 3rd Earl of Surrey *William de Warenne, 5th Earl of Surrey...
c 1077. The best-preserved Cluniac houses in England are Castle Acre Priory
Castle Acre Priory
Castle Acre Priory, in the village of Castle Acre, Norfolk, England, is thought to have been founded in 1089 by William de Warenne the son the 1st Earl of Surrey who had founded England's first Cluniac priory at Lewes in 1077. The order originated from Burgundy...
, Norfolk, and Much Wenlock Priory
Much Wenlock Priory
Much Wenlock Priory is a ruined 12th century monastery, located in Much Wenlock, Shropshire, at . The foundation was a part of the Cluniac order, which was refounded in 1079 and 1082, on the site of an earlier 7th century monastery, by Roger de Montgomery...
, Shropshire. It is thought that there were only three Cluniac nunneries in England, one of them being Delapré Abbey
Delapré Abbey
Delapré Abbey , or more properly, the Convent of St Mary De La Pré, was founded as a Cluniac nunnery about the year 1145, situated in the meadows of the River Nene to the south of Northampton ....
at Northampton
Northampton
Northampton is a large market town and local government district in the East Midlands region of England. Situated about north-west of London and around south-east of Birmingham, Northampton lies on the River Nene and is the county town of Northamptonshire. The demonym of Northampton is...
.
Until the reign of Henry VI
Henry VI of England
Henry VI was King of England from 1422 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471, and disputed King of France from 1422 to 1453. Until 1437, his realm was governed by regents. Contemporaneous accounts described him as peaceful and pious, not suited for the violent dynastic civil wars, known as the Wars...
, all Cluniac houses in England were French, governed by French priors and directly controlled from Cluny. Henry's act of raising the English priories to independent abbeys was a political gesture, a mark of England's nascent national consciousness.
The early Cluniac establishments had offered refuges from a disordered world but by the late 11th century, Cluniac piety permeated society. This is the period that achieved the final Christianization of the heartland of Europe.

Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor also known as St. Edward the Confessor , son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy, was one of the last Anglo-Saxon kings of England and is usually regarded as the last king of the House of Wessex, ruling from 1042 to 1066....
was later canonized. In Germany, the penetration of Cluniac ideals was effected in concert with Henry III
Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry III , called the Black or the Pious, was a member of the Salian Dynasty of Holy Roman Emperors...
of the Salian dynasty, who had married a daughter of the duke of Aquitaine. Henry was infused with a sense of his sacramental role as a delegate of Christ in the temporal sphere. He had a spiritual and intellectual grounding for his leadership of the German church, which culminated in the pontificate of his kinsman, Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX
Pope Saint Leo IX , born Bruno of Eguisheim-Dagsburg, was Pope from February 12, 1049 to his death. He was a German aristocrat and as well as being Pope was a powerful secular ruler of central Italy. He is regarded as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church, with the feast day of April 19...
. The new pious outlook of lay leaders enabled the enforcement of the Truce of God movement to curb aristocratic violence.
Within his order, the Abbot of Cluny was free to assign any monk to any house; he created a fluid structure around a central authority that was to become a feature of the royal chanceries of England and of France, and of the bureaucracy of the great independent dukes, such as that of Burgundy. Cluny's highly centralized hierarchy was a training ground for Catholic prelates: four monks of Cluny became pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
s: Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII
Pope St. Gregory VII , born Hildebrand of Sovana , was Pope from April 22, 1073, until his death. One of the great reforming popes, he is perhaps best known for the part he played in the Investiture Controversy, his dispute with Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor affirming the primacy of the papal...
, Urban II
Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II , born Otho de Lagery , was Pope from 12 March 1088 until his death on July 29 1099...
, Paschal II
Pope Paschal II
Pope Paschal II , born Ranierius, was Pope from August 13, 1099, until his death. A monk of the Cluniac order, he was created cardinal priest of the Titulus S...
and Urban V
Pope Urban V
Pope Urban V , born Guillaume Grimoard, was Pope from 1362 to 1370.-Biography:Grimoard was a native of Grizac in Languedoc . He became a Benedictine and a doctor in Canon Law, teaching at Montpellier and Avignon...
.
An orderly succession of able and educated abbots, drawn from the highest aristocratic circles, led Cluny, and three were canonized: Saints Odo of Cluny
Odo of Cluny
Saint Odo of Cluny , a saint of the Roman Catholic Church, was the second abbot of Cluny. He enacted various reforms in the Cluniac monastery system of France and Italy....
, the second abbot (died 942); Hugh of Cluny
Hugh of Cluny
Hugh of Cluny was an Abbot of Cluny. He is sometimes referred to as "Hugh the Great" or "Hugh of Semur" and was canonized by the Roman Catholic Church as Saint Hugh . He was one of the most influential leaders of one of the most influential monastic orders of the Middle Ages.Abbot Hugh built the...
, the sixth abbot (died 1109); and Odilo, the fifth abbot (died 1049). Odilo continued to reform other monasteries, but as Abbot of Cluny, he also exercised tighter control of the order's far-flung priories.
Cluny and the Gregorian reforms
Gregorian Reform
The Gregorian Reforms were a series of reforms initiated by Pope Gregory VII and the circle he formed in the papal curia, circa 1050–80, which dealt with the moral integrity and independence of the clergy...
of Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII
Pope St. Gregory VII , born Hildebrand of Sovana , was Pope from April 22, 1073, until his death. One of the great reforming popes, he is perhaps best known for the part he played in the Investiture Controversy, his dispute with Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor affirming the primacy of the papal...
. The Cluniac establishment found itself closely identified with the Papacy. In the early 12th century, the order lost momentum under poor government. It was subsequently revitalized under Abbot Peter the Venerable
Peter the Venerable
Peter the Venerable , also known as Peter of Montboissier, abbot of the Benedictine abbey of Cluny, born to Blessed Raingarde in Auvergne, France. He has been honored as a saint but has never been formally canonized.-Life:Peter was "Dedicated to God" at birth and given to the monastery at...
(died 1156), who brought lax priories back into line and returned to stricter discipline. Cluny reached its apogee of power and influence under Peter, as its monks became bishops, legates, and cardinals throughout France and the Holy Roman Empire. But by the time Peter died, newer and more austere orders such as the Cistercians were generating the next wave of ecclesiastical reform. Outside monastic structures, the rise of English and French nationalism
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
created a climate unfavourable to the existence of monasteries autocratically ruled by a head residing in Burgundy. The Papal Schism
Western Schism
The Western Schism or Papal Schism was a split within the Catholic Church from 1378 to 1417. Two men simultaneously claimed to be the true pope. Driven by politics rather than any theological disagreement, the schism was ended by the Council of Constance . The simultaneous claims to the papal chair...
of 1378 to 1409 further divided loyalties: France recognizing a pope at Avignon and England one at Rome, interfered with the relations between Cluny and its dependent houses. Under the strain, some English houses, such as Lenton Priory
Lenton Priory
Lenton Priory was a Cluniac house founded by William Peverel in the early 12th century. The exact date of foundation is unknown but 1102 is frequently quoted.-Cluniac Priory:...
, Nottingham
Nottingham
Nottingham is a city and unitary authority in the East Midlands of England. It is located in the ceremonial county of Nottinghamshire and represents one of eight members of the English Core Cities Group...
, were naturalized (Lenton
Lenton, Nottingham
Lenton is an area of the City of Nottingham in the county of Nottinghamshire, England. Politically, it falls within the Nottingham South constituency. Most of the area lies within the electoral ward of "Dunkirk and Lenton", however the "Lenton Triangle" area, considered by most residents to be part...
in 1392) and no longer regarded as alien priories, weakening the Cluniac structure.
By the time of the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, the monks were so thoroughly identified with the Ancien Régime that the order was suppressed in France in 1790 and the monastery at Cluny almost totally demolished in 1810. Later, it was sold and used as a quarry until 1823. Today, little more than one of the original eight towers remains of the whole monastery.
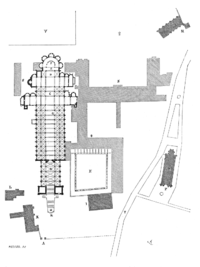
Modern excavations of the Abbey began in 1927 under the direction of Kenneth John Conant
Kenneth John Conant
Kenneth John Conant was an American architectural historian specializing in medieval architecture.Conant was born in Neenah, Wisconsin and studied at Harvard University in 1911...
, American architectural historian of Harvard University
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
, and continued (although not continuously) until 1950.
Decline and destruction of the buildings
Starting from the 12th century, Cluny had serious financial problems, caused mainly by the construction of the third abbey. Charity given to the poor increased the expenditure. The influence of the abbey weakened gradually as other religious orders rose (Cistercians in the 12th, then MendicantMendicant
The term mendicant refers to begging or relying on charitable donations, and is most widely used for religious followers or ascetics who rely exclusively on charity to survive....
s in the 13th century). Bad management of the grounds and unwillingness of the subsidiary companies to pay the annual taxable quota helped to lessen Cluny's revenue. Cluny raised loans and ended up being involved in debt to its creditors, who were merchants of Cluny or Jews of Mâcon
Mâcon
Mâcon is a small city in central France. It is prefecture of the Saône-et-Loire department, in the region of Bourgogne, and the capital of the Mâconnais district. Mâcon is home to over 35,000 residents, called Mâconnais.-Geography:...
. The conflicts with the priories multiplied and the authority of the pope became heavier. To the 14th century, the pope frequently named the abbots. The crises of the end of the Middle Ages and the wars of religion in the 16th century weakened the abbey a little more. The monks lived in luxury and there were not more than about 60 monks in the middle of the 15th century. With the Concordat of Bologna
Concordat of Bologna
The Concordat of Bologna , marking a stage in the evolution of the Gallican Church, was an agreement between King Francis I of France and Pope Leo X that Francis negotiated in the wake of his victory at Marignano in September 1515...
in 1516 overseen by Antoine Duprat
Antoine Duprat
Antoine Duprat was a French Cardinal and politician, who was chancellor of France.-Life:Duprat was born in Issoire in Auvergne. Educated for the law, he won a high position in his profession and in 1507 became first president of the Parlement of Paris...
, the king gained the power to appoint the abbot of Cluny.
The years following the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
were fatal to all the monastic buildings and its church. In 1793, its archives were burned and the church was delivered to plundering. The abbey estate was sold in 1798 for 2,140,000 francs. Until 1813, the abbey was used as a stone quarry to build houses in the town.
Today, there remain only the buildings built under the Old Mode as well as a small portion of Cluny III. Only the southern transept and its bell-tower still exist. The remaining structure represents less than 10% of the floor area of Cluny III, which was the largest church of Christendom, until the construction of St. Peter's Basilica
St. Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter , officially known in Italian as ' and commonly known as Saint Peter's Basilica, is a Late Renaissance church located within the Vatican City. Saint Peter's Basilica has the largest interior of any Christian church in the world...
in Rome, five centuries later. The abbey has sheltered since 1901 a forming center of the École nationale supérieure d'arts et métiers
École Nationale Supérieure d'Arts et Métiers
Arts et Métiers ParisTech is the French leading engineering school in the fields of mechanics and industrialization.The school trained 85,000 engineers since its foundation in 1780 by the Duke of La Rochefoucauld-Liancourt....
(ENSAM) of the engineers of the Art-and-Trades (Gadzarts
Gadzarts
Gadz'Arts or Gadzarts is the nickame given to the students and the alumni of École Nationale Supérieure d'Arts et Métiers - a prestigious university specialised in engineering....
, in student's slang).
In 1928, the site was excavated and recognized by the American archaeologist Kenneth J. Conant
Kenneth John Conant
Kenneth John Conant was an American architectural historian specializing in medieval architecture.Conant was born in Neenah, Wisconsin and studied at Harvard University in 1911...
with the backing of the Medieval Academy of America
Medieval Academy of America
The Medieval Academy of America is the largest organization in the United States promoting excellence in the field of medieval studies. It was founded in 1925 and is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts...
.
External links
- (Universität Münster: Institut für Frühmittelalterforschung) Cluny. (in English) Scholarly portal to many aspects of Cluny.
- Catholic Encyclopedia: Congregation of Cluny
- Christopher Golden, "Cluniac Order"
- Societas Christiana Encyclopedia: The Cluniac movement
- Charter of the Abbey of Cluny
- Large archive of photographs of the abbey
- The History of Romanesque Cluny Clarified by Excavations and Comparisons, by K.J. Conant (pdf)
- Paradoxplace – Cluny Page – Photos

