
Color quantization
Encyclopedia
 |
In computer graphics
Computer graphics
Computer graphics are graphics created using computers and, more generally, the representation and manipulation of image data by a computer with help from specialized software and hardware....
, color quantization or color image quantization is a process that reduces the number of distinct colors used in an image, usually with the intention that the new image should be as visually similar as possible to the original image. Computer algorithms to perform color quantization on bitmaps have been studied since the 1970s. Color quantization is critical for displaying images with many colors on devices that can only display a limited number of colors, usually due to memory limitations, and enables efficient compression of certain types of images.
The name "color quantization" is primarily used in computer graphics research literature; in applications, terms such as optimized palette generation, optimal palette generation, or decreasing color depth are used. Some of these are misleading, as the palettes generated by standard algorithms are not necessarily the best possible.
Algorithms
Most standard techniques treat color quantization as a problem of clustering points in three-dimensional space, where the points represent colors found in the original image and the three axes represent the three color channels. Almost any three-dimensional clustering algorithmData clustering
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of assigning a set of objects into groups so that the objects in the same cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters....
can be applied to color quantization, and vice versa. After the clusters are located, typically the points in each cluster are averaged to obtain the representative color that all colors in that cluster are mapped to. The three color channels are usually red, green, and blue
RGB color model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which red, green, and blue light is added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors...
, but another popular choice is the Lab color space
Lab color space
A Lab color space is a color-opponent space with dimension L for lightness and a and b for the color-opponent dimensions, based on nonlinearly compressed CIE XYZ color space coordinates....
, in which Euclidean distance
Euclidean distance
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula. By using this formula as distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space...
is more consistent with perceptual difference.
The most popular algorithm by far for color quantization, invented by Paul Heckbert in 1980, is the median cut
Median cut
Median cut is an algorithm to sort data of an arbitrary number of dimensions into series of sets by cutting each set of data at the median point....
algorithm. Many variations on this scheme are in use. Before this time, most color quantization was done using the population algorithm or population method, which essentially constructs a histogram of equal-sized ranges and assigns colors to the ranges containing the most points. A more modern popular method is clustering using octree
Octree
An octree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly eight children. Octrees are most often used to partition a three dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into eight octants. Octrees are the three-dimensional analog of quadtrees. The name is formed from oct + tree,...
s, first conceived by Gervautz and Purgathofer and improved by Xerox PARC
Xerox PARC
PARC , formerly Xerox PARC, is a research and co-development company in Palo Alto, California, with a distinguished reputation for its contributions to information technology and hardware systems....
researcher Dan Bloomberg.
If the palette is fixed, as is often the case in real-time color quantization systems such as those used in operating systems, color quantization is usually done using the "straight-line distance" or "nearest color" algorithm, which simply takes each color in the original image and finds the closest palette entry, where distance is determined by the distance between the two corresponding points in three-dimensional space. In other words, if the colors are
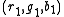 and
and 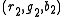 , we want to minimize the Euclidean distance
, we want to minimize the Euclidean distanceEuclidean distance
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula. By using this formula as distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space...
:
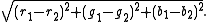
This effectively decomposes the color cube into a Voronoi diagram
Voronoi diagram
In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a special kind of decomposition of a given space, e.g., a metric space, determined by distances to a specified family of objects in the space...
, where the palette entries are the points and a cell contains all colors mapping to a single palette entry. There are efficient algorithms from computational geometry
Computational geometry
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical problems arise out of the study of computational geometric algorithms, and such problems are also considered to be part of computational...
for computing Voronoi diagrams and determining which region a given point falls in; in practice, indexed palettes are so small that these are usually overkill.
Color quantization is frequently combined with dither
Dither
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images...
ing, which can eliminate unpleasant artifacts such as banding that appear when quantizing smooth gradients and give the appearance of a larger number of colors. Some modern schemes for color quantization attempt to combine palette selection with dithering in one stage, rather than perform them independently.
A number of other much less frequently used methods have been invented that use entirely different approaches. The Local K-means algorithm, conceived by Oleg Verevka in 1995, is designed for use in windowing systems where a core set of "reserved colors" is fixed for use by the system and many images with different color schemes might be displayed simultaneously. It is a post-clustering scheme that makes an initial guess at the palette and then iteratively refines it.
The high quality but slow NeuQuant algorithm reduces images to 256 colors by training a Kohonen neural network
Self-organizing map
A self-organizing map or self-organizing feature map is a type of artificial neural network that is trained using unsupervised learning to produce a low-dimensional , discretized representation of the input space of the training samples, called a map...
"which self-organises through learning to match the distribution of colours in an input image. Taking the position in RGB-space of each neuron gives a high-quality colour map in which adjacent colours are similar." It is particularly advantageous for images with gradients.
Finally, one of the most promising new methods is spatial color quantization, conceived by Puzicha, Held, Ketterer, Buhmann, and Fellner of the University of Bonn
University of Bonn
The University of Bonn is a public research university located in Bonn, Germany. Founded in its present form in 1818, as the linear successor of earlier academic institutions, the University of Bonn is today one of the leading universities in Germany. The University of Bonn offers a large number...
, which combines dithering with palette generation and a simplified model of human perception to produce visually impressive results even for very small numbers of colors. It does not treat palette selection strictly as a clustering problem, in that the colors of nearby pixels in the original image also affect the color of a pixel. See sample images.
History and applications
In the early days of PCs, it was common for video adapters to support only 2, 4, 16, or (eventually) 256 colors due to video memory limitations; they preferred to dedicate the video memory to having more pixels (higher resolution) rather than more colors. Color quantization helped to justify this tradeoff by making it possible to display many high color images in 16- and 256-color modes with limited visual degradation. The Windows operating system and many other operating systems automatically perform quantization and dithering when viewing high color images in a 256 color video mode, which was important when video devices limited to 256 color modes were dominant. Modern computers can now display millions of colors at once, far more than can be distinguished by the human eye, limiting this application primarily to mobile devices and legacy hardware.Nowadays, color quantization is mainly used in GIF
GIF
The Graphics Interchange Format is a bitmap image format that was introduced by CompuServe in 1987 and has since come into widespread usage on the World Wide Web due to its wide support and portability....
and PNG images. GIF, for a long time the most popular lossless and animated bitmap format on the World Wide Web
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet...
, only supports up to 256 colors, necessitating quantization for many images. Some early web browsers constrained images to use a specific palette known as the web colors
Web colors
Web colors are colors used in designing web pages, and the methods for describing and specifying those colors. Hexadecimal color codes begin with a hash ....
, leading to severe degradation in quality compared to optimized palettes. PNG images support 24-bit color, but can often be made much smaller in filesize without much visual degradation by application of color quantization, since PNG files use fewer bits per pixel for palettized images.
The infinite number of colors available through the lens of a camera is impossible to display on a computer screen; thus converting any photograph to a digital representation necessarily involves some quantization. In practice, 24-bit color is sufficiently rich to represent almost all colors perceivable by humans with sufficiently small error as to be visually identical (if presented faithfully) .
With the few colors available on early computers, different quantization algorithms produced very different-looking output images. As a result, a lot of time was spent on writing sophisticated algorithms to be more lifelike.
In his PhD about color quantization, Andreas Schrader from the University of Siegen, Germany developed an evolutionary algorithm using natural selection of an artificial population consisting of color tables. This algorithm outperformed all
known algorithms at the time of writing in 1998 .
Editor support
Many bitmap graphics editors contain built-in support for color quantization, and will automatically perform it when converting an image with many colors to an image format with fewer colors. Most of these implementations allow the user to set exactly the number of desired colors. Examples of such support include:- Photoshop's Mode→Indexed Color function, supplies a number of quantization algorithms ranging from the fixed Windows system and Web palettes to the proprietary Local and Global algorithms for generating palettes suited to a particular image or images.
- Paint Shop Pro, in its Colors→Decrease Color Depth dialog, supplies three standard color quantization algorithms: median cut, octree, and the fixed standard "web safe" palette.
- The GIMP's Generate Optimal Palette with 256 Colours option, known to use the median cut algorithm. There has been some discussion in the developer community of adding support for spatial color quantization.
Color quantization is also used to create posterization
Posterization
Posterization of an image entails conversion of a continuous gradation of tone to several regions of fewer tones, with abrupt changes from one tone to another. This was originally done with photographic processes to create posters...
effects, although posterization has the slightly different goal of minimizing the number of colors used within the same color space, and typically uses a fixed palette.
Some vector graphics editor
Vector graphics editor
A vector graphics editor is a computer program that allows users to compose and edit vector graphics images interactively on a computer and save them in one of many popular vector graphics formats, such as EPS, PDF, WMF, SVG, or VML....
s also utilize color quantization, especially for raster-to-vector techniques that create tracings of bitmap images with the help of edge detection
Edge detection
Edge detection is a fundamental tool in image processing and computer vision, particularly in the areas of feature detection and feature extraction, which aim at identifying points in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities...
.
- Inkscape's Path→Trace Bitmap: Multiple Scans: Color function uses octree quantization to create color traces.
See also
- Indexed colorIndexed colorIn computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer memory and file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers...
- Palette (computing)Palette (computing)In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
- List of software palettes — Adaptive palettes section.
- Dithering
- Quantization (image processing)Quantization (image processing)Quantization, involved in image processing, is a lossy compression technique achieved by compressing a range of values to a single quantum value. When the number of discrete symbols in a given stream is reduced, the stream becomes more compressible. For example, reducing the number of colors...
Further reading
- Paul S. Heckbert. Color Image Quantization for Frame Buffer Display. ACM SIGGRAPH '82 Proceedings. First publication of the median cut algorithm.
- Dan Bloomberg. Color quantization using octrees. Leptonica.
- Oleg Verevka. Color Image Quantization in Windows Systems with Local K-means Algorithm. Proceedings of the Western Computer Graphics Symposium '95.
- J. Puzicha, M. Held, J. Ketterer, J. M. Buhmann, and D. Fellner. On Spatial Quantization of Color Images. (full text .ps.gz) Technical Report IAI-TR-98-1, University of Bonn. 1998.
- B. Freisleben, and A. Schrader. Color Quantization with a Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. Proceedings of the Sixth IEE International Conference on Image Processing and its Applications, Dublin, Irland, July 14-17, 1997, pp. 89-93.

