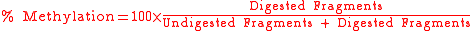Combined bisulfite restriction analysis
Encyclopedia
Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis (or COBRA) is a molecular biology technique that allows for the sensitive quantification of DNA methylation
levels at a specific genomic loci on a DNA sequence
in a small sample of genomic DNA. The technique is a variation of bisulfite sequencing
, and combines bisulfite conversion based polymerase chain reaction
with restriction digest
ion. Originally developed to reliably handle minute amounts of genomic DNA from microdissected paraffin
-embedded tissue samples, the technique has since seen widespread usage in cancer research
and epigenetics
studies.
, which introduces methylation-dependent sequence differences. During sodium bisulfite treatment, unmethylated cytosine
residues are converted to uracil
, while methylated cytosine
residues are unaffected.
, such as those for TaqI
(TCGA) and BstUI (CGCG), depending on whether the cytosine residue was originally methylated or not, respectively. Due to the methylation-independent amplification in the above step, the resulting PCR products will be a mixed population of fragments that have lost or retained CpG-containing restriction enzyme sites, whose respective percentages will be directly correlated to the original level of DNA methylation in the sample DNA.
PCR products are then treated with a restriction enzyme (e.g. BstUI), which will only cleave sites that were originally methylated (CGCG), while leaving sites that were originally unmethylated (TGTG). To ensure that all CpG sites are retained due to originally being methylated, and not a remnant of incomplete bisulfite conversion, a control digestion is performed, with enzymes such as Hsp92II which recognizes the sequence CATG, none of which should be remaining after bisulfite conversion (with the rare exception of non-CpG methylation) and thus no cleavage should occur if bisulfite conversion was complete.
, after which the methylation percentage of the original sample can be calculated by:
In medicine, COBRA has been used as a tool to help diagnose human disease involving aberrant DNA methylation. Researchers utilized COBRA in conjunction with denaturing high performance liquid chromatography in the diagnosis of the genetic imprinting disorder Russell-Silver syndrome where hypomethylation of the imprinted gene H19
is responsible for the disorder in up to 50% of patients.
DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biochemical process that is important for normal development in higher organisms. It involves the addition of a methyl group to the 5 position of the cytosine pyrimidine ring or the number 6 nitrogen of the adenine purine ring...
levels at a specific genomic loci on a DNA sequence
DNA sequence
The sequence or primary structure of a nucleic acid is the composition of atoms that make up the nucleic acid and the chemical bonds that bond those atoms. Because nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are unbranched polymers, this specification is equivalent to specifying the sequence of...
in a small sample of genomic DNA. The technique is a variation of bisulfite sequencing
Bisulfite sequencing
Bisulfite sequencing is the use of bisulfite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied...
, and combines bisulfite conversion based polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
with restriction digest
Restriction digest
A restriction digest is a procedure used in molecular biology to prepare DNA for analysis or other processing. It is sometimes termed DNA fragmentation...
ion. Originally developed to reliably handle minute amounts of genomic DNA from microdissected paraffin
Paraffin
In chemistry, paraffin is a term that can be used synonymously with "alkane", indicating hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. Paraffin wax refers to a mixture of alkanes that falls within the 20 ≤ n ≤ 40 range; they are found in the solid state at room temperature and begin to enter the...
-embedded tissue samples, the technique has since seen widespread usage in cancer research
Cancer research
Cancer research is basic research into cancer in order to identify causes and develop strategies for prevention, diagnosis, treatments and cure....
and epigenetics
Epigenetics
In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence – hence the name epi- -genetics...
studies.
Bisulfite Treatment
Genomic DNA of interest is treated with sodium bisulfiteSodium bisulfite
Sodium bisulfite is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite is a food additive with E number E222. This salt of bisulfite can be prepared by bubbling sulfur dioxide in a solution of sodium carbonate in water...
, which introduces methylation-dependent sequence differences. During sodium bisulfite treatment, unmethylated cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
residues are converted to uracil
Uracil
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine, cytosine, and guanine. In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine.Uracil is a common and...
, while methylated cytosine
5-Methylcytosine
5-Methylcytosine is a methylated form of the DNA base cytosine that may be involved in the regulation of gene transcription. When cytosine is methylated, the DNA maintains the same sequence, but the expression of methylated genes can be altered .In the figure on the right, a methyl group, is...
residues are unaffected.
PCR Amplificiation
Bisulfite treated DNA is then PCR amplified, resulting in cytosine residues at originally methylated positions, and thymine residues at originally unmethylated position (that were converted to uracil). Primers used during this step do not contain CpG sites (the common target of cytosine methylation), so the amplificiation process does not discriminate between templates based on methylation status. PCR products are purified to ensure complete digestion in the following step.Restriction Digest
The above steps lead to the methylation dependent retention or loss of CpG-containing restriction enzyme sitesRestriction sites
Restriction sites, or restriction recognition sites, are locations on a DNA molecule containing specific sequences of nucleotides, which are recognized by restriction enzymes...
, such as those for TaqI
TaqI
TaqI is a restriction enzyme isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in 1978. It has a recognition sequence of 5'TCGA 3'AGCTand makes the cut 5'---T CGA---3' 3'---AGC T---5'...
(TCGA) and BstUI (CGCG), depending on whether the cytosine residue was originally methylated or not, respectively. Due to the methylation-independent amplification in the above step, the resulting PCR products will be a mixed population of fragments that have lost or retained CpG-containing restriction enzyme sites, whose respective percentages will be directly correlated to the original level of DNA methylation in the sample DNA.
PCR products are then treated with a restriction enzyme (e.g. BstUI), which will only cleave sites that were originally methylated (CGCG), while leaving sites that were originally unmethylated (TGTG). To ensure that all CpG sites are retained due to originally being methylated, and not a remnant of incomplete bisulfite conversion, a control digestion is performed, with enzymes such as Hsp92II which recognizes the sequence CATG, none of which should be remaining after bisulfite conversion (with the rare exception of non-CpG methylation) and thus no cleavage should occur if bisulfite conversion was complete.
Quantification
The digested fragments are then separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with the expected appearance of bands corresponding to a single large undigested fragment, and multiple smaller bands corresponding to digested fragments. Quantitative amount of DNA in these bands can be determined with a device such as a phosphoimagerPhotostimulated luminescence
Photostimulated luminescence is the release of stored energy within a phosphor by stimulation with visible light, to produce a luminescent signal...
, after which the methylation percentage of the original sample can be calculated by:
Usage and Applications
COBRA has been used extensively in many research-based applications such as screening for DNA methylation changes at gene promoters in cancer studies, detecting altered methylation patterns at imprinted genes, and characterizing methylation patterns in the genome during development in mammals.In medicine, COBRA has been used as a tool to help diagnose human disease involving aberrant DNA methylation. Researchers utilized COBRA in conjunction with denaturing high performance liquid chromatography in the diagnosis of the genetic imprinting disorder Russell-Silver syndrome where hypomethylation of the imprinted gene H19
H19 (gene)
H19 is a gene for a long noncoding RNA, found in humans and elsewhere. This gene seems to have a role in some forms of cancer.The H19 gene is also known as ASM, ASM1 and BWS, among others....
is responsible for the disorder in up to 50% of patients.
Strengths
- Simple, fast and inexpensive: In COBRA, DNA methylation levels are easily and quickly measured without the need for laborious sub-cloning and sequencingDNA sequencingDNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA....
, as with bisulfite sequencing. The assay is straight-forward and can be done with standard inexpensive molecular biology reagents.
- High compatibility: Due to the PCR and purification steps, the method not only works with very small amounts of genomic DNA, but also samples that have been treated with paraffin, both of which can be problems in other DNA methylation quantification protocols such as Southern blotSouthern blotA Southern blot is a method routinely used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. Southern blotting combines transfer of electrophoresis-separated DNA fragments to a filter membrane and subsequent fragment detection by probe hybridization. The method is named...
ting and methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme digestion followed by PCR.
- Quantitative: This is in contrast to methylation-specific PCR, which is qualitative. With COBRA, DNA methylation levels can be directly quantified at a given locus, yielding more information per assay.
- Scalability for high-throughput sample processing: With COBRA, many regions of interest can be processed in parallel in separate samples digested with the same restriction enzyme. This is in contrast to bisulfite sequencing analysis, where each region needs to be examined rigorously by sequencing many clones per locus, costing more time.
- Multiple queries per assay: Methylation status can be interrogated at multiple CpG-containing restriction sites in a single digestion assay.
Weaknesses
- The assay is limited to using existing restriction sites in the region of interest, and methylation that does not occur in the context of a specific restriction site will not be assayed.
- Incomplete digestion by restriction enzymes after PCR can confound the analysis: incomplete digestion would suggest lack of DNA methylation (if cutting with a methylation-sensitive enzyme such as HpaII). It is also known that BstUI can cut at uncoverted sites, leading to overestimation of methylation levels and so the use of HpaII is often needed.
- In complex samples, cell-type heterogeneity can confound the analysis since the DNA is not being sequenced, heterogeneity in sequences from different cells in the sample (i.e. different cell populations within a tumor) that have acquired mutations in the interrogated region, such as changing the CG dinucleotide to CA or CT, would result in loss of the restriction site giving rise to an apparently methylated region due to lack of digestion. This would skew the quantification of DNA methylation levels in a given sample.