Common drain
Encyclopedia
In electronics
, a common-drain amplifier
, also known as a source follower, is one of three basic single-stage field effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage
buffer
. In this circuit the gate terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the source is the output, and the drain is common to both (input and output), hence its name. The analogous bipolar junction transistor
circuit is the common-collector amplifier
.
In addition, this circuit is used to transform impedance
s. For example, the Thévenin resistance
of a combination of a voltage follower driven by a voltage source with high Thévenin resistance is reduced to only the output resistance of the voltage follower, a small resistance. That resistance reduction makes the combination a more ideal voltage source. Conversely, a voltage follower inserted between a driving stage and a high load (ie a low resistance) presents an infinite resistance (low load) to the driving stage, an advantage in coupling a voltage signal to a large load.
 At low frequencies, the source follower pictured at right has the following small signal characteristics.
At low frequencies, the source follower pictured at right has the following small signal characteristics.
Voltage gain:
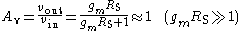
Current gain:
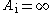
Input impedance
:
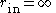
Output impedance
: (the parallel
notation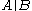 indicates the impedance of components
indicates the impedance of components 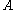 and
and 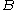 that are connected in parallel)
that are connected in parallel)
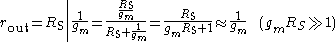
The variable gm that is not listed in Figure 1 is the transconductance
of the device (usually given in units of siemens
).
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, a common-drain amplifier
Electronic amplifier
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
, also known as a source follower, is one of three basic single-stage field effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
buffer
Buffer amplifier
A buffer amplifier is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another...
. In this circuit the gate terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the source is the output, and the drain is common to both (input and output), hence its name. The analogous bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
circuit is the common-collector amplifier
Common collector
In electronics, a common-collector amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer...
.
In addition, this circuit is used to transform impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
s. For example, the Thévenin resistance
Thévenin's theorem
In circuit theory, Thévenin's theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. For single frequency AC systems the theorem...
of a combination of a voltage follower driven by a voltage source with high Thévenin resistance is reduced to only the output resistance of the voltage follower, a small resistance. That resistance reduction makes the combination a more ideal voltage source. Conversely, a voltage follower inserted between a driving stage and a high load (ie a low resistance) presents an infinite resistance (low load) to the driving stage, an advantage in coupling a voltage signal to a large load.
Characteristics

Voltage gain:
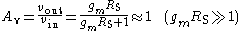
Current gain:
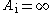
Input impedance
Input impedance
The input impedance of an electrical network is the equivalent impedance "seen" by a power source connected to that network. If the source provides known voltage and current, such impedance can be calculated using Ohm's Law...
:
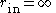
Output impedance
Output impedance
The output impedance, source impedance, or internal impedance of an electronic device is the opposition exhibited by its output terminals to an alternating current of a particular frequency as a result of resistance, inductance and capacitance...
: (the parallel
Parallel (geometry)
Parallelism is a term in geometry and in everyday life that refers to a property in Euclidean space of two or more lines or planes, or a combination of these. The assumed existence and properties of parallel lines are the basis of Euclid's parallel postulate. Two lines in a plane that do not...
notation
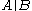 indicates the impedance of components
indicates the impedance of components 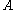 and
and 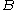 that are connected in parallel)
that are connected in parallel)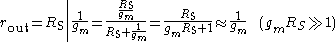
The variable gm that is not listed in Figure 1 is the transconductance
Transconductance
Transconductance, also known as mutual conductance, is a property of certain electronic components. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance; transconductance, meanwhile, is the ratio of the current change at the output port to the voltage change at the input port. It is written as gm...
of the device (usually given in units of siemens
Siemens (unit)
The siemens is the SI derived unit of electric conductance and electric admittance. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance and impedance respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term...
).

