
CompactFlash
Encyclopedia
CompactFlash is a mass storage device format used in portable electronic devices. Most CompactFlash devices contain flash memory
in a standardized enclosure. The format was first specified and produced by SanDisk
in 1994. The physical format is now used for a variety of devices.
CompactFlash became the most successful of the early memory card formats, surpassing Miniature Card
, SmartMedia
, and PC Card Type I in popularity. Subsequent formats, such as MMC/SD
, various Memory Stick
formats, and xD-Picture Card
offered stiff competition. Most of these cards are smaller than CompactFlash while offering comparable capacity and speed. Proprietary memory card formats for use in professional audio and video, such as P2
and SxS, are physically larger, faster, and costlier.
CompactFlash remains popular and is even supported in some new devices. For example, in 2008, Sony
chose CompactFlash as the recording medium for the HVR-MRC1K tapeless video recorder over smaller MemoryStick cards or expensive SxS cards. In 2010, Canon chose CompactFlash as the recording medium for its new professional high-definition video cameras, and Ikegami devices record digital video onto CompactFlash cards through an adaptor.
In November 2010, Sandisk, Sony and Nikon proposed a next generation card format targeted at high-definition camcorders and high-resolution digital photo cameras; not backward compatible, the proposed format would come in a similar form factor as CF/CFast but be based on SATA
instead of ATA and would offer read speed of 500 Mbyte/s and storage capabilities beyond 2 TiB. It remains unclear whether the CFA will adopt this proposal, as CF 5.0 already supports media up to 128 PiB and CF 6.0 adds speeds up to 167 Mbyte/s, while the SATA-based CFast already defines speeds up to 300 Mbyte/s.
 There are two main subdivisions of CF cards, Type I (3.3 mm thick) and the thicker Type II (CF2) cards (5 mm thick). The CF Type II slot is used by Microdrive
There are two main subdivisions of CF cards, Type I (3.3 mm thick) and the thicker Type II (CF2) cards (5 mm thick). The CF Type II slot is used by Microdrive
s and some other devices, such as the Hasselblad CFV Digital Back for the Hasselblad series of medium format cameras. There are four main speeds of cards including the original CF, CF High Speed (using CF+/CF2.0), a faster CF 3.0 standard and a yet faster CF 4.0 standard that is being adopted as of 2007. The thickness of the CF card type is dictated by the preceding PC Card
standard.
CompactFlash was originally built around Intel's NOR-based flash memory, but has switched to NAND technology. CF is among the oldest and most successful formats, and has held a niche in the professional camera market especially well. It has benefited from both a better cost to memory-size ratio than other formats, (for much of its life) and generally from greater available capacity than other formats.
CF cards can be used directly in a PC Card slot with a plug adapter, used as an ATA (IDE) or PCMCIA storage device with a passive adapter or with a reader, or attached to other types of ports such as USB
or FireWire. As some newer card types are smaller, they can be used directly in a CF card slot with an adapter. Formats that can be used this way include SD
/MMC, Memory Stick Duo, xD-Picture Card
in a Type I slot, and SmartMedia
in a Type II slot, as of 2005. Some multi-card readers use CF for I/O as well.
(0x7FF address limit) or as an IDE (PATA) interface.
 CompactFlash IDE mode defines an interface that is smaller than, but electrically identical to, the ATA interface. That is, it appears to the host device as if it were a hard disk
CompactFlash IDE mode defines an interface that is smaller than, but electrically identical to, the ATA interface. That is, it appears to the host device as if it were a hard disk
. The CF device contains an ATA controller. CF devices operate at 3.3 volt
s or 5 volts, and can be swapped from system to system. CompactFlash supports C-H-S
and 28-bit Logical block addressing
(CF 5.0 introduced support for LBA-48). CF cards may be set to master or slave, but have issues sharing the IDE bus. CF cards with flash memory are able to cope with extremely rapid changes in temperature. Industrial versions of flash memory cards can operate at a range of −45 to +85 °C.
NOR-based flash has lower density than newer NAND-based systems, and CompactFlash is therefore the physically largest of the three memory card formats introduced in the early 1990s, being derived from the JEIDA/PCMCIA Memory Card formats. The other two are Miniature Card
(MiniCard) and SmartMedia
(SSFDC). However, CF did switch to NAND type memory later. The IBM
Microdrive
format implements the CF Type II interface, but is not solid-state memory. Hitachi
and Seagate
also make microdrives.
s and indicates the maximum transfer rate in the form of a multiplier based on the original audio CD data transfer rate, which is 150 kbyte/s.
where R = transfer rate, K = speed rating. For example, 133x rating means transfer speed of: 133 * 150 kbyte/s = 19,950 kbyte/s ~ 20 Mbyte/s.
These are manufacturer speed ratings. Actual transfer speed may be higher, or lower, than shown on the card depending on several factors.
Because the USB 2.0 interface is limited to 60 Mbyte/s and lacks bus mastering hardware, USB implementation results in slower access.
A direct motherboard connection is often limited to 33 Mbyte/s because IDE to CF adapters lack high speed ATA (66 Mbyte/s plus) cable support. Power on from sleep/off takes longer than power up from standby.
") typically spin at 3600 rpm so rotational latency is a consideration, as is spin-up from standby or idle. Seagate's 8 GB ST68022CF drive spins up fully within a few revolutions but power draw can reach up to 350 milliamps and runs at 40-50 mA average power. Its average seek time is 8 ms
and can sustain 9 Mbyte/s read and write, and has an interface speed of 33 Mbyte/s. Hitachi's 4 GB Microdrive is 12 ms seek, sustained 6 Mbyte/s.
The CF Specification (support 28 bit LBA
) can support capacities up to 137 GB (128 GiB). Prior to 2006, CF drives using on magnetic media offered the highest capacities. But with the advent of 16 GiB and higher solid-state CF cards, they have offered the higher capacities.
Though, as of 2011, solid-state drives (SSDs) had supplanted both kinds of CF drives for large capacity requirements. Consequently, commercially available solid-state CF cards rarely go above 64 GiB, and 1-inch hard drives generally top out at 8 GiB.
announced its 16 GiB Extreme III card at the Photokina
trade fair, in September, 2006. That same month, Samsung
announced 16, 32 and 64 GiB CF cards. Two years later, in September, 2008, PRETEC announced 100GB cards.
interface. Several companies make adapters to allow CF cards to be connected to PCI
, IDE
, 44-pin laptop mini-IDE, and SATA
connections, allowing a CF card to act as a solid-state drive
with virtually any operating system or BIOS, and even in a RAID
configuration.
(EWF) to eliminate unnecessary writes to flash memory. Additionally, when formatting a flash-memory drive, the Quick Format method should be used, as one need not write every block on the drive, as may be necessary for a new magnetic disk.
Most CompactFlash flash-memory devices limit wear on blocks by varying the physical location to which a block is written. This process is called wear leveling
. When using CompactFlash in ATA mode to take the place of the hard disk drive, wear leveling becomes critical because low-numbered blocks contain tables whose contents change frequently. Current CompactFlash cards spread the wear-leveling across the entire drive. The more advanced CompactFlash cards will move data that rarely changes to ensure all blocks wear evenly.
NAND flash memory is prone to frequent soft read errors. The CompactFlash card includes error checking and correcting
(ECC) that detects the error and re-reads the block. The process is transparent to the user, although it may slow data access.
As flash memory devices are solid-state
, they are more shock-proof than rotating disks. For example, the ST68022CF Microdrive is shock rated at 175G operating and 750G non-operating.
The possibility for electrical damage from upside-down insertion is prevented by asymmetrical side slots, assuming that the host device uses a suitable connector.
Small cards consume around 5% of the power required by small disk drives and still have reasonable transfer rates of over 45 Mbyte/s for the more expensive 'high-speed' cards. However, the manufacturer's warning on the flash memory used for ReadyBoost
indicates a current draw in excess of 500 mA.
and JFFS
to work around low-level technical issues. Hardware now hides much of the complexity from the end user, and CompactFlash cards for use in consumer devices are typically formatted as FAT12 (for media up to 16 MiB), FAT16 (for media up to 2 GiB, sometimes up to 4 GiB) and FAT32 (for media larger than 2 GiB). This lets the devices be read by personal computers but also suits the limited processing ability of some consumer devices such as camera
s.
There are varying levels of compatibility among FAT32-compatible cameras, MP3 players, PDAs, and other devices. While any device that claims FAT32-capability should read and write to a FAT32-formatted card without problems, some devices are tripped up by cards larger than 2 GB that are completely unformatted, while others may take longer to apply a FAT32 format.
The way many digital cameras update the file system as they write to the card creates a FAT32 bottleneck. Writing to a FAT32-formatted card generally takes a little longer than writing to a FAT16-formatted card with similar performance capabilities. For instance, the Canon EOS 10D
writes the same photo to a FAT16-formatted 2 GB CompactFlash card somewhat faster than to a same speed 4 GB FAT32-formatted CompactFlash card, although the memory chips in both cards have the same write speed specification. Although FAT16 is more wasteful of disk space with its larger clusters, it works better with the write strategy that flash memory chips require.
The cards themselves can of course be formatted with any type of file system such as Ext
, JFS and NTFS
. It can be divided into partitions as long as the host device can read them. CompactFlash cards are often used instead of hard drives in embedded systems, dumb terminals and various small form-factor PCs that are built for low noise output or power consumption. CompactFlash cards are often more readily available and smaller than purpose-built solid-state drive
s and often have faster seek times than hard drives.
mode.
standard.
bus, rather than the Parallel ATA/IDE bus for which all previous versions of CompactFlash are designed.
CFast supports a higher maximum transfer rate than current CompactFlash cards. , SATA supports transfer rates up to 600 Mbyte/s while PATA is limited to 133 Mbyte/s using UDMA 6.
CFast cards are not physically or electrically compatible with CompactFlash cards. However, since SATA can emulate the PATA command protocol, existing CompactFlash software drivers can be used, although writing new drivers to use AHCI
instead of PATA emulation will almost always result in significant performance gains. CFast cards use a 7-pin SATA data connector (identical to the standard SATA connector), but a 17-pin power connector that appears incompatible with the standard 15-pin SATA power connector, so an adaptor is required to connect CFast cards in place of standard SATA hard drives.
The first CFast cards reached the market in late 2009. At CES
2009, Pretec showed a 32 GB CFast and announced that they should reach the market within a few months.
Delock began distributing CFast cards in 2010 and offers several card readers with USB3.0 port and eSATAp (power over eSATA) port to support CFast cards.
The vast majority of all Type II devices are Microdrives and other miniature hard drives. Flash based Type II devices are rare but a few examples do exist. Compact Flash — Secure Digital adapters usually are Type II.
Even the largest capacity cards commonly available are Type I cards. Most card readers will read both formats, with the exception of some early CF based cameras or poorer quality USB card readers where the slot is too small. Various manufacturers of 4 GB Compact Flash cards such as Sandisk, Toshiba, Alcotek and Hynix have developed devices that support mainly type I slots. Some of the latest DSLRs, like the Nikon D700
, have also dropped Type II support.
s—about 25 mm (1 inch) wide—packaged with a CompactFlash Type II form factor and interface. They were developed and released in 1999 by IBM
with a capacity of 170 Mbyte. IBM sold its disk drive division, including the Microdrive trademark, to Hitachi
in December 2002. There are now other brands of Microdrives (such as Seagate, Sony, etc.), and, over the years, these have become available in increasing capacities (up to 8 GB as of late 2008).
While these drives fit into and work in any CF II slot, the early versions drew more current (500 mA maximum) than flash memory (100 mA maximum). However current Microdrives use less than 200 mA for reads and writes (300 mA peak), and some flash devices used for high speed data e.g. Readyboost (memory can't power down to standby) draw more than the USB standard allows (500 mA). As they are mechanical devices, Microdrives are susceptible to damage from physical shock or temperature changes. However, Microdrives are not subject to the write cycle limitation inherent to flash memory.
The iPod mini
, Nokia N91
, iriver H10 (5 or 6 GB model), PalmOne LifeDrive
, and Rio Carbon
all used a CF Microdrive to store data.
, the CompactFlash form factor is also used for a variety of Input/Output and interface devices; many standard PC cards have CF counterparts, some examples include:
Flash memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It was developed from EEPROM and must be erased in fairly large blocks before these can be rewritten with new data...
in a standardized enclosure. The format was first specified and produced by SanDisk
SanDisk
SanDisk Corporation is an American multinational corporation that designs, develops and manufactures data storage solutions in a range of form factors using the flash memory, controller and firmware technologies. It was founded in 1988 by Dr. Eli Harari and Sanjay Mehrotra, non-volatile memory...
in 1994. The physical format is now used for a variety of devices.
CompactFlash became the most successful of the early memory card formats, surpassing Miniature Card
Miniature Card
Miniature Card or MiniCard is a flash or SRAM memory card standard first promoted by Intel Corp. in 1995 and backed by Advanced Micro Devices, Fujitsu and Sharp Electronics. Miniature Card Implementers Forum promoted this standard for consumer electronics: PDA/Palmtops, Digital Audio Recorders,...
, SmartMedia
SmartMedia
SmartMedia is a flash memory card standard owned by Toshiba, with capacities ranging from 2 MB to 128 MB. SmartMedia memory cards are no longer manufactured.- History :...
, and PC Card Type I in popularity. Subsequent formats, such as MMC/SD
Secure Digital card
Secure Digital is a non-volatile memory card format developed by the SD Card Association for use in portable devices. The SD technology is used by more than 400 brands across dozens of product categories and more than 8,000 models, and is considered the de-facto industry standard.Secure Digital...
, various Memory Stick
Memory Stick
Memory Stick is a removable flash memory card format, launched by Sony in October 1998, and is also used in general to describe the whole family of Memory Sticks...
formats, and xD-Picture Card
XD-Picture Card
xD-Picture Card is a flash memory card format, used mainly in older digital cameras. xD stands for Extreme Digital.xD cards are available in capacities of 16 MiB up to 2 GiB.- History :...
offered stiff competition. Most of these cards are smaller than CompactFlash while offering comparable capacity and speed. Proprietary memory card formats for use in professional audio and video, such as P2
P2 (storage media)
P2 is a professional digital recording solid-state memory storage media format introduced by Panasonic in 2004, and especially tailored to electronic news-gathering applications. It features tapeless recording of DV, DVCPRO, DVCPRO25, DVCPRO50, DVCPRO-HD, or AVC-Intra streams on a solid-state...
and SxS, are physically larger, faster, and costlier.
CompactFlash remains popular and is even supported in some new devices. For example, in 2008, Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
chose CompactFlash as the recording medium for the HVR-MRC1K tapeless video recorder over smaller MemoryStick cards or expensive SxS cards. In 2010, Canon chose CompactFlash as the recording medium for its new professional high-definition video cameras, and Ikegami devices record digital video onto CompactFlash cards through an adaptor.
In November 2010, Sandisk, Sony and Nikon proposed a next generation card format targeted at high-definition camcorders and high-resolution digital photo cameras; not backward compatible, the proposed format would come in a similar form factor as CF/CFast but be based on SATA
Sata
Sata is a traditional dish from the Malaysian state of Terengganu, consisting of spiced fish meat wrapped in banana leaves and cooked on a grill.It is a type of Malaysian fish cake, or otak-otak...
instead of ATA and would offer read speed of 500 Mbyte/s and storage capabilities beyond 2 TiB. It remains unclear whether the CFA will adopt this proposal, as CF 5.0 already supports media up to 128 PiB and CF 6.0 adds speeds up to 167 Mbyte/s, while the SATA-based CFast already defines speeds up to 300 Mbyte/s.
Description

Microdrive
Microdrive is a brand name for a miniature, 1-inch hard disk designed to fit in a CompactFlash Type II slot. The release of similar drives by other makers has led to them often being referred to as 'microdrives'...
s and some other devices, such as the Hasselblad CFV Digital Back for the Hasselblad series of medium format cameras. There are four main speeds of cards including the original CF, CF High Speed (using CF+/CF2.0), a faster CF 3.0 standard and a yet faster CF 4.0 standard that is being adopted as of 2007. The thickness of the CF card type is dictated by the preceding PC Card
PC Card
In computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
standard.
CompactFlash was originally built around Intel's NOR-based flash memory, but has switched to NAND technology. CF is among the oldest and most successful formats, and has held a niche in the professional camera market especially well. It has benefited from both a better cost to memory-size ratio than other formats, (for much of its life) and generally from greater available capacity than other formats.
CF cards can be used directly in a PC Card slot with a plug adapter, used as an ATA (IDE) or PCMCIA storage device with a passive adapter or with a reader, or attached to other types of ports such as USB
Universal Serial Bus
USB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
or FireWire. As some newer card types are smaller, they can be used directly in a CF card slot with an adapter. Formats that can be used this way include SD
Secure Digital card
Secure Digital is a non-volatile memory card format developed by the SD Card Association for use in portable devices. The SD technology is used by more than 400 brands across dozens of product categories and more than 8,000 models, and is considered the de-facto industry standard.Secure Digital...
/MMC, Memory Stick Duo, xD-Picture Card
XD-Picture Card
xD-Picture Card is a flash memory card format, used mainly in older digital cameras. xD stands for Extreme Digital.xD cards are available in capacities of 16 MiB up to 2 GiB.- History :...
in a Type I slot, and SmartMedia
SmartMedia
SmartMedia is a flash memory card standard owned by Toshiba, with capacities ranging from 2 MB to 128 MB. SmartMedia memory cards are no longer manufactured.- History :...
in a Type II slot, as of 2005. Some multi-card readers use CF for I/O as well.
Technical details
CompactFlash interface is a 50 pin subset of the 68 pin PCMCIA connector. "It can be easily slipped into a passive 68-pin PCMCIA Type II to CF Type I adapter that fully meets PCMCIA electrical and mechanical interface specifications." The Compactflash interface operates, depending on the state of a mode pin on powerup, as either 16-bit PC CardPC Card
In computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
(0x7FF address limit) or as an IDE (PATA) interface.

Hard disk
A hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the...
. The CF device contains an ATA controller. CF devices operate at 3.3 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
s or 5 volts, and can be swapped from system to system. CompactFlash supports C-H-S
Cylinder-head-sector
Cylinder-head-sector, also known as CHS, was an early method for giving addresses to each physical block of data on a hard disk drive. In the case of floppy drives, for which the same exact diskette medium can be truly low-level formatted to different capacities, this is still true.Though CHS...
and 28-bit Logical block addressing
Logical block addressing
Logical block addressing is a common scheme used for specifying the location of blocks of data stored on computer storage devices, generally secondary storage systems such as hard disks....
(CF 5.0 introduced support for LBA-48). CF cards may be set to master or slave, but have issues sharing the IDE bus. CF cards with flash memory are able to cope with extremely rapid changes in temperature. Industrial versions of flash memory cards can operate at a range of −45 to +85 °C.
NOR-based flash has lower density than newer NAND-based systems, and CompactFlash is therefore the physically largest of the three memory card formats introduced in the early 1990s, being derived from the JEIDA/PCMCIA Memory Card formats. The other two are Miniature Card
Miniature Card
Miniature Card or MiniCard is a flash or SRAM memory card standard first promoted by Intel Corp. in 1995 and backed by Advanced Micro Devices, Fujitsu and Sharp Electronics. Miniature Card Implementers Forum promoted this standard for consumer electronics: PDA/Palmtops, Digital Audio Recorders,...
(MiniCard) and SmartMedia
SmartMedia
SmartMedia is a flash memory card standard owned by Toshiba, with capacities ranging from 2 MB to 128 MB. SmartMedia memory cards are no longer manufactured.- History :...
(SSFDC). However, CF did switch to NAND type memory later. The IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
Microdrive
Microdrive
Microdrive is a brand name for a miniature, 1-inch hard disk designed to fit in a CompactFlash Type II slot. The release of similar drives by other makers has led to them often being referred to as 'microdrives'...
format implements the CF Type II interface, but is not solid-state memory. Hitachi
Hitachi
Hitachi is a multinational corporation specializing in high-technology.Hitachi may also refer to:*Hitachi, Ibaraki, Japan*Hitachi province, former province of Japan*Prince Hitachi and Princess Hitachi, members of the Japanese imperial family...
and Seagate
Seagate Technology
Seagate Technology is one of the world's largest manufacturers of hard disk drives. Incorporated in 1978 as Shugart Technology, Seagate is currently incorporated in Dublin, Ireland and has its principal executive offices in Scotts Valley, California, United States.-1970s:On November 1, 1979...
also make microdrives.
Speed
CompactFlash IDE (ATA) emulation speed is usually specified in "x" ratings, e.g. 8x, 20x, 133x. This is the same system used for CD-ROMCD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
s and indicates the maximum transfer rate in the form of a multiplier based on the original audio CD data transfer rate, which is 150 kbyte/s.
-
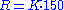 , kbyte/s
, kbyte/s
where R = transfer rate, K = speed rating. For example, 133x rating means transfer speed of: 133 * 150 kbyte/s = 19,950 kbyte/s ~ 20 Mbyte/s.
These are manufacturer speed ratings. Actual transfer speed may be higher, or lower, than shown on the card depending on several factors.
Solid state
For reads, the onboard controller first powers up the memory chips from standby. Reads are usually in parallel, error correction is done on the data, then transferred through the interface 16 bits at a time. Error checking is required due to soft read errors. Writes require powerup from standby, wear leveling calculation, a block erase of the area to be written to, ECC calculation, write itself (an individual memory cell read takes around 100 ns, a write to the chip takes 1ms+ or 10,000 times longer).Because the USB 2.0 interface is limited to 60 Mbyte/s and lacks bus mastering hardware, USB implementation results in slower access.
A direct motherboard connection is often limited to 33 Mbyte/s because IDE to CF adapters lack high speed ATA (66 Mbyte/s plus) cable support. Power on from sleep/off takes longer than power up from standby.
Magnetic media
Many 1 inches (25.4 mm) hard drives (often referred to by the trademarked name "MicrodriveMicrodrive
Microdrive is a brand name for a miniature, 1-inch hard disk designed to fit in a CompactFlash Type II slot. The release of similar drives by other makers has led to them often being referred to as 'microdrives'...
") typically spin at 3600 rpm so rotational latency is a consideration, as is spin-up from standby or idle. Seagate's 8 GB ST68022CF drive spins up fully within a few revolutions but power draw can reach up to 350 milliamps and runs at 40-50 mA average power. Its average seek time is 8 ms
Millisecond
A millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond....
and can sustain 9 Mbyte/s read and write, and has an interface speed of 33 Mbyte/s. Hitachi's 4 GB Microdrive is 12 ms seek, sustained 6 Mbyte/s.
Capacities and compatibility
- Since flash memory is generally produced in capacities that are multiples of powers of 2, IEC standard binary prefixes are used throughout this article.
The CF Specification (support 28 bit LBA
Logical block addressing
Logical block addressing is a common scheme used for specifying the location of blocks of data stored on computer storage devices, generally secondary storage systems such as hard disks....
) can support capacities up to 137 GB (128 GiB). Prior to 2006, CF drives using on magnetic media offered the highest capacities. But with the advent of 16 GiB and higher solid-state CF cards, they have offered the higher capacities.
Though, as of 2011, solid-state drives (SSDs) had supplanted both kinds of CF drives for large capacity requirements. Consequently, commercially available solid-state CF cards rarely go above 64 GiB, and 1-inch hard drives generally top out at 8 GiB.
Solid state capacities
SanDiskSanDisk
SanDisk Corporation is an American multinational corporation that designs, develops and manufactures data storage solutions in a range of form factors using the flash memory, controller and firmware technologies. It was founded in 1988 by Dr. Eli Harari and Sanjay Mehrotra, non-volatile memory...
announced its 16 GiB Extreme III card at the Photokina
Photokina
The photokina is the world's largest trade fair for the photographic and imaging industries. The first photokina was held in Cologne, Germany, in 1950, and it is now held biannually in September at the koelnmesse Trade Fair and Exhibition Centre...
trade fair, in September, 2006. That same month, Samsung
Samsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
announced 16, 32 and 64 GiB CF cards. Two years later, in September, 2008, PRETEC announced 100GB cards.
Magnetic media capacities
Seagate announced a 5 GiB "1-inch hard drive" in June, 2004, and an 8 GiB version in June, 2005.Use in place of a hard disk drive
In early 2008 the CFA demonstrated CompactFlash cards with a built in SATASata
Sata is a traditional dish from the Malaysian state of Terengganu, consisting of spiced fish meat wrapped in banana leaves and cooked on a grill.It is a type of Malaysian fish cake, or otak-otak...
interface. Several companies make adapters to allow CF cards to be connected to PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
, IDE
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA , originally ATA, is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disks, solid-state drives, floppy drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by X3/INCITS committee...
, 44-pin laptop mini-IDE, and SATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
connections, allowing a CF card to act as a solid-state drive
Solid-state drive
A solid-state drive , sometimes called a solid-state disk or electronic disk, is a data storage device that uses solid-state memory to store persistent data with the intention of providing access in the same manner of a traditional block i/o hard disk drive...
with virtually any operating system or BIOS, and even in a RAID
RAID
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit...
configuration.
Reliability
Original PC Card memory cards used an internal battery to maintain data when power was removed; the rated life of the battery was the only reliability issue. CompactFlash cards that use flash memory, like other flash-memory devices, are rated for a limited number of erase/write cycles for any "block." (Read cycles do not cause wear to the device.) Cards using NOR flash had a write endurance of 10,000 cycles. Current cards using NAND flash are rated for 1,000,000 writes per block before hard failure. This is less reliable than magnetic media. Car PC Hacks suggests disabling the Windows swap file and using its Enhanced Write FilterEnhanced Write Filter
Enhanced Write Filter is a component of Windows XP Embedded which filters writes to another medium instead of being physically written to the volume itself. EWF allows the writes to be discarded or committed to the physical volume later...
(EWF) to eliminate unnecessary writes to flash memory. Additionally, when formatting a flash-memory drive, the Quick Format method should be used, as one need not write every block on the drive, as may be necessary for a new magnetic disk.
Most CompactFlash flash-memory devices limit wear on blocks by varying the physical location to which a block is written. This process is called wear leveling
Wear leveling
Wear leveling is a technique for prolonging the service life of some kinds of erasable computer storage media, such as Flash memory used in solid-state drives and USB Flash drives...
. When using CompactFlash in ATA mode to take the place of the hard disk drive, wear leveling becomes critical because low-numbered blocks contain tables whose contents change frequently. Current CompactFlash cards spread the wear-leveling across the entire drive. The more advanced CompactFlash cards will move data that rarely changes to ensure all blocks wear evenly.
NAND flash memory is prone to frequent soft read errors. The CompactFlash card includes error checking and correcting
Error detection and correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunication, error detection and correction or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels...
(ECC) that detects the error and re-reads the block. The process is transparent to the user, although it may slow data access.
As flash memory devices are solid-state
Solid-state drive
A solid-state drive , sometimes called a solid-state disk or electronic disk, is a data storage device that uses solid-state memory to store persistent data with the intention of providing access in the same manner of a traditional block i/o hard disk drive...
, they are more shock-proof than rotating disks. For example, the ST68022CF Microdrive is shock rated at 175G operating and 750G non-operating.
The possibility for electrical damage from upside-down insertion is prevented by asymmetrical side slots, assuming that the host device uses a suitable connector.
Small cards consume around 5% of the power required by small disk drives and still have reasonable transfer rates of over 45 Mbyte/s for the more expensive 'high-speed' cards. However, the manufacturer's warning on the flash memory used for ReadyBoost
ReadyBoost
ReadyBoost is a disk cache component of Microsoft Windows, first introduced with Microsoft's Windows Vista in 2006 and bundled with Windows 7 in 2009...
indicates a current draw in excess of 500 mA.
File systems
Originally, flash memory used Flash File SystemFlash file system
A flash file system is a file system designed for storing files on flash memory devices. These are becoming more prevalent as the number of mobile devices is increasing, the cost per memory size decreases, and the capacity of flash memories increases....
and JFFS
JFFS
The Journaling Flash File System is a log-structured file system for use on NOR flash memory devices on the Linux operating system. It has been superseded by JFFS2.- Design :...
to work around low-level technical issues. Hardware now hides much of the complexity from the end user, and CompactFlash cards for use in consumer devices are typically formatted as FAT12 (for media up to 16 MiB), FAT16 (for media up to 2 GiB, sometimes up to 4 GiB) and FAT32 (for media larger than 2 GiB). This lets the devices be read by personal computers but also suits the limited processing ability of some consumer devices such as camera
Camera
A camera is a device that records and stores images. These images may be still photographs or moving images such as videos or movies. The term camera comes from the camera obscura , an early mechanism for projecting images...
s.
There are varying levels of compatibility among FAT32-compatible cameras, MP3 players, PDAs, and other devices. While any device that claims FAT32-capability should read and write to a FAT32-formatted card without problems, some devices are tripped up by cards larger than 2 GB that are completely unformatted, while others may take longer to apply a FAT32 format.
The way many digital cameras update the file system as they write to the card creates a FAT32 bottleneck. Writing to a FAT32-formatted card generally takes a little longer than writing to a FAT16-formatted card with similar performance capabilities. For instance, the Canon EOS 10D
Canon EOS 10D
The Canon EOS 10D is a discontinued 6.3-megapixel semi-professional digital SLR camera, initially announced on February 27, 2003. It replaced the EOS D60, which is also a 6.3-megapixel digital SLR camera. It was succeeded by the EOS 20D in August 2004....
writes the same photo to a FAT16-formatted 2 GB CompactFlash card somewhat faster than to a same speed 4 GB FAT32-formatted CompactFlash card, although the memory chips in both cards have the same write speed specification. Although FAT16 is more wasteful of disk space with its larger clusters, it works better with the write strategy that flash memory chips require.
The cards themselves can of course be formatted with any type of file system such as Ext
Extended file system
The extended file system or ext was implemented in April 1992 as the first file system created specifically for the Linux operating system. It has metadata structure inspired by the traditional Unix File System and was designed by Rémy Card to overcome certain limitations of the Minix file...
, JFS and NTFS
NTFS
NTFS is the standard file system of Windows NT, including its later versions Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, and Windows 7....
. It can be divided into partitions as long as the host device can read them. CompactFlash cards are often used instead of hard drives in embedded systems, dumb terminals and various small form-factor PCs that are built for low noise output or power consumption. CompactFlash cards are often more readily available and smaller than purpose-built solid-state drive
Solid-state drive
A solid-state drive , sometimes called a solid-state disk or electronic disk, is a data storage device that uses solid-state memory to store persistent data with the intention of providing access in the same manner of a traditional block i/o hard disk drive...
s and often have faster seek times than hard drives.
CF+ and Compact Flash specification revisions
When CompactFlash was first being standardized, even full-sized hard disks were rarely larger than 4 GB in size, and so the limitations of the ATA standard were considered acceptable. However, CF cards manufactured after the original Revision 1.0 specification are available in capacities up to 128 GiB. While the current revision 6.0 works in [P]ATA mode, future revisions are expected to implement SATASata
Sata is a traditional dish from the Malaysian state of Terengganu, consisting of spiced fish meat wrapped in banana leaves and cooked on a grill.It is a type of Malaysian fish cake, or otak-otak...
mode.
- CompactFlash Revision 1.0 (1995), 8.3 Mbyte/s (PIO mode 2), support for up to 128 GiB (137 GB) storage space.
- CompactFlash+ aka CompactFlash I/O (1997)
- CF+ and CompactFlash Revision 2.0 (2003) added an increase in speed to 16.6 Mbyte/s data-transfer (PIO mode 4). At the end of 2003, DMADirect memory accessDirect memory access is a feature of modern computers that allows certain hardware subsystems within the computer to access system memory independently of the central processing unit ....
33 transfers were added as well, available since mid 2004.
- CF+ and CompactFlash Revision 3.0 (2004) added support for up to a 66 Mbyte/s data transfer rate (UDMAUDMAFor the main article about the controller, see Parallel ATAThe Ultra DMA interface was the fastest method used to transfer data between the computer and an ATA device until Serial ATA....
66), 25 Mbyte/s in PC Card mode, added password protection, along with a number of other features. CFA recommends usage of the FAT32 filesystem for storage cards larger than 2 GiB.
- CF+ and CompactFlash Revision 4.0 (2006) added support for IDE Ultra DMA Mode 6 for a maximum data transfer rate of 133 Mbyte/s (UDMA 133).
- CF+ and CompactFlash Revision 4.1 (2007) added support for Power Enhanced CF Storage Cards.
- CompactFlash Revision 5.0 (2010) added a number of features, including 48-bit addressing (supporting 128 Petabyte of storage), larger block transfers of up to 32 Megabytes, quality-of-service and video performance guarantees, and other enhancements
- CompactFlash Revision 6.0 (November 2010) added UltraDMA Mode 7 (167 Mbyte/s), ATA-8/ACS-2 sanitize command, TRIMTrimTrim may refer to:* Cutting small pieces off something** Book trimming, a stage of the publishing process** Editing*** Editing a posting style in online discourse** Pruning, trimming as a form of pruning often used on trees-Places:...
and an optional card capability to report the operating temperature range of the card.
CE-ATA
CE-ATA is a Serial ATA interface based on the MultiMediaCardMultiMediaCard
The MultiMediaCard is a flash memory memory card standard. Unveiled in 1997 by Siemens AG and SanDisk, it is based on Toshiba's NAND-based flash memory, and is therefore much smaller than earlier systems based on Intel NOR-based memory such as CompactFlash. MMC is about the size of a postage...
standard.
CFast
A variant of CompactFlash known as CFast is based on the Serial ATASerial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
bus, rather than the Parallel ATA/IDE bus for which all previous versions of CompactFlash are designed.
CFast supports a higher maximum transfer rate than current CompactFlash cards. , SATA supports transfer rates up to 600 Mbyte/s while PATA is limited to 133 Mbyte/s using UDMA 6.
CFast cards are not physically or electrically compatible with CompactFlash cards. However, since SATA can emulate the PATA command protocol, existing CompactFlash software drivers can be used, although writing new drivers to use AHCI
Advanced Host Controller Interface
The Advanced Host Controller Interface is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the operation of Serial ATA host bus adapters in a non-implementation-specific manner....
instead of PATA emulation will almost always result in significant performance gains. CFast cards use a 7-pin SATA data connector (identical to the standard SATA connector), but a 17-pin power connector that appears incompatible with the standard 15-pin SATA power connector, so an adaptor is required to connect CFast cards in place of standard SATA hard drives.
The first CFast cards reached the market in late 2009. At CES
Consumer Electronics Show
The International Consumer Electronics Show is a major technology-related trade show held each January in the Las Vegas Convention Center, Las Vegas, Nevada, United States. Not open to the public, the Consumer Electronics Association-sponsored show typically hosts previews of products and new...
2009, Pretec showed a 32 GB CFast and announced that they should reach the market within a few months.
Delock began distributing CFast cards in 2010 and offers several card readers with USB3.0 port and eSATAp (power over eSATA) port to support CFast cards.
Type I and Type II
The only physical difference between the two types is that Type I devices are 3.3 mm thick while Type II devices are 5 mm thick. Electrically, the two interfaces are the same except that Type I devices are permitted to draw up to 70 mA supply current from the interface, while type II devices may draw up to 500 mA.The vast majority of all Type II devices are Microdrives and other miniature hard drives. Flash based Type II devices are rare but a few examples do exist. Compact Flash — Secure Digital adapters usually are Type II.
Even the largest capacity cards commonly available are Type I cards. Most card readers will read both formats, with the exception of some early CF based cameras or poorer quality USB card readers where the slot is too small. Various manufacturers of 4 GB Compact Flash cards such as Sandisk, Toshiba, Alcotek and Hynix have developed devices that support mainly type I slots. Some of the latest DSLRs, like the Nikon D700
Nikon D700
The Nikon D700 is a professional grade full-frame digital single-lens reflex camera introduced by the Nikon Corporation in July 2008 and manufactured in Japan. It uses the same 12.1 megapixel "FX" CMOS image sensor as the Nikon D3, and is Nikon's second full-frame digital SLR camera...
, have also dropped Type II support.
Microdrives
Microdrives are tiny hard diskHard disk
A hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the...
s—about 25 mm (1 inch) wide—packaged with a CompactFlash Type II form factor and interface. They were developed and released in 1999 by IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
with a capacity of 170 Mbyte. IBM sold its disk drive division, including the Microdrive trademark, to Hitachi
Hitachi, Ltd.
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate headquartered in Marunouchi 1-chome, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. The company is the parent of the Hitachi Group as part of the larger DKB Group companies...
in December 2002. There are now other brands of Microdrives (such as Seagate, Sony, etc.), and, over the years, these have become available in increasing capacities (up to 8 GB as of late 2008).
While these drives fit into and work in any CF II slot, the early versions drew more current (500 mA maximum) than flash memory (100 mA maximum). However current Microdrives use less than 200 mA for reads and writes (300 mA peak), and some flash devices used for high speed data e.g. Readyboost (memory can't power down to standby) draw more than the USB standard allows (500 mA). As they are mechanical devices, Microdrives are susceptible to damage from physical shock or temperature changes. However, Microdrives are not subject to the write cycle limitation inherent to flash memory.
The iPod mini
IPod mini
The iPod Mini is a digital audio player designed and marketed by Apple Inc. It was the midrange model in Apple's iPod product line. It was announced on January 6, 2004 and released on February 20 of the same year. A second-generation version was announced on February 23, 2005 and released later...
, Nokia N91
Nokia N91
The Nokia N91 is a mobile phone that was released to the public in April of 2006. It is part of the Nokia Nseries range of mobile phones. At the time of release, it was the most advanced music phone ever launched by nokia. N91 also won the 'Most Innovative Product' award in recognition of its true...
, iriver H10 (5 or 6 GB model), PalmOne LifeDrive
LifeDrive
The LifeDrive was a Palm OS-based handheld personal digital assistant device that was produced by PalmOne, a former incarnation of Palm, Inc. The device was PalmOne's first and only foray into the "Mobile Manager" device category...
, and Rio Carbon
Rio Carbon
The Rio Carbon is a line of digital audio players that was produced by the now defunct Rio from 2004 to 2005. It was similar in size, capacity, and cost with Apple's iPod Mini which debuted earlier the same year...
all used a CF Microdrive to store data.
Compared to other portable storage
- CompactFlash cards that use flash memory are more rugged than some competing solutions because they are solid-state. (See also Reliability above.) Separately, CompactFlash cards are thicker than other card formats, which may render them less susceptible to breakage from harsh treatment.
- As CompactFlash cards support the IDE/ATA command protocol with the host device, they are the removable memory medium most often used as the hard disk drive of a personal computerPersonal computerA personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
. (See above.)
- CompactFlash does not have any built in DRMDigital rights managementDigital rights management is a class of access control technologies that are used by hardware manufacturers, publishers, copyright holders and individuals with the intent to limit the use of digital content and devices after sale. DRM is any technology that inhibits uses of digital content that...
or cryptographic features found on some USB flash driveUSB flash driveA flash drive is a data storage device that consists of flash memory with an integrated Universal Serial Bus interface. flash drives are typically removable and rewritable, and physically much smaller than a floppy disk. Most weigh less than 30 g...
s and other card formats. The lack of such features contributes to the openness of the standard, since card standards with such features are subject to restrictive licensing agreements.
- The initial CompactFlash specification envisaged a higher maximum capacity than other card formats. For this reason, many early CompactFlash host devices are usable with modern multi-gigabyte memories, where users of other families such as SecureDigital have had to migrate to SDHC and SDXC.
- CompactFlash lacks the mechanical write protection switch that some other devices have, as seen in a comparison of memory cardsComparison of memory cardsThis table provides summary of comparison of various flash memory cards, .- Common information :-Physical details:Note that a memory card's dimensions are determined while holding the card with contact pins upwards. The length of cards is often greater than their width...
.
- CompactFlash is physically larger than other card formats. This limits its use, especially in miniature consumer devices where internal space is limited, such as point-and-shootPoint and shoot cameraA point-and-shoot camera, also called a compact camera, is a still camera designed primarily for simple operation. Most use focus free lenses or autofocus for focusing, automatic systems for setting the exposure options, and have flash units built in....
digital cameras. (An offsetting benefit of larger size is that the card is easier to insert and remove, and harder to misplace.)
Counterfeiting
The marketplace for CompactFlash is extensive and includes counterfeits. Off-brand or counterfeit cards may be mislabeled, might not contain the actual amount of memory their controllers report to the host device, and may use types of memory that are not rated for the number of erase/rewrite cycles that the purchaser expects.Other devices in the CF form factor
Since CompactFlash interface is electrically identical to the 16-bit PC cardPC card
In computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
, the CompactFlash form factor is also used for a variety of Input/Output and interface devices; many standard PC cards have CF counterparts, some examples include:
- EthernetEthernetEthernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
- BluetoothBluetoothBluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
- ModemModemA modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
and GSM Modem, including GPRSGeneral Packet Radio ServiceGeneral packet radio service is a packet oriented mobile data service on the 2G and 3G cellular communication system's global system for mobile communications . GPRS was originally standardized by European Telecommunications Standards Institute in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode...
and EDGEEnhanced Data Rates for GSM EvolutionEnhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution is a digital mobile phone technology that allows improved data transmission rates as a backward-compatible extension of GSM... - Wi-FiWi-FiWi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
- Digital CameraDigital cameraA digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
- GPSGPS navigation deviceA GPS navigation device is any device that receives Global Positioning System signals for the purpose of determining the device's current location on Earth...
- Barcode scanner
- RFID
- Magnetic stripe reader
- Super VGA display adapter
- Serial portSerial portIn computing, a serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time...
and USB 1.1 host adapters - readers for various other Flash media
CompactFlash card manufacturers
- A-DATA
- ATP
- Alcotek
- ApacerApacerApacer Technology Inc. is a Taiwanese multinational corporation that designs and markets consumer electronics, memory modules and digital storage hardware and software. Founded in 1997 as a DRAM module supplier, in 1999, Apacer Technology expanded its product range to include mobile storage...
- Cactus-tech
- Canon
- e c o SolidStateDrive Corporation
- FujiFilmFujifilmis a multinational photography and imaging company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan.Fujifilm's principal activities are the development, production, sale and servicing of color photographic film, digital cameras, photofinishing equipment, color paper, photofinishing chemicals, medical imaging...
- Hitachi Maxell
- Kingston TechnologyKingston TechnologyKingston Technology Company, Inc. is an American privately held, multinational computer technology corporation that develops, manufactures, sells and supports flash memory products and other computer-related memory products. Headquartered in Fountain Valley, California, USA, Kingston Technology...
- Kodak
- LexarLexarLexar Media, Inc. is an American manufacturer of digital media products based in Fremont, CA. Products manufactured by Lexar include SD cards, Memory Sticks, keydrives, CompactFlash cards and card readers. Lexar's Memory Stick Duos also have versions adapted for the PSP which includes a version of...
- MemorexMemorexMemorex began as a computer tape producer and expanded to become a major IBM plug compatible peripheral supplier. It is now a consumer electronics brand of Imation specializing in disk recordable media for CD and DVD drives, flash memory, computer accessories and other electronics.Established in...
- OlympusOlympus Corporationis a Japan-based manufacturer of optics and reprography products. Olympus was established on 12 October 1919, initially specializing in microscope and thermometer businesses. Its global headquarters are in Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan, while its USA operations are based in Center Valley, Pennsylvania,...
- PanasonicPanasonicPanasonic is an international brand name for Japanese electric products manufacturer Panasonic Corporation, which was formerly known as Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd...
- PNY
- PQI
- Ritek
- SanDiskSanDiskSanDisk Corporation is an American multinational corporation that designs, develops and manufactures data storage solutions in a range of form factors using the flash memory, controller and firmware technologies. It was founded in 1988 by Dr. Eli Harari and Sanjay Mehrotra, non-volatile memory...
- SamsungSamsungThe Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
- Silicon PowerSilicon PowerSilicon Power Computer & Communications Incorporated , commonly referred to as Silicon Power, is an international brand and a Taiwan based manufacturer of flash memory products including: flash memory cards, USB flash drives, portable hard drives, DRAM modules, card readers, solid state drives, USB...
- SonySony, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
- Swissbit
- ToshibaToshibais a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
- TranscendTranscendTranscend Information, Inc. is a Taiwanese company that manufactures and distributes of memory products headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan. Transcend's product portfolio consists of over 2,000 devices including memory modules, flash memory cards, USB flash drives, digital audio players, Portable...
- TwinMOS
- UMAXUmaxUMAX Technologies is a manufacturer of computer products, including scanners, mice, and flash drives, based in Taiwan. The company also uses the Yamada and Vaova brand names.-History:...
- Verbatim CorporationVerbatim CorporationVerbatim Americas, LLC is a US company that markets storage media and flash memory products. It is a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation of Japan and is based in Charlotte, North Carolina.-History:...
- Wintec Industries Inc.Wintec Industries Inc.Wintec Industries Inc. is a privately held maker of computer components founded in 1988 and headquartered in Milpitas, California.Wintec belongs to the standard-setting organization, JEDEC....
See also
- Comparison of memory cardsComparison of memory cardsThis table provides summary of comparison of various flash memory cards, .- Common information :-Physical details:Note that a memory card's dimensions are determined while holding the card with contact pins upwards. The length of cards is often greater than their width...
- MicrodriveMicrodriveMicrodrive is a brand name for a miniature, 1-inch hard disk designed to fit in a CompactFlash Type II slot. The release of similar drives by other makers has led to them often being referred to as 'microdrives'...
- PC CardPC CardIn computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
- ExpressCardExpressCardExpressCard is an interface to allow peripheral devices to be connected to a computer, usually a laptop computer. Formerly called NEWCARD, the ExpressCard standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of cards which can be inserted into ExpressCard slots. The cards contain...
- Random access memory

