
Compact tension specimen
Encyclopedia
A compact tension specimen is a notched sample and is a standard specimen in accordance with ASTM and ISO standards. The purpose of using a notched sample is to create a fatigue
crack by cycling the sample to maximum and minimum loads. The fatigue crack will begin on the point of the notch and extend through the sample, the fatigue crack is a good representation of 'real life' inconsistencies which are introduced to a material due to processing techniques or welding. CT specimens are used extensively in the area of fracture mechanics
and corrosion
testing, in order to establish fracture toughness
values for a material. According to the standards the constraining dimension of the CT specimen is the thickness of the material. CT specimens are used for experiments where there is a shortage of material available due to their compact design. For rolled materials the notch should be aligned with the roll direction where the material is weakest. This will allow the user to insure that all results achieved are conservative (worst case scenario)
at the crack tip of a compact tension specimen is
where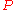 is the applied load,
is the applied load, 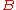 is the thickness of the specimen,
is the thickness of the specimen,  is the crack length, and
is the crack length, and
 is the width of the specimen. The above equation has been fitted using numerical computations for various specimen geometries.
is the width of the specimen. The above equation has been fitted using numerical computations for various specimen geometries.
Fatigue (material)
'In materials science, fatigue is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. The nominal maximum stress values are less than the ultimate tensile stress limit, and may be below the yield stress limit of the material.Fatigue occurs...
crack by cycling the sample to maximum and minimum loads. The fatigue crack will begin on the point of the notch and extend through the sample, the fatigue crack is a good representation of 'real life' inconsistencies which are introduced to a material due to processing techniques or welding. CT specimens are used extensively in the area of fracture mechanics
Fracture mechanics
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material's resistance to fracture.In...
and corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
testing, in order to establish fracture toughness
Fracture toughness
In materials science, fracture toughness is a property which describes the ability of a material containing a crack to resist fracture, and is one of the most important properties of any material for virtually all design applications. The fracture toughness of a material is determined from the...
values for a material. According to the standards the constraining dimension of the CT specimen is the thickness of the material. CT specimens are used for experiments where there is a shortage of material available due to their compact design. For rolled materials the notch should be aligned with the roll direction where the material is weakest. This will allow the user to insure that all results achieved are conservative (worst case scenario)
Stress intensity factor
The stress intensity factorStress Intensity Factor
The stress intensity factor, K, is used in fracture mechanics to predict the stress state near the tip of a crack caused by a remote load or residual stresses. It is a theoretical construct usually applied to a homogeneous, linear elastic material and is useful for providing a failure criterion...
at the crack tip of a compact tension specimen is

where
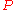 is the applied load,
is the applied load,  is the thickness of the specimen,
is the thickness of the specimen,  is the crack length, and
is the crack length, and is the width of the specimen. The above equation has been fitted using numerical computations for various specimen geometries.
is the width of the specimen. The above equation has been fitted using numerical computations for various specimen geometries.

