Comparison of mobile phone standards
Encyclopedia
Issues
Global System for Mobile CommunicationsGlobal System for Mobile Communications
GSM , is a standard set developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute to describe technologies for second generation digital cellular networks...
(GSM, around 80–85 % market share) and IS-95
IS-95
Interim Standard 95 is the first CDMA-based digital cellular standard by Qualcomm. The brand name for IS-95 is cdmaOne. IS-95 is also known as TIA-EIA-95....
(around 10–15 % market share) were the two most prevalent 2G mobile communication technologies in 2007. In 3G, the most prevalent technology was UMTS with CDMA-2000 in close contention.
All radio access technologies have to solve the same problems: to divide the finite RF spectrum among multiple users as efficiently as possible. GSM uses TDMA
Time division multiple access
Time division multiple access is a channel access method for shared medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This...
and FDMA for user and cell separation. UMTS, IS-95 and CDMA-2000 use CDMA. WIMAX
WiMAX
WiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
and LTE
3GPP Long Term Evolution
3GPP Long Term Evolution, usually referred to as LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals. It is based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA network technologies, increasing the capacity and speed using new modulation techniques...
use OFDM.
- Time-division multiple access (TDMA)Time division multiple accessTime division multiple access is a channel access method for shared medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This...
provides multiuser access by chopping up the channel into sequential time slices. Each user of the channel takes turns to transmit and receive signals. In reality, only one person is actually using the channel at a specific moment. This is analogous to time-sharingTime-sharingTime-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many users by means of multiprogramming and multi-tasking. Its introduction in the 1960s, and emergence as the prominent model of computing in the 1970s, represents a major technological shift in the history of computing.By allowing a large...
on a large computer server.
- Frequency-division multiple access (FDMA) provides multiuser access by separating the used frequencies. This is used in GSM to separate cells, which then use TDMA to separate users within the cell.
- Code-division multiple access (CDMA) This uses a digital modulation called spread spectrumSpread spectrumSpread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
which spreads the voice data over a very wide channel in pseudorandom fashion using a user or cell specific pseudorandom code. The receiver undoes the randomization to collect the bits together and produce the original data. As the codes are pseudorandom and selected in such a way as to cause minimal interference to one another, multiple users can talk at the same time and multiple cells can share the same frequency. This causes an added signal noise forcing all users to use more power, which in exchange decreases cell range and battery life.
- OFDM uses bundling of multiple small frequency bands that are orthogonal to one another to provide for separation of users. The users are multiplexed in the frequency domain by allocating specific sub-bands to individual users. This is often enhanced by also performing TDMA and changing the allocation periodically so that different users get different sub-bands at different times.
In theory, CDMA, TDMA and FDMA have exactly the same spectral efficiency but practically, each has its own challenges – power control in the case of CDMA, timing in the case of TDMA, and frequency generation/filtering in the case of FDMA.
For a classic example for understanding the fundamental difference of TDMA and CDMA imagine a cocktail party, where couples are talking to each other in a single room. The room represents the available bandwidth:
- TDMA: A speaker takes turns talking to a listener. The speaker talks for a short time and then stops to let another couple talk. There is never more than one speaker talking in the room, no one has to worry about two conversations mixing. The drawback is that it limits the practical number of discussions in the room (bandwidth wise).
- CDMA: any speaker can talk at any time; however each uses a different language. Each listener can only understand the language of their partner. As more and more couples talk, the background noise (representing the noise floor) gets louder, but because of the difference in languages, conversations do not mix. The drawback is that at some point, one cannot talk any louder. After this if the noise still rises (more people join the party/cell) the listener cannot make out what the talker is talking about without coming closer to the talker. In effect, CDMA cell coverage decreases as the number of active users increases. This is called cell breathing.
Comparison table
| Feature | NMT Nordic Mobile Telephone NMT is the first fully automatic cellular phone system... |
GSM | UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunications System Universal Mobile Telecommunications System is a third generation mobile cellular technology for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed by the 3GPP , UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunications Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for... (3GSM) |
IS-95 IS-95 Interim Standard 95 is the first CDMA-based digital cellular standard by Qualcomm. The brand name for IS-95 is cdmaOne. IS-95 is also known as TIA-EIA-95.... (CDMA one) |
IS-2000 (CDMA 2000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | FDMA | TDMA Time division multiple access Time division multiple access is a channel access method for shared medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This... and FDMA |
W-CDMA W-CDMA W-CDMA , UMTS-FDD, UTRA-FDD, or IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread is an air interface standard found in 3G mobile telecommunications networks. It is the basis of Japan's NTT DoCoMo's FOMA service and the most-commonly used member of the UMTS family and sometimes used as a synonym for UMTS... |
CDMA | CDMA |
| Generation | 1G 1G 1G refers to the first-generation of wireless telephone technology, mobile telecommunications. These are the analog telecommunications standards that were introduced in the 1980s and continued until being replaced by 2G digital telecommunications... |
2G 2G 2G is short for second-generation wireless telephone technology. Second generation 2G cellular telecom networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja in 1991... |
3G 3G 3G or 3rd generation mobile telecommunications is a generation of standards for mobile phones and mobile telecommunication services fulfilling the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 specifications by the International Telecommunication Union... |
2G 2G 2G is short for second-generation wireless telephone technology. Second generation 2G cellular telecom networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja in 1991... |
3G 3G 3G or 3rd generation mobile telecommunications is a generation of standards for mobile phones and mobile telecommunication services fulfilling the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 specifications by the International Telecommunication Union... |
| Encoding Code A code is a rule for converting a piece of information into another form or representation , not necessarily of the same type.... |
Analog Analog signal An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are... |
Digital Digital signal A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal... |
Digital Digital signal A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal... |
Digital Digital signal A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal... |
Digital Digital signal A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal... |
| Year of First Use | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 1995 | 2000 / 2002 |
| Global market share | 0% | 72% | 12% | 0.6% | 12% |
| Roaming Roaming In wireless telecommunications, roaming is a general term referring to the extension of connectivity service in a location that is different from the home location where the service was registered. Roaming ensures that the wireless device is kept connected to the network, without losing the... |
Nordics and several other European countries | Worldwide, all countries except Japan and South Korea | Worldwide | Limited | Limited |
| Handset interoperability | None | SIM card | SIM card | None | RUIM (rarely used) |
| Operator locking | Monopoly | Unlockable | Unlockable | ESN Electronic Serial Number Electronic serial numbers were created by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission to uniquely identify mobile devices, from the days of AMPS in the United States from the early 1980s. The administrative role was taken over by the Telecommunications Industry Association in 1997 and is still... |
ESN Electronic Serial Number Electronic serial numbers were created by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission to uniquely identify mobile devices, from the days of AMPS in the United States from the early 1980s. The administrative role was taken over by the Telecommunications Industry Association in 1997 and is still... |
| Common Interference | None | Some electronics, e.g. amplifiers | None | None | None |
| Signal quality/coverage area | Good coverage due to low frequencies | Good coverage indoors on 850/900 MHz. Repeaters possible. 35 km hard limit. | Smaller cells and lower indoors coverage on 2100 MHz; equivalent coverage indoors and superior range to GSM on 850/900 MHz. | Unlimited cell size, low transmitter power permits large cells | Unlimited cell size, low transmitter power permits large cells |
| Frequency utilization/Call density | Very low density | 0.2 MHz = 8 timeslots. Each timeslot can hold up to 2 calls (4 calls with VAMOS) through interleaving. | 5 MHz = 2 Mbit/s. 42Mbit/s for HSPA+. Each call uses 1.8-12 kbit/s depending on chosen quality and audio complexity. | Lower than CDMA-2000? | 1.228 MHz = 3Mbit/s |
| Battery life | Low, due to high transmitter power (1 watt) | Very good due to simple protocol, good coverage and mature, power-efficient chipsets. | Originally lower than GSM, but with new chipsets, DTX/DRX and Voice over HSPA all improve battery life close to that of GSM. | Lower due to high demands of CDMA power control. | Lower due to high demands of CDMA power control and young chipsets. |
| Handoff | Hard | Hard | Soft | Soft | Soft |
| Cell Breathing Cell breathing (telephony) In CDMA-based mobile telephone systems, the effect of radio interference from other mobile transmitters in the same cell or coverage area is very marked and has a special name, cell breathing.... |
No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Voice and Data at the same time | No | Yes GPRS General Packet Radio Service General packet radio service is a packet oriented mobile data service on the 2G and 3G cellular communication system's global system for mobile communications . GPRS was originally standardized by European Telecommunications Standards Institute in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode... Class A |
Yes | No | Yes SVDO |
| Intellectual property | Scandinavian telecom operators | Concentrated among a few manufacturers | Concentrated among a few manufacturers | Qualcomm Qualcomm Qualcomm is an American global telecommunication corporation that designs, manufactures and markets digital wireless telecommunications products and services based on its code division multiple access technology and other technologies. Headquartered in San Diego, CA, USA... |
Qualcomm Qualcomm Qualcomm is an American global telecommunication corporation that designs, manufactures and markets digital wireless telecommunications products and services based on its code division multiple access technology and other technologies. Headquartered in San Diego, CA, USA... |
Advantages of GSM
- GSM is mature; this maturity means a more stable network with robust features.
- Less signal deterioration inside buildings.
- Ability to use repeaters.
- TalktimeTalktimeTalktime is usually measured in hours for any rechargeable communications device .This is the maximum expected duration a fully charged battery is expected to last under perfect conditions .A safe rule of thumb is to use the following guide to expected talktimes as your phone battery ages Talktime...
is generally higher in GSM phones due to the pulse nature of transmission. - The availability of Subscriber Identity ModuleSubscriber Identity ModuleA subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module is an integrated circuit that securely stores the International Mobile Subscriber Identity and the related key used to identify and authenticate subscriber on mobile telephony devices .A SIM is held on a removable SIM card, which...
s allows users to switch networks and handsets at will, aside from a subsidy lockSIM lockA SIM lock, simlock, network lock or subsidy lock is a capability built into GSM phones by mobile phone manufacturers. Network providers use this capability to restrict the use of these phones to specific countries and network providers...
. - GSM covers virtually all parts of the world so international roamingRoamingIn wireless telecommunications, roaming is a general term referring to the extension of connectivity service in a location that is different from the home location where the service was registered. Roaming ensures that the wireless device is kept connected to the network, without losing the...
is not a problem. - The much bigger number of subscribers globally creates a better network effectNetwork effectIn economics and business, a network effect is the effect that one user of a good or service has on the value of that product to other people. When network effect is present, the value of a product or service is dependent on the number of others using it.The classic example is the telephone...
for GSM handset makers, carriers and end users.
Disadvantages of GSM
- Interferes with some electronics, especially certain audio amplifiers.
- Intellectual property is concentrated among a few industry participants, creating barriers to entry for new entrants and limiting competition among phone manufacturers. Situation is however worse in CDMA-based systems like IS-95, where Qualcomm is the major IP holder.
- GSM has a fixed maximum cell site range of 120 km, which is imposed by technical limitationsTiming advanceIn the GSM cellular mobile phone standard, timing advance value corresponds to the length of time a signal takes to reach the base station from a mobile phone. GSM uses TDMA technology in the radio interface to share a single frequency between several users, assigning sequential timeslots to the...
. This is expanded from the old limit of 35 km.
Advantages of IS-95
- Capacity is IS-95's biggest asset; it can accommodate more users per MHz of bandwidth than any other technology.
- Has no built-in limit to the number of concurrent users.
- Uses precise clocks that do not limit the distance a tower can cover.
- Consumes less power and covers large areas so cell size in IS-95 is larger.
- Able to produce a reasonable call with lower signal (cell phone reception) levels.
- Uses soft handoffSoft handoverSoft handover or soft handoff refers to a feature used by the CDMA and WCDMA standards, where a cell phone is simultaneously connected to two or more cells during a call. If the sectors are from the same physical cell site , it is referred to as softer handoff...
, reducing the likelihood of dropped calls. - IS-95's variable rate voice coders reduce the rate being transmitted when speaker is not talking, which allows the channel to be packed more efficiently.
- Has a well-defined path to higher data rates.
Disadvantages of IS-95
- Most technologies are patented and must be licensed from QualcommQualcommQualcomm is an American global telecommunication corporation that designs, manufactures and markets digital wireless telecommunications products and services based on its code division multiple access technology and other technologies. Headquartered in San Diego, CA, USA...
. - Breathing of base stations, where coverage area shrinks under load. As the number of subscribers using a particular site goes up, the range of that site goes down.
- Because IS-95 towers interfere with each other, they are normally installed on much shorter towers. Because of this, IS-95 may not perform well in hilly terrain.
- IS-95 covers a smaller portion of the world, and IS-95 phones are generally unable to roam internationally.
- Manufacturers are often hesitant to release IS-95 devices due to the smaller market, so features are sometimes late in coming to IS-95 devices.
- Even barring subsidy locksSIM lockA SIM lock, simlock, network lock or subsidy lock is a capability built into GSM phones by mobile phone manufacturers. Network providers use this capability to restrict the use of these phones to specific countries and network providers...
, CDMA phones are linked by ESNElectronic Serial NumberElectronic serial numbers were created by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission to uniquely identify mobile devices, from the days of AMPS in the United States from the early 1980s. The administrative role was taken over by the Telecommunications Industry Association in 1997 and is still...
to a specific network, thus phones are typically not portable across providers.
Development of the Market Share of Mobile Standards
This graphic compares the market shares of the different mobile standards.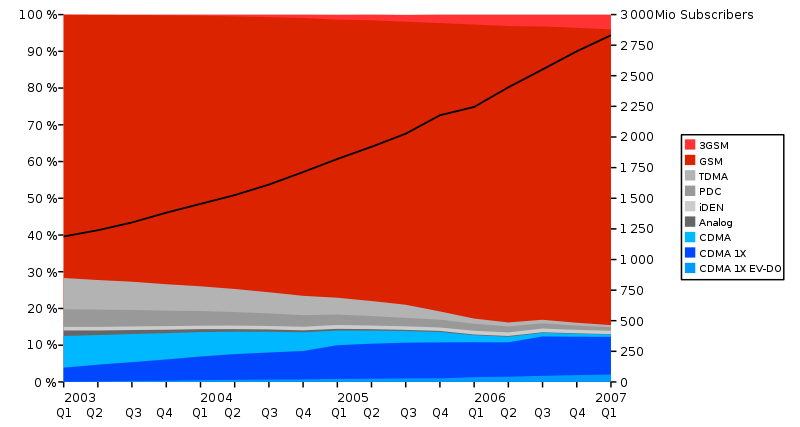
Comparison of wireless Internet standards
As a reference, a comparison of mobile and non-mobile wireless Internet standards follows.See also
- Comparison of wireless data standardsComparison of wireless data standards- Introduction :A wide variety of different wireless data technologies exist, some in direct competition with one another, others designed for specific applications...
- Spectral efficiency comparison table
- SMSSMSSMS is a form of text messaging communication on phones and mobile phones. The terms SMS or sms may also refer to:- Computer hardware :...
- contain the content of its standardization

