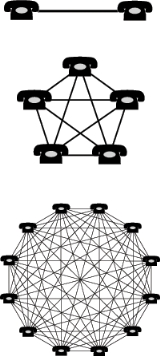
Network effect
Encyclopedia
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and business
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
, a network effect (also called network externality or demand-side economies of scale) is the effect that one user of a good or service has on the value
Value (economics)
An economic value is the worth of a good or service as determined by the market.The economic value of a good or service has puzzled economists since the beginning of the discipline. First, economists tried to estimate the value of a good to an individual alone, and extend that definition to goods...
of that product to other people. When network effect is present, the value of a product or service is dependent on the number of others using it.
The classic example is the telephone
Telephone
The telephone , colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that transmits and receives sounds, usually the human voice. Telephones are a point-to-point communication system whose most basic function is to allow two people separated by large distances to talk to each other...
. The more people own telephones, the more valuable the telephone is to each owner. This creates a positive externality
Externality
In economics, an externality is a cost or benefit, not transmitted through prices, incurred by a party who did not agree to the action causing the cost or benefit...
because a user may purchase a telephone without intending to create value for other users, but does so in any case. Online social network
Social network service
A social networking service is an online service, platform, or site that focuses on building and reflecting of social networks or social relations among people, who, for example, share interests and/or activities. A social network service consists of a representation of each user , his/her social...
s work in the same way, with sites like Twitter
Twitter
Twitter is an online social networking and microblogging service that enables its users to send and read text-based posts of up to 140 characters, informally known as "tweets".Twitter was created in March 2006 by Jack Dorsey and launched that July...
and Facebook
Facebook
Facebook is a social networking service and website launched in February 2004, operated and privately owned by Facebook, Inc. , Facebook has more than 800 million active users. Users must register before using the site, after which they may create a personal profile, add other users as...
being more useful the more users join.
The expression "network effect" is applied most commonly to positive network externalities as in the case of the telephone. Negative network externalities can also occur, where more users make a product less valuable, but are more commonly referred to as "congestion" (as in traffic congestion
Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition on road networks that occurs as use increases, and is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. The most common example is the physical use of roads by vehicles. When traffic demand is great enough that the interaction...
or network congestion
Network congestion
In data networking and queueing theory, network congestion occurs when a link or node is carrying so much data that its quality of service deteriorates. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections...
).
Over time, positive network effects can create a bandwagon effect
Bandwagon effect
The bandwagon effect is a well documented form of groupthink in behavioral science and has many applications. The general rule is that conduct or beliefs spread among people, as fads and trends clearly do, with "the probability of any individual adopting it increasing with the proportion who have...
as the network becomes more valuable and more people join, in a positive feedback
Positive feedback
Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small disturbance on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system that responds to a perturbation in a way that reduces its effect is...
loop.
Origins
Network effects were a central theme in the arguments of Theodore Vail, the first post patent president of Bell TelephoneBell Telephone
Bell Telephone may refer to:* Bell Telephone Company, several telephone companies with similar names* Bell Telephone Building , various* The Bell Telephone Hour, a long-running radio and television concert program...
, in gaining a monopoly on US telephone services. In 1908, when he presented the concept in Bell's annual report, there were over 4000 local and regional telephone exchanges, most of which were eventually merged into the Bell System. The economics of network effects were presented in a paper by Bell employee N. Lytkins in 1917.
The economic theory of the network effect was advanced significantly between 1985 and 1995 by researchers Michael L. Katz, Carl Shapiro, Joseph Farrell and Garth Saloner.
Network effects were popularized by Robert Metcalfe
Robert Metcalfe
Robert Melancton Metcalfe is an electrical engineer from the United States who co-invented Ethernet, founded 3Com and formulated Metcalfe's Law., he is a general partner of Polaris Venture Partners...
, stated as the Metcalfe's law
Metcalfe's law
Metcalfe's law states that the value of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected usersof the system...
. Metcalfe was one of the co-inventors of Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
and a co-founder of the company 3Com
3Com
3Com was a pioneering digital electronics manufacturer best known for its computer network infrastructure products. The company was co-founded in 1979 by Robert Metcalfe, Howard Charney, Bruce Borden, and Greg Shaw...
. In selling the product, Metcalfe argued that customers needed Ethernet cards to grow above a certain critical mass
Critical mass (sociodynamics)
Critical mass is a sociodynamic term to describe the existence of sufficient momentum in a social system such that the momentum becomes self-sustaining and creates further growth....
if they were to reap the benefits of their network.
According to Metcalfe, the rationale behind the sale of networking cards was that (1) the cost of cards was directly proportional to the number of cards installed, but (2) the value of the network was proportional to the square of the number of users. This was expressed algebraically as having a cost of N, and a value of N². While the actual numbers behind this definition were never firm, the concept allowed customers to share access to expensive resources like disk drives and printers, send e-mail, and access the Internet.
Rod Beckstrom
Rod Beckstrom
Rod Beckstrom is an author, high-tech entrepreneur, and CEO and President of ICANN.He previously served as Director of the National Cyber Security Center. Prior to that Beckstrom was Chairman and Chief Catalyst of TWIKI.NET, a company which supports TWiki, an open source wiki...
presented a mathematical model for describing networks that are in a state of positive network effect at BlackHat and Defcon in 2009 and also presented the "inverse network effect" with an economic model for defining it as well.
Benefits
Network effects become significant after a certain subscription percentage has been achieved, called critical mass. At the critical mass point, the value obtained from the good or service is greater than or equal to the price paid for the good or service. As the value of the good is determined by the user base, this implies that after a certain number of people have subscribed to the service or purchased the good, additional people will subscribe to the service or purchase the good due to the value exceeding the price.A key business concern must then be how to attract users prior to reaching critical mass. One way is to rely on extrinsic motivation, such as a payment, a fee waiver, or a request for friends to sign up. A more natural strategy is to build a system that has enough value without network effects, at least to early adopters. Then, as the number of users increases, the system becomes even more valuable and is able to attract a wider user base.
Beyond critical mass, the increasing number of subscribers generally cannot continue indefinitely. After a certain point, most networks become either congested or saturated, stopping future uptake. Congestion occurs due to overuse. The applicable analogy is that of a telephone network. While the number of users is below the congestion point, each additional user adds additional value to every other customer. However, at some point the addition of an extra user exceeds the capacity of the existing system. After this point, each additional user decreases the value obtained by every other user. In practical terms, each additional user increases the total system load
Load (computing)
In UNIX computing, the system load is a measure of the amount of work that a computer system performs. The load average represents the average system load over a period of time...
, leading to busy signal
Busy signal
A busy signal in telephony is an audible or visual signal to the calling party that indicates failure to complete the requested connection of that particular telephone call....
s, the inability to get a dial tone
Dial tone
A dial tone is a telephony signal used to indicate that the telephone exchange is working, has recognized an off-hook, and is ready to accept a call. The tone stops when the first numeral is dialed...
, and poor customer support
Customer support
Customer support is a range of customer services to assist customers in making cost effective and correct use of a product. It includes assistance in planning, installation, training, trouble shooting, maintenance, upgrading, and disposal of a product....
. The next critical point is where the value obtained again equals the price paid. The network will cease to grow at this point, and the system must be enlarged. The congestion point may be larger than the market size. New Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
technological models may always defy congestion. Peer-to-peer systems, or "P2P," are networks designed to distribute load among their user pool. This theoretically allows true P2P networks to scale indefinitely. The P2P based telephony service Skype
Skype
Skype is a software application that allows users to make voice and video calls and chat over the Internet. Calls to other users within the Skype service are free, while calls to both traditional landline telephones and mobile phones can be made for a fee using a debit-based user account system...
benefits greatly from this effect (though market saturation
Market saturation
In economics, "market saturation" is a term used to describe a situation in which a product has become diffused within a market; the actual level of saturation can depend on consumer purchasing power; as well as competition, prices, and technology....
will still occur).
Network effects are commonly mistaken for economies of scale
Economies of scale
Economies of scale, in microeconomics, refers to the cost advantages that an enterprise obtains due to expansion. There are factors that cause a producer’s average cost per unit to fall as the scale of output is increased. "Economies of scale" is a long run concept and refers to reductions in unit...
, which result from business size rather than interoperability
Interoperability
Interoperability is a property referring to the ability of diverse systems and organizations to work together . The term is often used in a technical systems engineering sense, or alternatively in a broad sense, taking into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system to...
. To help clarify the distinction, people speak of demand side vs. supply side economies of scale. Classical economies of scale are on the production side, while network effects arise on the demand side. Network effects are also mistaken for economies of scope
Economies of scope
Economies of scope are conceptually similar to economies of scale. Whereas 'economies of scale' for a firm primarily refers to reductions in average cost associated with increasing the scale of production for a single product type, 'economies of scope' refers to lowering average cost for a firm in...
.
The network effect has a lot of similarities with the description of phenomenon in reinforcing positive feedback loops described in system dynamics
System dynamics
System dynamics is an approach to understanding the behaviour of complex systems over time. It deals with internal feedback loops and time delays that affect the behaviour of the entire system. What makes using system dynamics different from other approaches to studying complex systems is the use...
. System dynamics could be used as a modelling method to describe phenomena such as word of mouth
Word of mouth
Word of mouth, or viva voce, is the passing of information from person to person by oral communication. Storytelling is the oldest form of word-of-mouth communication where one person tells others of something, whether a real event or something made up. Oral tradition is cultural material and...
and Bass model of marketing.
Technology lifecycle
If some existing technology or company whose benefits are largely based on network effects starts to lose market share against a challenger such as a disruptive technologyDisruptive technology
A disruptive technology or disruptive innovation is an innovation that helps create a new market and value network, and eventually goes on to disrupt an existing market and value network , displacing an earlier technology there...
or open standards based competition, the benefits of network effects will reduce for the incumbent, and increase for the challenger. In this model, a tipping point
Tipping point
In sociology, a tipping point is the event of a previously rare phenomenon becoming rapidly and dramatically more common. The phrase was coined in its sociological use by Morton Grodzins, by analogy with the fact in physics that adding a small amount of weight to a balanced object can cause it to...
is eventually reached at which the network effects of the challenger dominate those of the former incumbent, and the incumbent is forced into an accelerating decline, whilst the challenger takes over the incumbent's former position.
Lock-in
Not surprisingly network economicsNetwork economics
Network economics refers to business economics that benefit from the network effect. This is when the value of a good or service increases when others buy the same good or service...
became a hot topic after the diffusion of the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
across academia
Academia
Academia is the community of students and scholars engaged in higher education and research.-Etymology:The word comes from the akademeia in ancient Greece. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning...
. Most people know only of Metcalfe's law
Metcalfe's law
Metcalfe's law states that the value of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected usersof the system...
as part of network effects. Network effects are notorious for causing lock-in
Vendor lock-in
In economics, vendor lock-in, also known as proprietary lock-in or customer lock-in, makes a customer dependent on a vendor for products and services, unable to use another vendor without substantial switching costs...
with the most-cited examples being Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
products and the QWERTY
QWERTY
QWERTY is the most common modern-day keyboard layout. The name comes from the first six letters appearing in the topleft letter row of the keyboard, read left to right: Q-W-E-R-T-Y. The QWERTY design is based on a layout created for the Sholes and Glidden typewriter and sold to Remington in the...
keyboard.
Network effects are a source of, but distinct from, lock-in. Lock-in can result from network effects, and network effects generate increasing returns that are associated with lock-in. However, the presence of a network effect does not guarantee that lock-in will result. For example, if the network standards are open, enabling competitive implementation by different vendors, there is no vendor lock-in. One example of this would be email, which has a considerable network effect but there is interoperability between different email providers.
Lock-in can also result because users perceive that their switching costs do not cover the value of switching to the new service. For example, relationships developed in one service do not transfer to the new service. In other words, you are not willing to use a possibly better service because you have vested data in the service you are locked into.
Types of network effects
There are many ways to classify networks effects. One popular segmentation views network effects as being of four kinds- Two-sided network effects: An increase in usage by one set of users increases the value to and participation of a complementary and distinct set of users, and vice versa. An example is developers choosing to code for an operating system with many users, with users choosing to adopt an operating system with many developers. This is a special case of a two-sided market.
- Direct network effects: An increase in usage leads to a direct increase in value for other users. For example, telephone systems, fax machines, and social networks all imply direct contact among users. In two-sided networks, a direct network effect is called a same-side network effect. An example is online gamers who benefit from participation of other gamers as distinct from how they benefit from game developers.
- Indirect network effects: Increases in usage of one product or network spawn increases in the value of a complementary product or network, which can in turn increase the value of the original. Examples of complementary goods include software (such as an Office suite for operating systems) and DVDs (for DVD players). This is why Windows and Linux might compete not just for users, but for software developerSoftware developerA software developer is a person concerned with facets of the software development process. Their work includes researching, designing, developing, and testing software. A software developer may take part in design, computer programming, or software project management...
s. This is more accurately called a cross-side network effect in order to distinguish network benefits that cross distinct markets.
- Local network effects: The structure of an underlying social network affects who benefits from whom. For example, a good displays local network effects when rather than being influenced by an increase in the size of a product's user base in general, each consumer is influenced directly by the decisions of only a typically small subset of other consumers, for instance those he or she is "connected" to via an underlying social or business network. Instant messaging is an example of a product that displays local network effects.
Additionally, there are two sources of economic value that are relevant when analyzing products that display network effects:
- Inherent value: I derive value from my use of the product
- Network value: I derive value from other people's use of the product
Negative network effects
There are negative network effects beyond lock-in.- Congestion occurs when the efficiency of a network decreases as more people use it, and this reduces the value to people already using it. Traffic congestionTraffic congestionTraffic congestion is a condition on road networks that occurs as use increases, and is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. The most common example is the physical use of roads by vehicles. When traffic demand is great enough that the interaction...
that overloads the freeway and network congestionNetwork congestionIn data networking and queueing theory, network congestion occurs when a link or node is carrying so much data that its quality of service deteriorates. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections...
over limited bandwidth both display negative network externalities.
Open versus closed standards
In communication and information technologies, open standards and interfaces are often developed through the participation of multiple companies and are usually perceived to provide mutual benefit. But, in cases in which the relevant communication protocols or interfaces are closed standards the network effect can give the company controlling those standards monopoly power. The MicrosoftMicrosoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
corporation is widely seen by computer professionals as maintaining its monopoly through these means. One observed method Microsoft uses to put the network effect to its advantage is called Embrace, extend and extinguish
Embrace, extend and extinguish
"Embrace, extend and extinguish," also known as "Embrace, extend and exterminate," is a phrase that the U.S. Department of Justice found was used internally by Microsoft to describe its strategy for entering product categories involving widely used standards, extending those standards with...
.
Mirabilis
Mirabilis (company)
Mirabilis is an Israeli company that developed the ICQ instant messaging program, a pioneer of online chatting that revolutionized communication over the Internet.-History:...
is an Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
i start-up which pioneered instant messaging
Instant messaging
Instant Messaging is a form of real-time direct text-based chatting communication in push mode between two or more people using personal computers or other devices, along with shared clients. The user's text is conveyed over a network, such as the Internet...
(IM) and was bought by America Online
AOL
AOL Inc. is an American global Internet services and media company. AOL is headquartered at 770 Broadway in New York. Founded in 1983 as Control Video Corporation, it has franchised its services to companies in several nations around the world or set up international versions of its services...
. By giving away their ICQ
ICQ
ICQ is an instant messaging computer program, which was first developed and popularized by the Israeli company Mirabilis, then bought by America Online, and since April 2010 owned by Mail.ru Group. The name ICQ is a homophone for the phrase "I seek you"...
product for free and preventing interoperability
Interoperability
Interoperability is a property referring to the ability of diverse systems and organizations to work together . The term is often used in a technical systems engineering sense, or alternatively in a broad sense, taking into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system to...
between their client software and other products, they were able to temporarily dominate the market for instant messaging. Because of the network effect, new IM users gained much more value by choosing to use the Mirabilis system (and join its large network of users) than they would using a competing system. As was typical for that era, the company never made any attempt to generate profits from their dominant position before selling the company.
Financial exchanges
Stock exchangeStock exchange
A stock exchange is an entity that provides services for stock brokers and traders to trade stocks, bonds, and other securities. Stock exchanges also provide facilities for issue and redemption of securities and other financial instruments, and capital events including the payment of income and...
s and derivatives exchanges feature a network effect. Market liquidity
Market liquidity
In business, economics or investment, market liquidity is an asset's ability to be sold without causing a significant movement in the price and with minimum loss of value...
is a major determinant of transaction cost in the sale or purchase of a security, as a bid-ask spread exists between the price at which a purchase can be done versus the price at which the sale of the same security can be done. As the number of buyers and sellers on an exchange increases, liquidity increases, and transaction costs decrease. This then attracts a larger number of buyers and sellers to the exchange. See, for example, the work of Steve Wunsch (1999).
The network advantage of financial exchanges is apparent in the difficulty that startup exchanges have in dislodging a dominant exchange. For example, the Chicago Board of Trade
Chicago Board of Trade
The Chicago Board of Trade , established in 1848, is the world's oldest futures and options exchange. More than 50 different options and futures contracts are traded by over 3,600 CBOT members through open outcry and eTrading. Volumes at the exchange in 2003 were a record breaking 454 million...
has retained overwhelming dominance of trading in US Treasury Bond futures despite the startup of Eurex
Eurex
Eurex is one of the world's leading derivatives exchanges, providing European benchmark derivatives featuring open and low-cost electronic access globally...
US trading of identical futures contracts. Similarly, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
Chicago Mercantile Exchange
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange is an American financial and commodity derivative exchange based in Chicago. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board. Originally, the exchange was a non-profit organization...
has maintained a dominance in trading of Eurobond interest rate futures despite a challenge from Euronext.Liffe.
Software
There are very strong network effects operating in the market for widely used computer software.Take, for example, Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office is a non-free commercial office suite of inter-related desktop applications, servers and services for the Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X operating systems, introduced by Microsoft in August 1, 1989. Initially a marketing term for a bundled set of applications, the first version of...
. For many people choosing an office suite
Office suite
In computing, an office suite, sometimes called an office software suite or productivity suite is a collection of programs intended to be used by knowledge workers...
, prime considerations include how valuable having learned that office suite will prove to potential employers, and how well the software interoperates with other users. That is, since learning to use an office suite takes many hours, they want to invest that time learning the office suite that will make them most attractive to potential employers (or consulting client
Consumer
Consumer is a broad label for any individuals or households that use goods generated within the economy. The concept of a consumer occurs in different contexts, so that the usage and significance of the term may vary.-Economics and marketing:...
s, etc.), and they also want to be able to share documents. (Additionally, an example of an indirect network effect in this case is the notable similarity in user-interfaces and operability menus of most new software - since that similarity directly translates into less time spent learning new environments, therefore potentially greater acceptance and adoption of those products.)
Similarly, finding already-trained employees is a big concern for employers when deciding which office suite to purchase or standardize on. The lack of cross-platform
Cross-platform
In computing, cross-platform, or multi-platform, is an attribute conferred to computer software or computing methods and concepts that are implemented and inter-operate on multiple computer platforms...
user-interface standards results in a situation in which one firm is in control of almost 100% of the market.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
is a further example of network effect. The most-vaunted advantage of Windows, and that most publicised by Microsoft, is that Windows is compatible with the widest range of hardware and software. Although this claim is justified, it is in reality the result of network effect: hardware and software manufacturers ensure that their products are compatible with Windows in order to have access to the large market of Windows users. Thus, Windows is popular because it is well supported, but is well supported because it is popular.
However, network effects need not lead to market dominance by one firm, when there are standards which allow multiple firms to interoperate, thus allowing the network externalities to benefit the entire market. This is true for the case of x86-based personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
hardware
Hardware
Hardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
, in which there are extremely strong market pressures to interoperate with pre-existing standards, but in which no one firm dominates in the market. Also, it is true for the development of enterprise software applications where the Internet (HTTP), databases (SQL), and to a moderate degree, service-oriented message buses (SOA) have become common interfaces. Further up the development chain there are network effects as well in language back-end base platforms (JVM, CLR, LLVM), programming models (FP, OOP) and languages themselves.
Telecommunications
The same holds true for the market for long-distance telephone service within the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. In fact, the existence of these types of networks discourages dominance of the market by one company, as it creates pressures which work against one company attempting to establish a proprietary protocol or to even distinguish itself by means of product differentiation.
Web sites
Many web sites also feature a network effect. One example is web marketplaces and exchanges, in that the value of the marketplace to a new user is proportional to the number of other users in the market. For example, eBayEBay
eBay Inc. is an American internet consumer-to-consumer corporation that manages eBay.com, an online auction and shopping website in which people and businesses buy and sell a broad variety of goods and services worldwide...
would not be a particularly useful site if auction
Auction
An auction is a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bid, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder...
s were not competitive. However, as the number of users grows on eBay, auctions grow more competitive, pushing up the prices of bids on items. This makes it more worthwhile to sell on eBay and brings more sellers onto eBay, which drives prices down again as this increases supply, while bringing more people onto eBay because there are more things being sold that people want. Essentially, as the number of users of eBay grows, prices fall and supply increases, and more and more people find the site to be useful.
The collaborative encyclopedia Wikipedia
Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a free, web-based, collaborative, multilingual encyclopedia project supported by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its 20 million articles have been written collaboratively by volunteers around the world. Almost all of its articles can be edited by anyone with access to the site,...
also benefits from a network effect. The theory goes that as the number of editors grows, the quality of information on the website improves, encouraging more users to turn to it as a source of information; some of the new users in turn become editors, continuing the process.
Social networking websites are also good examples. The more people register onto a social networking website, the more useful the website is to its registrants.
By contrast, the value of a news site is primarily proportional to the quality of the articles, not to the number of other people using the site. Similarly, the first generation of search sites experienced little network effect, as the value of the site was based on the value of the search results. This allowed Google
Google
Google Inc. is an American multinational public corporation invested in Internet search, cloud computing, and advertising technologies. Google hosts and develops a number of Internet-based services and products, and generates profit primarily from advertising through its AdWords program...
to win users away from Yahoo!
Yahoo!
Yahoo! Inc. is an American multinational internet corporation headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, United States. The company is perhaps best known for its web portal, search engine , Yahoo! Directory, Yahoo! Mail, Yahoo! News, Yahoo! Groups, Yahoo! Answers, advertising, online mapping ,...
without much trouble, once users believed that Google's search results were superior. Some commentators mistook the value of the Yahoo! brand (which does increase as more people know of it) for a network effect protecting its advertising business.
Alexa Internet
Alexa Internet
Alexa Internet, Inc. is a California-based subsidiary company of Amazon.com that is known for its toolbar and Web site. Once installed, the toolbar collects data on browsing behavior which is transmitted to the Web site where it is stored and analyzed and is the basis for the company's Web traffic...
uses a technology that tracks users' surfing patterns; thus Alexa's Related Sites results improve as more users use the technology. Alexa's network relies heavily on a small number of browser software relationships, which makes the network more vulnerable to competition.
Google has also attempted to create a network effect in its advertising business with its Google AdSense service. Google AdSense places ads on many small sites, such as blog
Blog
A blog is a type of website or part of a website supposed to be updated with new content from time to time. Blogs are usually maintained by an individual with regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material such as graphics or video. Entries are commonly displayed in...
s, using Google technology to determine which ads are relevant to which blogs. Thus, the service appears to aim to serve as an exchange (or ad network) for matching many advertisers with many small sites (such as blogs). In general, the more blogs Google AdSense can reach, the more advertisers it will attract, making it the most attractive option for more blogs, and so on, making the network more valuable for all participants.
Network effects were used as justification for some of the dot-com
Dot-com company
A dot-com company, or simply a dot-com , is a company that does most of its business on the Internet, usually through a website that uses the popular top-level domain, ".com" .While the term can refer to present-day companies, it is also used specifically to refer to companies with...
business model
Business model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
s in the late 1990s. These firms operated under the belief that when a new market
Market
A market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
comes into being which contains strong network effects, firms should care more about growing their market share
Market share
Market share is the percentage of a market accounted for by a specific entity. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 67 percent responded that they found the "dollar market share" metric very useful, while 61% found "unit market share" very useful.Marketers need to be able to...
than about becoming profitable
Profit (accounting)
In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
. This was believed because market share will determine which firm can set technical and marketing standards and thus determine the basis of future competition
Competition
Competition is a contest between individuals, groups, animals, etc. for territory, a niche, or a location of resources. It arises whenever two and only two strive for a goal which cannot be shared. Competition occurs naturally between living organisms which co-exist in the same environment. For...
.
Rail gauge
Rail gauge
Track gauge or rail gauge is the distance between the inner sides of the heads of the two load bearing rails that make up a single railway line. Sixty percent of the world's railways use a standard gauge of . Wider gauges are called broad gauge; smaller gauges, narrow gauge. Break-of-gauge refers...
, and in gauge conversion
Gauge conversion
In rail transport, gauge conversion is the process of converting a railway from one rail gauge to another, through the alteration of the railway tracks...
decisions.
Even when placing isolated rails not connected to any other lines, track layers usually choose a standard rail gauge so they can use off-the-shelf rolling stock.
Although a few manufacturers make rolling stock that can adjust to different rail gauges, most manufacturers make rolling stock that only works with one of the standard rail gauges.
See also
- Anti-rival good
- Beckstrom's lawBeckstrom's lawIn economics, Beckstrom's law is a model or theorem formulated by Rod Beckstrom. It purports to answer "the decades old question of 'how valuable is a network.'" According to its creator, it can be used to value any network be it social networks, electronic networks, support groups and even the...
- BetamaxBetamaxBetamax was a consumer-level analog videocassette magnetic tape recording format developed by Sony, released on May 10, 1975. The cassettes contain -wide videotape in a design similar to the earlier, professional wide, U-matic format...
- Cluster effectCluster effectThe cluster effect is the effect of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service congregating in a certain place and hence inducing other buyers and sellers to relocate there as well.- The Silicon Valley case :...
- Open formatOpen formatAn open file format is a published specification for storing digital data, usually maintained by a standards organization, which can therefore be used and implemented by anyone. For example, an open format can be implementable by both proprietary and free and open source software, using the typical...
- Open system (computing)Open system (computing)Open systems are computer systems that provide some combination of interoperability, portability, and open software standards. The term was popularized in the early 1980s, mainly to describe systems based on Unix,...
- Reed's lawReed's lawReed's law is the assertion of David P. Reed that the utility of large networks, particularly social networks, can scale exponentially with the size of the network....
- Returns to scaleReturns to scaleIn economics, returns to scale and economies of scale are related terms that describe what happens as the scale of production increases in the long run, when all input levels including physical capital usage are variable...
(increasing returns) - Semantic WebSemantic WebThe Semantic Web is a collaborative movement led by the World Wide Web Consortium that promotes common formats for data on the World Wide Web. By encouraging the inclusion of semantic content in web pages, the Semantic Web aims at converting the current web of unstructured documents into a "web of...
- Two-sided market
External links
- Coordination and Lock-In: Competition with Switching Costs and Network Effects, Joseph Farrell and Paul Klemperer.
- Network Externalities (Effects), S. J. Liebowitz, Stephen E. Margolis.
- An Overview of Network Effects, Arun SundararajanArun SundararajanArun Sundararajan is the NEC Faculty Fellow, Associate Professor of Information, Operations and Management Sciences and a Doctoral Coordinator at the Stern School of Business, New York University. For 2010-12, he is the Distinguished Academic Fellow at the Center for IT and the Networked...
. - The Economics of Networks, Nicholas Economides.
- Network Economics in Farsi/Persian, Behrooz Hassani M
- Beckstrom's Law & The Economics Of Networks - ICANN

