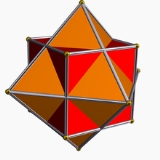
Compound of cube and octahedron
Encyclopedia
| Compound of cube and octahedron | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Type | Compound Polyhedral compound A polyhedral compound is a polyhedron that is itself composed of several other polyhedra sharing a common centre. They are the three-dimensional analogs of polygonal compounds such as the hexagram.... |
| Stellation Stellation Stellation is a process of constructing new polygons , new polyhedra in three dimensions, or, in general, new polytopes in n dimensions. The process consists of extending elements such as edges or face planes, usually in a symmetrical way, until they meet each other again... core |
cuboctahedron |
| Convex hull Convex hull In mathematics, the convex hull or convex envelope for a set of points X in a real vector space V is the minimal convex set containing X.... |
Rhombic dodecahedron Rhombic dodecahedron In geometry, the rhombic dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 12 rhombic faces. It is an Archimedean dual solid, or a Catalan solid. Its dual is the cuboctahedron.-Properties:... |
| Index | W43 |
| Polyhedra | 1 octahedron Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... 1 cube Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
| Faces | 8 triangle Triangle A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted .... s 6 squares Square (geometry) In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles... |
| Edges | 24 |
| Vertices | 14 |
| Symmetry group Symmetry group The symmetry group of an object is the group of all isometries under which it is invariant with composition as the operation... |
octahedral Octahedral symmetry 150px|thumb|right|The [[cube]] is the most common shape with octahedral symmetryA regular octahedron has 24 rotational symmetries, and a symmetry order of 48 including transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation... (Oh) |
This polyhedron can be seen as either a polyhedral stellation
Stellation
Stellation is a process of constructing new polygons , new polyhedra in three dimensions, or, in general, new polytopes in n dimensions. The process consists of extending elements such as edges or face planes, usually in a symmetrical way, until they meet each other again...
or a compound.
As a compound
It can be seen as the compound of an octahedronOctahedron
In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex....
and a cube
Cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and...
. It is one of four compounds constructed from a Platonic solid
Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex polyhedron that is regular, in the sense of a regular polygon. Specifically, the faces of a Platonic solid are congruent regular polygons, with the same number of faces meeting at each vertex; thus, all its edges are congruent, as are its vertices and...
or Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron and its dual.
It has octahedral symmetry
Octahedral symmetry
150px|thumb|right|The [[cube]] is the most common shape with octahedral symmetryA regular octahedron has 24 rotational symmetries, and a symmetry order of 48 including transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation...
(Oh) and shares the same vertices as a rhombic dodecahedron
Rhombic dodecahedron
In geometry, the rhombic dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 12 rhombic faces. It is an Archimedean dual solid, or a Catalan solid. Its dual is the cuboctahedron.-Properties:...
.
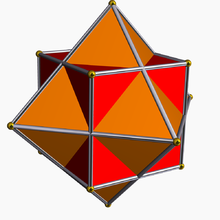
As a stellation
It is also the first stellationStellation
Stellation is a process of constructing new polygons , new polyhedra in three dimensions, or, in general, new polytopes in n dimensions. The process consists of extending elements such as edges or face planes, usually in a symmetrical way, until they meet each other again...
of the cuboctahedron
Cuboctahedron
In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,...
and given as Wenninger model index 43.
It can be seen as a cuboctahedron
Cuboctahedron
In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,...
with square
Square (geometry)
In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles...
and triangular
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
pyramid
Pyramid (geometry)
In geometry, a pyramid is a polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point, called the apex. Each base edge and apex form a triangle. It is a conic solid with polygonal base....
s added to each face.
The stellation facets for construction are:



