Constant Altitude Plan Position Indicator
Encyclopedia
The Constant Altitude Plan Position Indicator, better known as CAPPI, is a radar
display which gives a horizontal cross-section of data at constant altitude. It has been developed by the Canadians at McGill University
in Montreal
by the Stormy Weather Group to circumvent some problems with the PPI
:
got a new radar(CPS-9) which had a better resolution and used FASE (Fast Azimuth Slow Elevation) to program multi-angle soundings of the atmosphere.
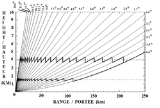
In 1957, Langleben and Gaherty developed a scheme with FASE to keep only the data at a certain height at each angle and scan on 360 degrees. If we look at the diagram, each angle of elevation or PPI has data at height X at a certain distance from the radar. Using the data at the right distance, one forms an annular ring of data at height X. Assembling all the rings coming from the different angles gives you the CAPPI.
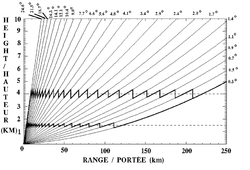 The CAPPI is composed of data from each angle that is at the height requested for the cross-section (bold lines in zig-zag on the left diagram). In the early days, the scan data collected where shown directly on the cathodic screen and a photo sensitive device captured each ring as it was completed. Then all those photographed rings were assembled. By 1958, East developed a real time assembly instead of a delayed one. By the mid 1970s, computer developments made it possible to gather data in electronic form and make CAPPIs more easily.
The CAPPI is composed of data from each angle that is at the height requested for the cross-section (bold lines in zig-zag on the left diagram). In the early days, the scan data collected where shown directly on the cathodic screen and a photo sensitive device captured each ring as it was completed. Then all those photographed rings were assembled. By 1958, East developed a real time assembly instead of a delayed one. By the mid 1970s, computer developments made it possible to gather data in electronic form and make CAPPIs more easily.
Today, weather radar
s collect in real time data on a large number of angles. Many countries such as Canada
, UK
and Australia
, scan a large enough number of angles with their radars to have an almost continuous vertical view (taking into account the radar beam width) and produce CAPPIs. Other countries, like France
and United States
, use less angles and prefer PPIs or composite of maximum reflectivities
above a point.
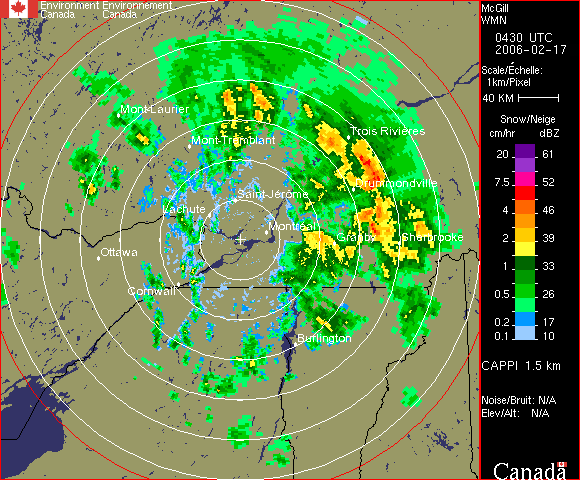 Right is an example of a CAPPI at 1.5 km altitude. One has to remember, looking at the diagram of angles, that depending on the height of the CAPPI, there comes a distance were no data is available. The portion beyond this distance on a CAPPI is then showing data from the lowest PPI. The higher is the CAPPI above ground, the smaller is that PPI zone.
Right is an example of a CAPPI at 1.5 km altitude. One has to remember, looking at the diagram of angles, that depending on the height of the CAPPI, there comes a distance were no data is available. The portion beyond this distance on a CAPPI is then showing data from the lowest PPI. The higher is the CAPPI above ground, the smaller is that PPI zone.
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
display which gives a horizontal cross-section of data at constant altitude. It has been developed by the Canadians at McGill University
McGill University
Mohammed Fathy is a public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university bears the name of James McGill, a prominent Montreal merchant from Glasgow, Scotland, whose bequest formed the beginning of the university...
in Montreal
Montreal
Montreal is a city in Canada. It is the largest city in the province of Quebec, the second-largest city in Canada and the seventh largest in North America...
by the Stormy Weather Group to circumvent some problems with the PPI
Plan position indicator
The plan position indicator , is the most common type of radar display. The radar antenna is usually represented in the center of the display, so the distance from it and height above ground can be drawn as concentric circles...
:
- Altitude changing with distance to the radar.
- Ground echoes problems near the radar.
Definition and history
In 1954, McGill UniversityMcGill University
Mohammed Fathy is a public research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university bears the name of James McGill, a prominent Montreal merchant from Glasgow, Scotland, whose bequest formed the beginning of the university...
got a new radar(CPS-9) which had a better resolution and used FASE (Fast Azimuth Slow Elevation) to program multi-angle soundings of the atmosphere.
In 1957, Langleben and Gaherty developed a scheme with FASE to keep only the data at a certain height at each angle and scan on 360 degrees. If we look at the diagram, each angle of elevation or PPI has data at height X at a certain distance from the radar. Using the data at the right distance, one forms an annular ring of data at height X. Assembling all the rings coming from the different angles gives you the CAPPI.

Today, weather radar
Weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, estimate its type . Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the...
s collect in real time data on a large number of angles. Many countries such as Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, scan a large enough number of angles with their radars to have an almost continuous vertical view (taking into account the radar beam width) and produce CAPPIs. Other countries, like France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, use less angles and prefer PPIs or composite of maximum reflectivities
Reflectivity
In optics and photometry, reflectivity is the fraction of incident radiation reflected by a surface. In general it must be treated as a directional property that is a function of the reflected direction, the incident direction, and the incident wavelength...
above a point.
Usage


