Constituent country
Encyclopedia
Constituent country is a phrase sometimes used in contexts in which a country
makes up a part of a larger entity. The term constituent country does not have any defined legal meaning, and is used simply to refer to a country
which is a part (i.e. a constituent) of something else.
However, this terminology is not consistent. The Faroes are also referred to as a "self-governing territory" or similar by (e.g.) the Prime Minister of the Faroe Islands
and the Royal Danish Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Similarly, the Danish Government also refers to Greenland as an "autonomous province" and neither of the laws forming Greenland's constitution refer to Greenland as a country.
, Pays de la Loire
, and Pays de Caux
) often bear the appellation ("land"), which is sometimes also used in reference to other nations (e.g., Pays-Bas is the French name of the Netherlands
).
In 2004, the French overseas collectivity of French Polynesia
was legally designated as a pays d'outre-mer au sein de la République. Although some translated this as an "overseas country inside the Republic", the Constitutional Council of France
ruled that this was merely a change of appellation and did not represent an unconstitutional change in legal status.
and of Austria
are referred to as ("Federal Lands") and ("Member States") in German, a usage implying their former sovereignty
in a manner parallel to the American use of "" ( and Gliedstaaten). However, they are never considered countries in their own right and are referred to as Bundesländer or terms such as "states" in other languages to avoid confusion.
Each is expressly designated as a land in Dutch law by the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands
. Unlike the German and Austrian bundesländer, landen is consistently translated as "countries" by the Dutch government.
consists of three parts usually referred to as countries:
However, the Constitutions of the Cook Islands and of Niue do not describe either as a country, nor do the New Zealand Acts which brought those constitutions into force.
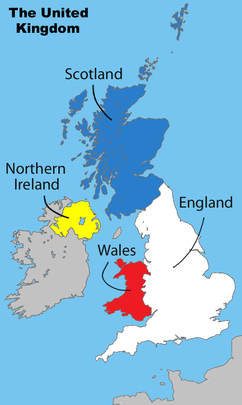 The United Kingdom is generally considered to comprise four countries:
The United Kingdom is generally considered to comprise four countries:
However, the kingdom itself is a unitary one and not a personal union
: properly speaking, the principality of Wales
ceased to exist in 1542, the kingdoms of England
and Scotland
in 1707
, and the kingdom of Ireland
in 1800 or 1953. Further, the current usage "country" does not always appear in the acts of union which established the modern nation and can therefore be particularly controversial when applied to Northern Ireland, which did not exist prior to 1921 (See: Countries of the United Kingdom
).
Northern Ireland had a devolved parliament
from 19211973 and an assembly
from 19731974 and from 19821986. After referenda in Wales and Scotland in 1997, new devolved governments
were created in Scotland
, Wales
, and Northern Ireland
but not England, which remains directly under Parliament
.
At sporting events such as rugby union
, the alternate title Home Nations
is used. In such contexts, "Ireland
" may refer to the team of the entire island as a whole.
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
makes up a part of a larger entity. The term constituent country does not have any defined legal meaning, and is used simply to refer to a country
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
which is a part (i.e. a constituent) of something else.
Denmark
The Kingdom of Denmark consists of three constituent parts, each part sometimes referred to as a country:- DenmarkDenmarkDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
proper - The Faroe IslandsFaroe IslandsThe Faroe Islands are an island group situated between the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately halfway between Scotland and Iceland. The Faroe Islands are a self-governing territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark proper and Greenland...
- GreenlandGreenlandGreenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
However, this terminology is not consistent. The Faroes are also referred to as a "self-governing territory" or similar by (e.g.) the Prime Minister of the Faroe Islands
Prime Minister of the Faroe Islands
This is a list of Prime Ministers of the Faroe Islands.The Faroese term for the function, Løgmaður literally means "Lawman".-First Ministers :-First Ministers :-See also:...
and the Royal Danish Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Similarly, the Danish Government also refers to Greenland as an "autonomous province" and neither of the laws forming Greenland's constitution refer to Greenland as a country.
France
French regions (e.g., Pays d'AugePays d'Auge
The Pays d'Auge is an area in Normandy, straddling the départements of Calvados and Orne . The chief town is Lisieux.-Geography:Generally it consists of the basin of the Touques River....
, Pays de la Loire
Pays de la Loire
Pays de la Loire is one of the 27 regions of France. It is one of the regions created in the late 20th century to serve as a zone of influence for its capital, Nantes, one of a handful so-called "balancing metropolises" ¹...
, and Pays de Caux
Pays de Caux
The Pays de Caux is an area in Normandy occupying the greater part of the French département of Seine Maritime in Haute-Normandie. It is a chalk plateau to the north of the Seine Estuary and extending to the cliffs on the English Channel coast - its coastline is known as the Côte d'Albâtre...
) often bear the appellation ("land"), which is sometimes also used in reference to other nations (e.g., Pays-Bas is the French name of the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
).
In 2004, the French overseas collectivity of French Polynesia
French Polynesia
French Polynesia is an overseas country of the French Republic . It is made up of several groups of Polynesian islands, the most famous island being Tahiti in the Society Islands group, which is also the most populous island and the seat of the capital of the territory...
was legally designated as a pays d'outre-mer au sein de la République. Although some translated this as an "overseas country inside the Republic", the Constitutional Council of France
Constitutional Council of France
The Constitutional Council is the highest constitutional authority in France. It was established by the Constitution of the Fifth Republic on 4 October 1958, and its duty is to ensure that the principles and rules of the constitution are upheld.Its main activity is to rule on whether proposed...
ruled that this was merely a change of appellation and did not represent an unconstitutional change in legal status.
Germany and Austria
The states of GermanyStates of Germany
Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
and of Austria
States of Austria
Austria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder . Since Land is also the German word for a country, the term Bundesländer is often used instead to avoid ambiguity. The Constitution of Austria uses both terms...
are referred to as ("Federal Lands") and ("Member States") in German, a usage implying their former sovereignty
Unification of Germany
The formal unification of Germany into a politically and administratively integrated nation state officially occurred on 18 January 1871 at the Versailles Palace's Hall of Mirrors in France. Princes of the German states gathered there to proclaim Wilhelm of Prussia as Emperor Wilhelm of the German...
in a manner parallel to the American use of "" ( and Gliedstaaten). However, they are never considered countries in their own right and are referred to as Bundesländer or terms such as "states" in other languages to avoid confusion.
Netherlands
As of 10 October 2010, the Kingdom of the Netherlands consists of four countries:- ArubaArubaAruba is a 33 km-long island of the Lesser Antilles in the southern Caribbean Sea, located 27 km north of the coast of Venezuela and 130 km east of Guajira Peninsula...
- CuraçaoCuraçaoCuraçao is an island in the southern Caribbean Sea, off the Venezuelan coast. The Country of Curaçao , which includes the main island plus the small, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao , is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands...
- NetherlandsNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
- Sint Maarten
Each is expressly designated as a land in Dutch law by the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands describes the political relationship between the four different countries which form the Kingdom of the Netherlands: Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten in the Caribbean and the Netherlands in Europe...
. Unlike the German and Austrian bundesländer, landen is consistently translated as "countries" by the Dutch government.
New Zealand
The Realm of New ZealandRealm of New Zealand
The Realm of New Zealand is the entire area in which the Queen in right of New Zealand is head of state. The Realm comprises New Zealand, the Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau and the Ross Dependency in Antarctica, and is defined by a 1983 Letters Patent constituting the office of Governor-General of New...
consists of three parts usually referred to as countries:
- New ZealandNew ZealandNew Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
- Cook IslandsCook IslandsThe Cook Islands is a self-governing parliamentary democracy in the South Pacific Ocean in free association with New Zealand...
- NiueNiueNiue , is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean. It is commonly known as the "Rock of Polynesia", and inhabitants of the island call it "the Rock" for short. Niue is northeast of New Zealand in a triangle between Tonga to the southwest, the Samoas to the northwest, and the Cook Islands to...
However, the Constitutions of the Cook Islands and of Niue do not describe either as a country, nor do the New Zealand Acts which brought those constitutions into force.
United Kingdom

- EnglandEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
- ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
- WalesWalesWales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
- Northern IrelandNorthern IrelandNorthern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
However, the kingdom itself is a unitary one and not a personal union
Personal union
A personal union is the combination by which two or more different states have the same monarch while their boundaries, their laws and their interests remain distinct. It should not be confused with a federation which is internationally considered a single state...
: properly speaking, the principality of Wales
Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales existed between 1216 and 1542, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales.It was formally founded in 1216 at the Council of Aberdyfi, and later recognised by the 1218 Treaty of Worcester between Llywelyn the Great of Wales and Henry III of England...
ceased to exist in 1542, the kingdoms of England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
and Scotland
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a Sovereign state in North-West Europe that existed from 843 until 1707. It occupied the northern third of the island of Great Britain and shared a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England...
in 1707
Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union were two Parliamentary Acts - the Union with Scotland Act passed in 1706 by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland - which put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706,...
, and the kingdom of Ireland
Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland refers to the country of Ireland in the period between the proclamation of Henry VIII as King of Ireland by the Crown of Ireland Act 1542 and the Act of Union in 1800. It replaced the Lordship of Ireland, which had been created in 1171...
in 1800 or 1953. Further, the current usage "country" does not always appear in the acts of union which established the modern nation and can therefore be particularly controversial when applied to Northern Ireland, which did not exist prior to 1921 (See: Countries of the United Kingdom
Countries of the United Kingdom
Countries of the United Kingdom is a term used to describe England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. These four countries together form the sovereign state of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, which is also described as a country. The alternative terms, constituent...
).
Northern Ireland had a devolved parliament
Parliament of Northern Ireland
The Parliament of Northern Ireland was the home rule legislature of Northern Ireland, created under the Government of Ireland Act 1920, which sat from 7 June 1921 to 30 March 1972, when it was suspended...
from 19211973 and an assembly
Northern Ireland Assembly
The Northern Ireland Assembly is the devolved legislature of Northern Ireland. It has power to legislate in a wide range of areas that are not explicitly reserved to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, and to appoint the Northern Ireland Executive...
from 19731974 and from 19821986. After referenda in Wales and Scotland in 1997, new devolved governments
Devolution in the United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, devolution refers to the statutory granting of powers from the Parliament of the United Kingdom to the Scottish Parliament, the National Assembly for Wales and the Northern Ireland Assembly and to their associated executive bodies the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government...
were created in Scotland
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament is the devolved national, unicameral legislature of Scotland, located in the Holyrood area of the capital, Edinburgh. The Parliament, informally referred to as "Holyrood", is a democratically elected body comprising 129 members known as Members of the Scottish Parliament...
, Wales
National Assembly for Wales
The National Assembly for Wales is a devolved assembly with power to make legislation in Wales. The Assembly comprises 60 members, who are known as Assembly Members, or AMs...
, and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland Assembly
The Northern Ireland Assembly is the devolved legislature of Northern Ireland. It has power to legislate in a wide range of areas that are not explicitly reserved to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, and to appoint the Northern Ireland Executive...
but not England, which remains directly under Parliament
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
.
At sporting events such as rugby union
Rugby union
Rugby union, often simply referred to as rugby, is a full contact team sport which originated in England in the early 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand...
, the alternate title Home Nations
Home Nations
Home Nations is a collective term with one of two meanings depending on the context. Politically, it means the nations of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom...
is used. In such contexts, "Ireland
Ireland national rugby union team
The Ireland national rugby union team represents the island of Ireland in rugby union. The team competes annually in the Six Nations Championship and every four years in the Rugby World Cup, where they reached the quarter-final stage in all but two competitions The Ireland national rugby union...
" may refer to the team of the entire island as a whole.
See also
- Associated stateAssociated stateAn associated state is the minor partner in a formal, free relationship between a political territory with a degree of statehood and a nation, for which no other specific term, such as protectorate, is adopted...
- Constituent stateConstituent stateA constituent state, constituent entity, or constituent part, is a territorial and constitutional entity forming part of a sovereign state...
- DevolutionDevolutionDevolution is the statutory granting of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to government at a subnational level, such as a regional, local, or state level. Devolution can be mainly financial, e.g. giving areas a budget which was formerly administered by central government...
- FederacyFederacyA federacy is a form of government where one or several substate units enjoy considerably more independence than the majority of the substate units. To some extent, such an arrangement can be considered as similar to asymmetric federalism.-Description:...
- Political unionPolitical unionA political union is a type of state which is composed of or created out of smaller states. Unlike a personal union, the individual states share a common government and the union is recognized internationally as a single political entity...

