_sulfate_electrode.gif)
Copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode
Encyclopedia
Reference electrode
A reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant concentrations of each participants of the redox reaction.There are many ways reference...
of the first kind, based on the redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
reaction with participation of the metal (copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
) and its salt - copper(II) sulfate.
It is used for measuring electrochemical potential and is the most commonly used reference electrode for testing cathodic protection
Cathodic protection
Cathodic protection is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. The simplest method to apply CP is by connecting the metal to be protected with another more easily corroded "sacrificial metal" to act as the anode of the...
corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
control systems.
The corresponding equation can be presented as follow:
- Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu0(metal)
This reaction characterized by reversible and fast electrode kinetics, meaning that a sufficiently high current can be passed through the electrode with the 100% efficiency of the redox reaction (dissolution
Solvation
Solvation, also sometimes called dissolution, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute...
of the metal or cathodic deposition
Deposition (chemistry)
In chemistry, deposition is the settling of particles or sediment from a solution, suspension and mixture or vapor onto a pre-existing surface...
of the copper-ions).
The Nernst equation
Nernst equation
In electrochemistry, the Nernst equation is an equation that can be used to determine the equilibrium reduction potential of a half-cell in an electrochemical cell. It can also be used to determine the total voltage for a full electrochemical cell...
below shows the dependence of the potential of the copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode on the activity
Activity (chemistry)
In chemical thermodynamics, activity is a measure of the “effective concentration” of a species in a mixture, meaning that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution.By convention, activity...
or concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
copper-ions:
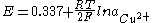
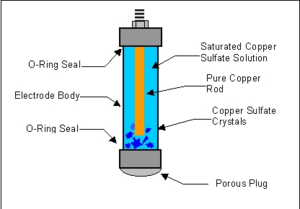
Commercial reference electrodes consist of a plastic tube holding the copper rod and saturated solution of copper sulfate. A porous plug on one end allows contact with the copper sulfate electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
. The copper rod protrudes out of the tube. A voltmeter
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to...
negative lead is connected to the copper rod.
The potential of a copper copper sulfate electrode is +0.314 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode
Standard hydrogen electrode
The standard hydrogen electrode , is a redox electrode which forms the basis of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potentials...
.
Applications
- Cathodic Protection
- Copper coulometerCopper coulometerThe copper coulometer is a one of the common application of the copper-copper sulfate electrode. Such a coulometer consists of two identical copper electrodes immersed in slightly acidic pH-buffered solution of copper sulfate. Passing of current through the element leads to the anodic dissolution...
- Copper-copper(II) sulfate electrode is also used as a one of the half cellHalf cellA half-cell is a structure that contains a conductive electrode and a surrounding conductive electrolyte separated by a naturally occurring Helmholtz double layer. Chemical reactions within this layer momentarily pump electric charges between the electrode and the electrolyte, resulting in a...
in the Daniel-Jakobi galvanic cell.

