
Corner-point grid
Encyclopedia
In geometry
, a corner-point grid is a tessellation
an Euclidean
3D volume where the base cell has 6 faces
(hexahedron
).
A set of straight lines defined by their end points define the pillars of the corner-point grid. The pillars have a lexiographical ordering that determines neighbouring pillars. On each pillar, a constant number of nodes (corner-points) is defined. A corner-point cell is now the volume between 4 neighbouring pillars and two neighbouring points on each pillar.
Each cell can be identified by integer coordinates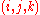 , where the
, where the 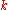 coordinate runs along the pillars, and
coordinate runs along the pillars, and 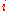 and
and 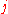 span each layer. The cells are ordered naturally, where the index
span each layer. The cells are ordered naturally, where the index  runs the fastest and
runs the fastest and 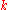 the slowest.
the slowest.
In the special case of all pillars being vertical, the top and bottom face of each corner-point cell are described by bilinear surfaces
and the side faces are planes.
Corner-point grids are supported by most reservoir simulation
software, and has become an industry standard.
surfaces in geological modelling, effectively done by collapsing nodes along each pillar. This means that the corner-point cells degenerate and may have less than 6 faces.
For the corner-point grids non-neighboring connections are supported, meaning that grid cells that are not neighboring in ijk-space can be defined as neighboring. This feature allows for representation of faults with significant throw/displacement. Moreover, the neighboring grid cells do not need to have matching cell faces (just overlap).
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a corner-point grid is a tessellation
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
an Euclidean
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
3D volume where the base cell has 6 faces
Face (geometry)
In geometry, a face of a polyhedron is any of the polygons that make up its boundaries. For example, any of the squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube...
(hexahedron
Hexahedron
A hexahedron is any polyhedron with six faces, although usually implies the cube as a regular hexahedron with all its faces square, and three squares around each vertex....
).
A set of straight lines defined by their end points define the pillars of the corner-point grid. The pillars have a lexiographical ordering that determines neighbouring pillars. On each pillar, a constant number of nodes (corner-points) is defined. A corner-point cell is now the volume between 4 neighbouring pillars and two neighbouring points on each pillar.
Each cell can be identified by integer coordinates
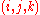 , where the
, where the 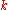 coordinate runs along the pillars, and
coordinate runs along the pillars, and 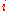 and
and 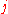 span each layer. The cells are ordered naturally, where the index
span each layer. The cells are ordered naturally, where the index  runs the fastest and
runs the fastest and 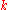 the slowest.
the slowest.In the special case of all pillars being vertical, the top and bottom face of each corner-point cell are described by bilinear surfaces
Bilinear interpolation
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is an extension of linear interpolation for interpolating functions of two variables on a regular grid. The interpolated function should not use the term of x^2 or y^2, but x y, which is the bilinear form of x and y.The key idea is to perform linear...
and the side faces are planes.
Corner-point grids are supported by most reservoir simulation
Reservoir simulation
Reservoir simulation is an area of reservoir engineering in which computer models are used to predict the flow of fluids through porous media.-Uses:...
software, and has become an industry standard.
Degeneracy
A main feature of the format is the ability to define erosionErosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
surfaces in geological modelling, effectively done by collapsing nodes along each pillar. This means that the corner-point cells degenerate and may have less than 6 faces.
For the corner-point grids non-neighboring connections are supported, meaning that grid cells that are not neighboring in ijk-space can be defined as neighboring. This feature allows for representation of faults with significant throw/displacement. Moreover, the neighboring grid cells do not need to have matching cell faces (just overlap).

