
Couple (mechanics)
Encyclopedia
In mechanics
, a couple is a system of force
s with a resultant (a.k.a. net, or sum) moment
but no resultant force. Another term for a couple is a pure moment. Its effect is to create rotation
without translation
, or more generally without any acceleration of the centre of mass
.
The resultant moment of a couple is called a torque. This is not to be confused with the term torque
as it is used in physics, where it is merely a synonym of moment. Instead, torque is a special case of moment. Torque has special properties that moment does not have, in particular the property of being independent of reference point, as described below.
A couple is a pair of forces, equal in magnitude, oppositely directed, and displaced by perpendicular
distance.
The simplest kind of couple consists of two equal and opposite force
s whose lines of action
do not coincide. This is called a "simple couple". The forces have a turning effect or moment called a torque
about an axis which is normal to the plane of the forces. The SI unit for the torque of the couple is newton metre
.
If the two forces are F and −F, then the magnitude
of the torque is given by the following formula:
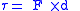
where is the torque
is the torque
The magnitude of the torque is always equal to Fd, with the direction of the torque given by the unit vector , which is perpendicular to the plane containing the two forces. When d is taken as a vector between the points of action of the forces, then the couple is the cross product
, which is perpendicular to the plane containing the two forces. When d is taken as a vector between the points of action of the forces, then the couple is the cross product
of d and F.
(This fact is called Varignon's Second Moment Theorem.)
The proof of this claim is as follows: Suppose there are a set of force vectors F1, F2, etc. that form a couple, with position vectors (about some origin P) r1, r2, etc., respectively. The moment about P is
Now we pick a new reference point P that differs from P by the vector r. The new moment is
Now the distributive property of the cross product
implies
However, the definition of a force couple means that
Therefore,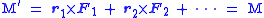
This proves that the moment is independent of reference point, which is proof that a couple is a free vector.
and the physical sciences. A few examples are:
In a liquid crystal
it is the rotation of an optic axis called the director that produces the functionality of these compounds. As Jerald Ericksen
explained
Mechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
, a couple is a system of force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
s with a resultant (a.k.a. net, or sum) moment
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
but no resultant force. Another term for a couple is a pure moment. Its effect is to create rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
without translation
Translation (physics)
In physics, translation is movement that changes the position of an object, as opposed to rotation. For example, according to Whittaker:...
, or more generally without any acceleration of the centre of mass
Center of mass
In physics, the center of mass or barycenter of a system is the average location of all of its mass. In the case of a rigid body, the position of the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body...
.
The resultant moment of a couple is called a torque. This is not to be confused with the term torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
as it is used in physics, where it is merely a synonym of moment. Instead, torque is a special case of moment. Torque has special properties that moment does not have, in particular the property of being independent of reference point, as described below.
Simple couple
Definition-A couple is a pair of forces, equal in magnitude, oppositely directed, and displaced by perpendicular
distance.
The simplest kind of couple consists of two equal and opposite force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
s whose lines of action
Line of action
In physics, the line of action of a force F expresses the geometry of how F is applied. It is the line through the point at which F is applied and along the direction in which F is applied....
do not coincide. This is called a "simple couple". The forces have a turning effect or moment called a torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
about an axis which is normal to the plane of the forces. The SI unit for the torque of the couple is newton metre
Newton metre
A newton metre is a unit of torque in the SI system. The symbolic form is N m or N·m, and sometimes hyphenated newton-metre...
.
If the two forces are F and −F, then the magnitude
Magnitude
Magnitude Is A Part Of An EarthquakesMagnitude may refer to:In mathematics:*Magnitude , the relative size of a mathematical object*Magnitude , a term for the size or length of a vector...
of the torque is given by the following formula:
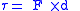
where
 is the torque
is the torque
- F is the magnitude of one of the forces
- d is the perpendicular distance between the forces, sometimes called the arm of the couple
The magnitude of the torque is always equal to Fd, with the direction of the torque given by the unit vector
 , which is perpendicular to the plane containing the two forces. When d is taken as a vector between the points of action of the forces, then the couple is the cross product
, which is perpendicular to the plane containing the two forces. When d is taken as a vector between the points of action of the forces, then the couple is the cross productCross product
In mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
of d and F.
Independence of reference point
The moment of a force is only defined with respect to a certain point P (it is said to be the "moment about P"), and in general when P is changed, the moment changes. However, the moment (torque) of a couple is independent of the reference point P: Any point will give the same moment. In other words, a torque vector, unlike any other moment vector, is a "free vector".(This fact is called Varignon's Second Moment Theorem.)
The proof of this claim is as follows: Suppose there are a set of force vectors F1, F2, etc. that form a couple, with position vectors (about some origin P) r1, r2, etc., respectively. The moment about P is

Now we pick a new reference point P that differs from P by the vector r. The new moment is

Now the distributive property of the cross product
Cross product
In mathematics, the cross product, vector product, or Gibbs vector product is a binary operation on two vectors in three-dimensional space. It results in a vector which is perpendicular to both of the vectors being multiplied and normal to the plane containing them...
implies

However, the definition of a force couple means that

Therefore,
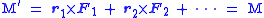
This proves that the moment is independent of reference point, which is proof that a couple is a free vector.
Forces and couples
A force F applied to a rigid body at a distance d from the center of mass has the same effect as the same force applied directly to the center of mass and a couple Cℓ = Fd. The couple produces an angular acceleration of the rigid body at right angles to the plane of the couple. The force at the center of mass accelerates the body in the direction of the force without change in orientation. The general theorems are:- A single force acting at any point O′ of a rigid body can be replaced by an equal and parallel force F acting at any given point O and a couple with forces parallel to F whose moment is M = Fd, d being the separation of O and O′. Conversely, a couple and a force in the plane of the couple can be replaced by a single force, appropriately located.
- Any couple can be replaced by another in the same plane of the same direction and moment, having any desired force or any desired arm.
Applications
Couples are very important in mechanical engineeringMechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
and the physical sciences. A few examples are:
- The forces exerted by your hand on a screw-driver
- The forces exerted by the tip of a screw-driver on the head of a screw
- Drag forces acting on a spinning propeller
- Forces on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field.
- The reaction control systemReaction control systemA reaction control system is a subsystem of a spacecraft whose purpose is attitude control and steering by the use of thrusters. An RCS system is capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow...
on a spacecraft.
In a liquid crystal
Liquid crystal
Liquid crystals are a state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal. For instance, an LC may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of LC phases, which can be...
it is the rotation of an optic axis called the director that produces the functionality of these compounds. As Jerald Ericksen
Jerald Ericksen
Jerald LaVerne Ericksen is an American mathematician specializing in continuum mechanics.Jerald was born 20 December 1924 in Portland, Oregon. His father Adolf worked at a Portland creamery and became adept at judging the quality of butter. Later his father acquired a small creamery in Vancouver,...
explained
- At first glance, it may seem that it is optics or electronics which is involved, rather than mechanics. Actually, the changes in optical behavior, etc. are associated with changes in orientation. In turn, these are produced by couples. Very roughly, it is similar to bending a wire, by applying couples.

