
Cricket
Encyclopedia
Cricket is a bat-and-ball
game played between two teams of 11 players on an oval-shaped field
, at the centre of which is a rectangular 22-yard long pitch
. One team bats, trying to score as many runs
as possible while the other team bowls
and fields
, trying to dismiss
the batsmen and thus limit the runs scored by the batting team. A run is scored by the striking batsman hitting the ball with his bat, running to the opposite end of the pitch and touching the crease
there without being dismissed. The teams switch between batting and fielding at the end of an innings
.
In professional cricket the length of a game ranges from 20 overs
of six bowling deliveries per side to Test cricket
played over five days. The Laws of Cricket
are maintained by the International Cricket Council
(ICC) and the Marylebone Cricket Club
(MCC) with additional Standard Playing Conditions for Test matches and One Day Internationals.
Cricket was first played in southern England in the 16th century. By the end of the 18th century, it had developed into the national sport of England. The expansion of the British Empire led to cricket being played overseas and by the mid-19th century the first international matches were being held. The ICC, the game's governing body, has ten full members. The game is played particularly in Australasia
, the Indian subcontinent
, the West Indies, Southern Africa and England.
, the son of Edward I (Longshanks)
, at Newenden, Kent in 1301 and there has been speculation, but no evidence, that this was a form of cricket.
A number of other words have been suggested as sources for the term "cricket". In the earliest definite reference to the sport in 1598, it is called creckett. Given the strong medieval trade connections between south-east England and the County of Flanders
when the latter belonged to the Duchy of Burgundy
, the name may have been derived from the Middle Dutch
krick(-e), meaning a stick (crook); or the Old English
cricc or cryce meaning a crutch or staff. In Old French
, the word criquet seems to have meant a kind of club or stick. In Samuel Johnson
's Dictionary, he derived cricket from "cryce, Saxon, a stick". Another possible source is the Middle Dutch word krickstoel, meaning a long low stool used for kneeling in church and which resembled the long low wicket
with two stumps
used in early cricket. According to Heiner Gillmeister, a European language expert of Bonn University, "cricket" derives from the Middle Dutch phrase for hockey
, met de (krik ket)sen (i.e., "with the stick chase"). Dr Gillmeister believes that not only the name but the sport itself is of Flemish origin.
 The earliest definite reference to cricket being played in England (and hence anywhere) is in evidence given at a 1598 court case which mentions that "creckett" was played on common land in Guildford
The earliest definite reference to cricket being played in England (and hence anywhere) is in evidence given at a 1598 court case which mentions that "creckett" was played on common land in Guildford
, Surrey, around 1550. The court in Guildford heard on Monday, 17 January 1597 (Julian date, equating to the year 1598 in the Gregorian calendar) from a 59 year-old coroner
, John Derrick
, who gave witness that when he was a scholar at the "Free School at Guildford", fifty years earlier, "hee and diverse of his fellows did runne and play [on the common land] at creckett and other plaies." It is believed that it was originally a children's game but references around 1610 indicate that adults had started playing it and the earliest reference to inter-parish or village cricket
occurs soon afterwards. In 1624, a player called Jasper Vinall
was killed when he was struck on the head during a match between two parish teams in Sussex.
During the 17th century, numerous references indicate the growth of cricket in the south-east of England. By the end of the century, it had become an organised activity being played for high stakes and it is believed that the first professionals appeared in the years following the Restoration
in 1660. A newspaper report survives of "a great cricket match" with eleven players a side that was played for high stakes in Sussex in 1697 and this is the earliest known reference to a cricket match of such importance.
The game underwent major development in the 18th century and became the national sport of England. Betting played a major part in that development with rich patrons forming their own "select XIs". Cricket was prominent in London as early as 1707 and large crowds flocked to matches on the Artillery Ground
in Finsbury. The single wicket
form of the sport attracted huge crowds and wagers to match. Bowling evolved around 1760 when bowlers began to pitch the ball instead of rolling or skimming it towards the batsman. This caused a revolution in bat design because, to deal with the bouncing ball, it was necessary to introduce the modern straight bat in place of the old "hockey stick" shape. The Hambledon Club
was founded in the 1760s and, for the next 20 years until the formation of MCC
and the opening of Lord's Old Ground
in 1787, Hambledon was both the game's greatest club and its focal point. MCC quickly became the sport's premier club and the custodian of the Laws of Cricket
. New Laws introduced in the latter part of the 18th century included the three stump wicket and leg before wicket (lbw).
 The 19th century saw underarm bowling
The 19th century saw underarm bowling
replaced by first roundarm
and then overarm bowling
. Both developments were controversial. Organisation of the game at county level led to the creation of the county clubs, starting with Sussex CCC in 1839, which ultimately formed the official County Championship
in 1890. Meanwhile, the British Empire had been instrumental in spreading the game overseas and by the middle of the 19th century it had become well established in India, North America, the Caribbean, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand. In 1844, the first international cricket match
took place between the United States and Canada (although neither has ever been ranked as a Test-playing nation).
In 1859, a team of England players went on the first overseas tour (to North America). The first Australian team to tour overseas was a team of Aboriginal
stockmen who travelled to England in 1868 to play matches against county teams. In 1862, an English team made the first tour of Australia and in 1876–77, an England team took part in the first-ever Test match
at the Melbourne Cricket Ground
against Australia.
W G Grace started his long career in 1865; his career is often said to have revolutionised the sport. The rivalry between England and Australia gave birth to The Ashes
in 1882 and this has remained Test cricket's most famous contest . Test cricket began to expand in 1888–89 when South Africa played England. The last two decades before the First World War
have been called the "Golden Age of cricket
". It is a nostalgic name prompted by the collective sense of loss resulting from the war, but the period did produce some great players and memorable matches, especially as organised competition at county and Test level developed.
The inter-war years were dominated by one player: Australia's Don Bradman, statistically the greatest batsman of all time. It was the determination of the England team to overcome his skill that brought about the infamous Bodyline
series in 1932–33, particularly from the accurate short-pitched bowling of Harold Larwood
. Test cricket continued to expand during the 20th century with the addition of the West Indies, India, and New Zealand before the Second World War
and then Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh in the post-war period. However, South Africa was banned from international cricket from 1970 to 1992 because of its government's apartheid policy.
Cricket entered a new era in 1963 when English counties introduced the limited overs variant. As it was sure to produce a result, limited overs cricket was lucrative and the number of matches increased. The first Limited Overs International was played in 1971. The governing International Cricket Council
(ICC) saw its potential and staged the first limited overs Cricket World Cup
in 1975. In the 21st century, a new limited overs form, Twenty20
, has made an immediate impact.
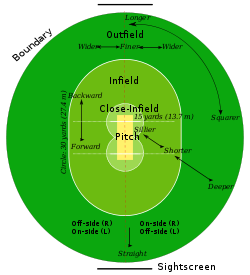
field
, typically 137–150 m (149.8–164 yd) in diameter. The Laws of Cricket do not specify the size or shape of the field but it is often oval.
A cricket match is divided into periods called innings. During an innings (innings ends with 's' in both singular and plural form), one team plays defense (the fielding team) and the other offense (the batting team). The two teams switch between fielding and batting after each innings. All eleven members of the fielding team take the field, but only two members of the batting team (two batsmen) are on the field at any given time.
The key action takes place in the pitch
, a rectangular strip in the centre of the field. The two batsmen face each other at opposite ends of the pitch. The fielding team's eleven members stand outside the pitch, spread out across the field.
Behind each batsman is a target called a wicket. One designated member of the fielding team, called the bowler, is given a ball, and attempts to throw (bowl) the ball from one end of the pitch to the wicket behind the batsman on the other side of the pitch. The batsman tries to prevent the ball from hitting the wicket by striking the ball with a bat. If the bowler succeeds in hitting the wicket, or if the ball, after being struck by the batsman, is caught by the fielding team before it touches the ground, the batsman is dismissed. A dismissed batsman must leave the field, to be replaced by another batsman from the batting team.
If the batsman is successful in striking the ball and the ball isn't caught before it hits the ground, the two batsmen may then try to score points (runs) for their team by running across the pitch, switching positions. Each switch of positions is worth one run. The batsmen may attempt multiple runs or they may attempt no runs. By attempting runs, the batsmen risk dismissal, which can happen if the fielding team retrieves the ball and hits a wicket with the ball before a batsman has reached that end of the pitch.
If the batsman hits the bowled ball over the field boundary without the ball touching the field, the batting team scores six runs and may not attempt more. If the ball touches the ground and then reaches the boundary, the batting team scores four runs and may not attempt more. When the batsmen have finished attempting their runs, the ball is returned to the bowler to be bowled again. The bowler continues to bowl toward the same wicket, regardless of any switch of the batsmen's positions.
After a bowler has bowled six times (an over), another member of the fielding team is designated as the new bowler. The new bowler bowls to the opposite wicket, and play continues. Fielding team members may bowl multiple times during an innings, but may not bowl two overs in succession.
The innings is complete when 10 of the 11 members of the batting team have been dismissed or a set number of overs has been played. The number of innings and the number of overs per innings vary depending on the match.
than the other team and to completely dismiss
the other team. In limited overs cricket, winning the game is achieved by scoring the most runs, even if the opposition has not been completely dismissed. In Test cricket, it is necessary to score the most runs and dismiss the opposition twice in order to win the match, which would otherwise be drawn.
 At either end of the pitch, 22 yards (20.1 m) apart, are placed the wicket
At either end of the pitch, 22 yards (20.1 m) apart, are placed the wicket
s. These serve as a target for the bowling
(aka fielding
) side and are defended by the batting
side which seeks to accumulate runs. The pitch
is 22 yards (20.1 m) or one chain in length between the wickets and is 10 feet (3 m) wide. It is a flat surface and has very short grass that tends to be worn away as the game progresses. The "condition" of the pitch has a significant bearing on the match and team tactics are always determined with the state of the pitch, both current and anticipated, as a deciding factor.
Each wicket consists of three wooden stumps
placed in a straight line and surmounted by two wooden crosspieces called bails
; the total height of the wicket including bails is 28.5 inches (72.4 cm) and the combined width of the three stumps is 9 inches (22.9 cm).
 Four lines, known as creases, are painted onto the pitch around the wicket areas to define the batsman's "safe territory" and to determine the limit of the bowler's approach. These are called the "popping" (or batting) crease, the bowling crease and two "return" creases.
Four lines, known as creases, are painted onto the pitch around the wicket areas to define the batsman's "safe territory" and to determine the limit of the bowler's approach. These are called the "popping" (or batting) crease, the bowling crease and two "return" creases.
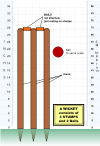 The stumps are placed in line on the bowling creases and so these must be 22 yards (20.1 m) apart. A bowling crease is 8 in 8 in (2.64 m) long with the middle stump placed dead centre. The popping crease has the same length, is parallel to the bowling crease and is 4 feet (1.2 m) in front of the wicket. The return creases are perpendicular to the other two; they are adjoined to the ends of the popping crease and are drawn through the ends of the bowling crease to a length of at least 8 feet (2.4 m).
The stumps are placed in line on the bowling creases and so these must be 22 yards (20.1 m) apart. A bowling crease is 8 in 8 in (2.64 m) long with the middle stump placed dead centre. The popping crease has the same length, is parallel to the bowling crease and is 4 feet (1.2 m) in front of the wicket. The return creases are perpendicular to the other two; they are adjoined to the ends of the popping crease and are drawn through the ends of the bowling crease to a length of at least 8 feet (2.4 m).
When bowling the ball, the bowler's back foot in his "delivery stride" must land within the two return creases while his front foot must land on or behind the popping crease. If the bowler breaks this rule, the umpire calls "No ball".
The importance of the popping crease to the batsman is that it marks the limit of his safe territory for he can be stumped or run out (see Dismissals below) if the wicket is broken while he is "out of his ground".
The bat
is made of wood (usually White Willow
) and has the shape of a blade topped by a cylindrical handle. The blade must not be more than 4.25 inches (10.8 cm) wide and the total length of the bat not more than 38 inches (96.5 cm).
The ball
is a hard leather-seamed spheroid
with a circumference of 9 inches (22.9 cm). The hardness of the ball, which can be delivered at speeds of more than 90 miles per hour (40.2 m/s), is a matter for concern and batsmen wear protective clothing including pads (designed to protect the knees and shins), batting gloves
for the hands, a helmet
for the head and a box inside the trousers (to protect the crotch
area). Some batsmen wear additional padding inside their shirts and trousers such as thigh pads, arm pads, rib protectors and shoulder pads.
, one of whom stands behind the wicket at the bowler's end, the other in a position called "square leg", a position 15–20 metres to the side of the "on strike" batsman. When the bowler delivers the ball, the umpire at the wicket is between the bowler and the non-striker. The umpires confer if there is doubt about playing conditions and can postpone the match by taking the players off the field if necessary, for example rain or deterioration of the light.
 Off the field and in televised matches, there is often a third umpire
Off the field and in televised matches, there is often a third umpire
who can make decisions on certain incidents with the aid of video evidence. The third umpire is mandatory under the playing conditions for Test matches and limited overs internationals played between two ICC full members. These matches also have a match referee whose job is to ensure that play is within the Laws of cricket
and the spirit of the game.
Off the field, the match details including runs and dismissals are recorded by two official scorer
s, one representing each team. The scorers are directed by the hand signals of an umpire. For example, the umpire raises a forefinger to signal that the batsman is out (has been dismissed); he raises both arms above his head if the batsman has hit the ball for six runs. The scorers are required by the Laws of cricket to record all runs scored, wickets taken and overs bowled. In practice, they accumulate much additional data such as bowling analyses and run rates.
Depending on the type of match being played, each team has one or two innings apiece. The term "innings" is also sometimes used to describe an individual batsman's contribution ("he played a fine innings").
The main aim of the bowler, supported by his fielders, is to dismiss the batsman. A batsman when dismissed is said to be "out" and that means he must leave the field of play and be replaced by the next batsman on his team. When ten batsmen have been dismissed (i.e., are out), then the whole team is dismissed and the innings is over. The last batsman, the one who has not been dismissed, is not allowed to continue alone as there must always be two batsmen "in". This batsman is termed "not out".
An innings can end early for three reasons: because the batting side's captain has chosen to "declare" the innings closed (which is a tactical decision), or because the batting side has achieved its target and won the game, or because the game has ended prematurely due to bad weather or running out of time. In each of these cases the team's innings ends with two "not out" batsmen, unless the innings is declared closed at the fall of a wicket and the next batsman has not joined in the play.
In limited overs cricket, there might be two batsmen still "not out" when the last of the allotted overs has been bowled.
. This name came about because the umpire calls "Over!" when six balls have been bowled. At this point, another bowler is deployed at the other end, and the fielding side changes ends while the batsmen do not. A bowler cannot bowl two successive overs, although a bowler can bowl unchanged at the same end for several overs. The batsmen do not change ends and so the one who was non-striker is now the striker and vice-versa. The umpires also change positions so that the one who was at square leg now stands behind the wicket at the non-striker's end and vice-versa.
because of the importance of this fielding position. Each team is headed by a captain
who is responsible for making tactical decisions such as determining the batting order, the placement of fielders and the rotation of bowlers.
A player who excels in both batting and bowling is known as an all-rounder
. One who excels as a batsman and wicket-keeper is known as a "wicket-keeper/batsman", sometimes regarded as a type of all-rounder. True all-rounders are rare as most players focus on either batting or bowling skills.
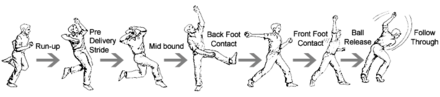 The bowler reaches his delivery stride by means of a "run-up", although some bowlers with a very slow delivery take no more than a couple of steps before bowling. A fast bowler needs momentum and takes quite a long run-up, running very fast as he does so.
The bowler reaches his delivery stride by means of a "run-up", although some bowlers with a very slow delivery take no more than a couple of steps before bowling. A fast bowler needs momentum and takes quite a long run-up, running very fast as he does so.
The fastest bowlers can deliver the ball at a speed of over 90 miles per hour (40.2 m/s) and they sometimes rely on sheer speed to try and defeat the batsman, who is forced to react very quickly. Other fast bowlers rely on a mixture of speed and guile. Some fast bowlers make use of the seam of the ball so that it "curves" or "swings" in flight. This type of delivery can deceive a batsman into mistiming his shot so that the ball touches the edge of the bat and can then be "caught behind" by the wicketkeeper or a slip fielder.
At the other end of the bowling scale is the "spinner" who bowls at a relatively slow pace and relies entirely on guile to deceive the batsman. A spinner will often "buy his wicket" by "tossing one up" (in a slower, higher parabolic
path) to lure the batsman into making a poor shot. The batsman has to be very wary of such deliveries as they are often "flighted" or spun so that the ball will not behave quite as he expects and he could be "trapped" into getting himself out.
In between the pacemen and the spinners are the "medium pacers" who rely on persistent accuracy to try and contain the rate of scoring and wear down the batsman's concentration.
All bowlers are classified according to their looks or style. The classifications
, as with much cricket terminology, can be very confusing. Hence, a bowler could be classified as LF, meaning he is a left arm fast bowler; or as LBG, meaning he is a right arm spin bowler who bowls deliveries that are called a "leg break
" and a "Googly
".
During the bowling action the elbow may be held at any angle and may bend further, but may not straighten out. If the elbow straightens illegally then the square-leg umpire may call no-ball: this is known as "throwing" or "chucking", and can be difficult to detect. The current laws allow a bowler to straighten his arm 15 degrees or less.
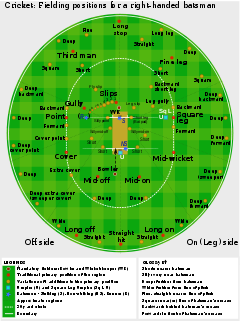 All eleven players on the fielding side take the field together. One of them is the wicket-keeper
All eleven players on the fielding side take the field together. One of them is the wicket-keeper
aka "keeper" who operates behind the wicket being defended by the batsman on strike. Wicket-keeping is normally a specialist occupation and his primary job is to gather deliveries that the batsman does not hit, so that the batsmen cannot run byes. He wears special gloves (he is the only fielder allowed to do so), a box over the groin, and pads to cover his lower legs. Owing to his position directly behind the striker, the wicket-keeper has a good chance of getting a batsman out caught off a fine edge from the bat. He is the only player who can get a batsman out stumped
.
Apart from the one currently bowling, the other nine fielders are tactically deployed by the team captain in chosen positions around the field. These positions are not fixed but they are known by specific and sometimes colourful names such as "slip", "third man", "silly mid on" and "long leg". There are always many unprotected areas.
The captain is the most important member of the fielding side as he determines all the tactics including who should bowl (and how); and he is responsible for "setting the field", though usually in consultation with the bowler.
In all forms of cricket, if a fielder gets injured or becomes ill during a match, a substitute
is allowed to field instead of him. The substitute cannot bowl, act as a captain or keep wicket. The substitute leaves the field when the injured player is fit to return.
 At any one time, there are two batsmen in the playing area. One takes station at the striker's end to defend the wicket as above and to score runs if possible. His partner, the non-striker, is at the end where the bowler is operating.
At any one time, there are two batsmen in the playing area. One takes station at the striker's end to defend the wicket as above and to score runs if possible. His partner, the non-striker, is at the end where the bowler is operating.
Batsmen come in to bat in a batting order
, decided by the team captain. The first two batsmen – the "openers" – usually face the hostile bowling from fresh fast bowlers with a new ball. The top batting positions are usually given to the most competent batsmen in the team, and the non-batsmen typically bat last. The pre-announced batting order is not mandatory and when a wicket falls any player who has not yet batted may be sent in next.
If a batsman "retires" (usually due to injury) and cannot return, he is actually "not out" and his retirement does not count as a dismissal, though in effect he has been dismissed because his innings is over. Substitute batsmen are not allowed.
A skilled batsman can use a wide array of "shots" or "strokes" in both defensive and attacking mode. The idea is to hit the ball to best effect with the flat surface of the bat's blade. If the ball touches the side of the bat it is called an "edge". Batsmen do not always seek to hit the ball as hard as possible, and a good player can score runs just by making a deft stroke with a turn of the wrists or by simply "blocking" the ball but directing it away from fielders so that he has time to take a run.
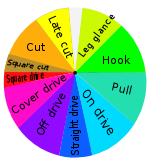
There is a wide variety of shots played in cricket. The batsman's repertoire includes strokes named according to the style of swing and the direction aimed: e.g., "cut", "drive", "hook", "pull".
Note that a batsman does not have to play a shot and can "leave" the ball to go through to the wicketkeeper, providing he thinks it will not hit his wicket. Equally, he does not have to attempt a run when he hits the ball with his bat. He can deliberately use his leg to block the ball and thereby "pad it away" but this is risky because of the leg before wicket
rule.
In the event of an injured batsman being fit to bat but not to run, the umpires and the fielding captain may allow another member of the batting side to be a runner
. The runner's only task is to run between the wickets instead of the injured batsman. The runner is required to wear and carry exactly the same equipment as the incapacitated batsman. It is possible for both batsmen to have runners.
 The primary concern of the batsman on strike (i.e., the "striker") is to prevent the ball hitting the wicket and secondarily to score runs
The primary concern of the batsman on strike (i.e., the "striker") is to prevent the ball hitting the wicket and secondarily to score runs
by hitting the ball with his bat so that he and his partner have time to run from one end of the pitch to the other before the fielding side can return the ball. To register a run, both runners must touch the ground behind the crease with either their bats or their bodies (the batsmen carry their bats as they run). Each completed run increments the score.
More than one run can be scored from a single hit; but, while hits worth one to three runs are common, the size of the field is such that it is usually difficult to run four or more. To compensate for this, hits that reach the boundary of the field are automatically awarded four runs if the ball touches the ground en route to the boundary or six runs if the ball clears the boundary on the full. The batsmen do not need to run if the ball reaches or crosses the boundary.
 Hits for five are unusual and generally rely on the help of "overthrows" by a fielder returning the ball. If an odd number of runs is scored by the striker, the two batsmen have changed ends, and the one who was non-striker is now the striker. Only the striker can score individual runs, but all runs are added to the team's total.
Hits for five are unusual and generally rely on the help of "overthrows" by a fielder returning the ball. If an odd number of runs is scored by the striker, the two batsmen have changed ends, and the one who was non-striker is now the striker. Only the striker can score individual runs, but all runs are added to the team's total.
The decision to attempt a run is ideally made by the batsman who has the better view of the ball's progress, and this is communicated by calling: "yes", "no" and "wait" are often heard.
Running is a calculated risk because if a fielder breaks the wicket with the ball while the nearest batsman is out of his ground (i.e., he does not have part of his body or bat in contact with the ground behind the popping crease), the batsman is run out
.
A team's score is reported in terms of the number of runs scored and the number of batsmen that have been dismissed. For example, if five batsmen are out and the team has scored 224 runs, they are said to have scored 224 for the loss of 5 wickets (commonly shortened to "224 for five" and written 224/5 or, in Australia, "five for 224" and 5/224).
(called "sundries" in Australia) due to errors made by the fielding side. This is achieved in four ways:
When the bowler has bowled a no ball or a wide, his team incurs an additional penalty because that ball (i.e., delivery) has to be bowled again and hence the batting side has the opportunity to score more runs from this extra ball. The batsmen have to run (i.e., unless the ball goes to the boundary for four) to claim byes and leg byes but these only count towards the team total, not to the striker's individual total for which runs must be scored off the bat.
Before the umpire will award a dismissal and declare the batsman to be out, a member of the fielding side (generally the bowler) must "appeal". This is invariably done by asking (or shouting) the term "Howzat?" which means, simply enough, "How is that?" If the umpire agrees with the appeal, he will raise a forefinger and say "Out!". Otherwise he will shake his head and say "Not out". Appeals are particularly loud when the circumstances of the claimed dismissal are unclear, as is always the case with lbw and often with run outs and stumpings.
In the vast majority of cases, it is the striker who is out when a dismissal occurs. If the non-striker is dismissed it is usually by being run out, but he could also be dismissed for obstructing the field, handling the ball or being timed out.
A batsman may leave the field without being dismissed. If injured or taken ill the batsman may temporarily retire, and be replaced by the next batsman. This is recorded as retired hurt
or retired ill
. The retiring batsman is not out, and may resume the innings later. An unimpaired batsman may retire, and this is treated as being dismissed retired out
; no player is credited with the dismissal. Batsmen cannot be out bowled, caught, leg before wicket, stumped or hit wicket off a no ball. They cannot be out bowled, caught, leg before wicket, or hit the ball twice off a wide. Some of these modes of dismissal can occur without the bowler bowling a delivery. The batsman who is not on strike may be run out by the bowler if he leaves his crease before the bowler bowls, and a batsman can be out obstructing the field or retired out at any time. Timed out is, by its nature, a dismissal without a delivery. With all other modes of dismissal, only one batsman can be dismissed per ball bowled.
In a two-innings-a-side match, one team's combined first and second innings total may be less than the other side's first innings total. The team with the greater score is then said to have won by an innings and n runs, and does not need to bat again: n is the difference between the two teams' aggregate scores.
If the team batting last is all out, and both sides have scored the same number of runs, then the match is a tie; this result is quite rare in matches of two innings a side. In the traditional form of the game, if the time allotted for the match expires before either side can win, then the game is declared a draw.
If the match has only a single innings per side, then a maximum number of deliveries for each innings is often imposed. Such a match is called a "limited overs" or "one-day" match, and the side scoring more runs wins regardless of the number of wickets lost, so that a draw cannot occur. If this kind of match is temporarily interrupted by bad weather, then a complex mathematical formula, known as the Duckworth-Lewis method
after its developers, is often used to recalculate a new target score. A one-day match can also be declared a "no-result" if fewer than a previously agreed number of overs have been bowled by either team, in circumstances that make normal resumption of play impossible; for example, wet weather.
than many other team sports in this regard: while the individual focus in cricket is slightly mitigated by the importance of the batting partnership
and the practicalities of running, it is enhanced by the fact that a batsman may occupy the wicket
for a long time.
, although players are still expected to abide by the umpires' rulings without argument, and for the most part they do. Even in the modern game fielders are known to signal to the umpire that a boundary was hit, despite what could have been considered a spectacular save (though they might be found out by the TV replays anyway). In addition to this, some cricket batsmen, like Sachin Tendulkar
and Adam Gilchrist
have been known to "walk" when they think they are out even if the umpire does not declare them out. This is a high level of sportsmanship, as a batsman can easily take advantage of incorrect umpiring decisions.
A scheduled game of cricket cannot be played in wet weather. Dampness affects the bounce of the ball on the wicket and is a risk to all players involved in the game. Many grounds have facilities to cover the cricket pitch (or the wicket). Covers can be in the form of sheets being laid over the wicket to elevated covers on wheels (using the same concept as an umbrella) to even hover covers which form an airtight seal around the wicket. However, most grounds do not have the facilities to cover the outfield. This means that in the event of heavy bouts of bad weather, games may be cancelled, abandoned or suspended due to an unsafe outfield.
Another factor in cricket is the amount of light available. At grounds without floodlights (or in game formats which disallow the use of floodlights), umpires can stop play in the event of bad light as it becomes too difficult for the batsmen to be able to see the ball coming at them, (and in extreme cases, members of the fielding team).
On the other hand, in instances of good light, batsmen can utilize sight-screens which enable batsmen to have a white background against which they can pick out the red ball (or black background for white ball) with greater ease.
The umpires always have the final decision on weather related issues.
are sometimes painted and sometimes marked by a rope. Pitch and outfield variations can have a significant effect on how balls behave and are fielded as well as on batting. Pitches vary in consistency, and thus in the amount of bounce, spin, and seam movement available to the bowler. Hard pitches are usually good to bat on because of high but even bounce. Dry pitches tend to deteriorate for batting as cracks often appear, and when this happens to the pitch, spinners can play a major role. Damp pitches, or pitches covered in grass (termed "green" pitches), allow good fast bowlers to extract extra bounce. Such pitches tend to offer help to fast bowlers throughout the match, but become better for batting as the game goes on. While players of other outdoor sports deal with similar variations of field surface and stadium covering, the size and shape of their fields are much more standardized. Other local factors, such as altitude and climate, can also significantly affect play. These physical variations create a distinctive set of playing conditions at each ground. A given ground may acquire a reputation as batsman friendly or bowler friendly if one or the other discipline notably benefits from its unique mix of elements. The absence of a standardized field affects not only how particular games play out, but the nature of team makeup and players' statistical records.
, has a duration of three to five days (there have been examples of "timeless" matches too); the latter, known as limited overs cricket because each team bowls a limit of typically 50 or 20 overs, has a planned duration of one day only (a match can be extended if necessary due to bad weather, etc.).
Typically, two-innings matches have at least six hours of playing time
each day. Limited overs matches often last six hours or more. There are usually formal intervals on each day for lunch and tea with brief informal breaks for drinks. There is also a short interval between innings. Historically, a form of cricket known as single wicket
had been extremely successful and many of these contests in the 18th and 19th centuries qualify as major cricket matches. In this form, although each team may have from one to six players, there is only one batsman at a time and he must face every delivery bowled while his innings lasts. Single wicket has rarely been played since limited overs cricket began.
 Test cricket
Test cricket
is the highest standard of first-class cricket. A Test match is an international fixture between teams representing those countries that are Full Members of the ICC.
Although the term "Test match" was not coined until much later, Test cricket is deemed to have begun with two matches between Australia and England in the 1876–77 Australian season. Subsequently, eight other national teams have achieved Test status: South Africa (1889), West Indies (1928), New Zealand (1929), India (1932), Pakistan (1952), Sri Lanka (1982), Zimbabwe (1992) and Bangladesh (2000). Zimbabwe suspended its Test status in 2006 due to its inability to compete against other Test teams, and returned in 2011.
Welsh players are eligible to play for England, which is in effect an England and Wales team. The West Indies team comprises players from numerous states in the Caribbean, notably Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, Trinidad & Tobago, the Leeward Islands and the Windward Islands.
Test matches between two teams are usually played in a group of matches called a "series". Matches last up to five days and a series normally consists of three to five matches. Test matches that are not finished within the allotted time are drawn. In the case of Test
and first-class cricket
: the possibility of a draw often encourages a team that is batting last and well behind to bat defensively, giving up any faint chance at a win to avoid a loss.
Since 1882, most Test series between England and Australia have been played for a trophy known as The Ashes
. Some other bilateral series have individual trophies too: for example, the Wisden Trophy
is contested by England and West Indies; the Frank Worrell Trophy
by Australia and West Indies and the Border-Gavaskar Trophy
between India and Australia.
 Standard limited overs cricket was introduced in England in the 1963 season in the form of a knockout cup contested by the first-class county clubs. In 1969, a national league competition was established. The concept was gradually introduced to the other major cricket countries and the first limited overs international was played in 1971. In 1975, the first Cricket World Cup
Standard limited overs cricket was introduced in England in the 1963 season in the form of a knockout cup contested by the first-class county clubs. In 1969, a national league competition was established. The concept was gradually introduced to the other major cricket countries and the first limited overs international was played in 1971. In 1975, the first Cricket World Cup
took place in England. Limited overs cricket has seen various innovations including the use of multi-coloured kit and floodlit matches using a white ball.
A "one day match", named so because each match is scheduled for completion in a single day, is the common form of limited overs cricket played on an international level. In practice, matches sometimes continue on a second day if they have been interrupted or postponed by bad weather. The main objective of a limited overs match is to produce a definite result and so a conventional draw is not possible, but matches can be undecided if the scores are tied or if bad weather prevents a result. Each team plays one innings only and faces a limited number of overs, usually a maximum of 50. The Cricket World Cup
is held in one day format and the last World Cup
in 2011 was won by the co-hosts, India. The next World Cup
will hosted by Australia
and New Zealand
in 2015.
Twenty20
is a new variant of limited overs itself with the purpose being to complete the match within about three hours, usually in an evening session. The original idea, when the concept was introduced in England in 2003, was to provide workers with an evening entertainment. It was commercially successful and has been adopted internationally. The inaugural Twenty20 World Championship was held in 2007 and won by India. 2009's Twenty20 World Championship
was staged in England and won by Pakistan. The next Twenty20 World Championship will be held in the West Indies. After the inaugural ICC World Twenty20
many domestic Twenty20 leagues were born. First of them was Indian Cricket League
which is a rebel league since it is unauthorized by BCCI
and led to form an official league called the Indian Premier League
. Both these leagues are cash rich and attracted players and audience around the globe. Recently Twenty20 Champions League
was formed as a tournament for domestic clubs of various countries.
 First-class cricket
First-class cricket
includes Test cricket but the term is generally used to refer to the highest level of domestic cricket in those countries with full ICC membership, although there are exceptions to this. First-class cricket in England is played for the most part by the 18 county clubs which contest the County Championship
. The concept of a champion county has existed since the 18th century but the official competition was not established until 1890. The most successful club has been Yorkshire County Cricket Club
with 30 official titles.
Australia established its national first-class championship in 1892–93 when the Sheffield Shield was introduced. In Australia, the first-class teams represent the various states. New South Wales has won the maximum number of titles with 45 to 2008.
National championship trophies to be established elsewhere included the Ranji Trophy
(India), Plunket Shield (New Zealand), Currie Cup
(South Africa) and Shell Shield (West Indies). Some of these competitions have been updated and renamed in recent years.
Domestic limited overs competitions began with England's Gillette Cup knockout in 1963. Countries usually stage seasonal limited overs competitions in both knockout and league format. In recent years, national Twenty20 competitions have been introduced, usually in knockout form though some incorporate mini-leagues.
, French cricket
, beach cricket
, Kwik cricket
and all sorts of card games and board games that have been inspired by cricket. In these variants, the rules are often changed to make the game playable with limited resources or to render it more convenient and enjoyable for the participants.
Indoor cricket
is played in a netted, indoor arena, and is quite formal but many of the outdoor variants are very informal.
Families and teenagers play backyard cricket in suburban yards or driveways, and the cities of India and Pakistan play host to countless games of "Gully Cricket" or "tapeball" in their long narrow streets. Sometimes the rules are improvised: e.g. it may be agreed that fielders can catch the ball with one hand after one bounce and claim a wicket; or if only a few people are available then everyone may field while the players take it in turns to bat and bowl. Tennis balls and homemade bats are often used, and a variety of objects may serve as wickets: for example, the batter's legs as in French cricket
, which did not in fact originate in France, and is usually played by small children.
In Kwik cricket
, the bowler does not have to wait for the batsman to be ready before a delivery, leading to a faster, more exhausting game designed to appeal to children, which is often used PE lessons at English schools. Another modification to increase the pace of the game is the "Tip and Run", "Tipity" Run, "Tipsy Run" or "Tippy-Go" rule, in which the batter must run when the ball touches the bat, even if it the contact is unintentional or minor. This rule, seen only in impromptu games, speeds the match up by removing the batsman's right to block the ball.
In Samoa a form of cricket called Kilikiti
is played in which hockey stick
-shaped bats are used. In original English cricket, the hockey stick shape was replaced by the modern straight bat in the 1760s after bowlers began to pitch the ball instead of rolling or skimming it. In Estonia
, teams gather over the winter for the annual Ice Cricket
tournament. The game juxtaposes the normal summer pursuit with harsh, wintry conditions. Rules are otherwise similar to those for the six-a-side game.
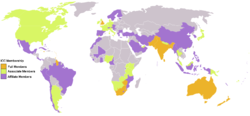 The International Cricket Council (ICC), which has its headquarters in Dubai, is the international governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1909 by representatives from England, Australia and South Africa, renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1965, and took up its current name in 1989.
The International Cricket Council (ICC), which has its headquarters in Dubai, is the international governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1909 by representatives from England, Australia and South Africa, renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1965, and took up its current name in 1989.
The ICC has 104 members: 10 Full Members that play official Test matches, 34 Associate Members, and 60 Affiliate Members. The ICC is responsible for the organisation and governance of cricket's major international tournaments, notably the Cricket World Cup. It also appoints the umpires and referees that officiate at all sanctioned Test matches, One Day International and Twenty20 Internationals. Each nation has a national cricket board which regulates cricket matches played in its country. The cricket board also selects the national squad and organises home and away tours for the national team. In the West Indies these matters are addressed by the West Indies Cricket Board
which consists of members appointed by four national boards and two multi-national boards.
and Twenty20 International
s. West Indies cricket team does not represent one country instead an amalgamation of over 20 countries from the Caribbean
. The English Cricket team represents both England and Wales.
AResigned May 1961, readmitted 10 July 1991.
, however ICC
grants One Day International status to its associate and affiliate members based on their success in the World Cricket League
. The top six teams will be awarded One day international and Twenty20 International
status, which will allow the associate and affiliate teams to be eligible to play the full members and play official ODI cricket.
The associate and affiliate teams who currently hold ODI and T20I
status:
to a greater degree than many other sports. Each play is discrete and has a relatively small number of possible outcomes. At the professional level, statistics for Test cricket, one-day internationals, and first-class cricket are recorded separately. However, since Test matches are a form of first-class cricket, a player's first-class statistics will include his Test match statistics—but not vice versa. The Guide to Cricketers
was a cricket annual edited by Fred Lillywhite
between 1849 and his death in 1866. Wisden Cricketers' Almanack
was founded in 1864 by the English cricketer John Wisden
(1826–1884) as a competitor to The Guide to Cricketers. Its annual publication has continued uninterrupted to the present day, making it the longest running sports annual in history.
Certain traditional statistics are familiar to most cricket fans. The basic batting statistics include:
The basic bowling statistics include:
and elsewhere. Cricket has had an influence on the lexicon of these nations, especially the English language, with such phrases as "that's not cricket" (unfair), "had a good innings", "sticky wicket", and "bowled over". There have been many cricket films. The term "Bradmanesque" from Don Bradman's name has become a generic term for outstanding excellence, both within cricket and in the wider world. The amateur game has also been spread further afield by expatriates from the Test-playing nations. In the late 19th century, a former cricket player, English-born Henry Chadwick of Brooklyn
, New York
, was responsible for the "development of the box score
, tabular standings, the annual baseball guide, the batting average
, and most of the common statistics and tables used to describe baseball". The statistical record is so central to the game's "historical essence" that Chadwick came to be known as Father Baseball.
Bat-and-ball games
Bat-and-ball games are field games played by two teams. The teams alternate between "batting" roles, sometimes called "in at bat" and "out in the field", or simply in and out. Only the batting team may score, so the fielding team is defending, but they have equal chances in both roles...
game played between two teams of 11 players on an oval-shaped field
Cricket field
A cricket field consists of a large circular or oval-shaped grassy ground on which the game of cricket is played. There are no fixed dimensions for the field but its diameter usually varies between 450 feet to 500 feet...
, at the centre of which is a rectangular 22-yard long pitch
Cricket pitch
In the game of cricket, the cricket pitch consists of the central strip of the cricket field between the wickets - 1 chain or 22 yards long and 10 feet wide. The surface is very flat and normally covered with extremely short grass though this grass is soon removed by wear at the ends of the...
. One team bats, trying to score as many runs
Run (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, a run is the basic unit of scoring. Runs are scored by a batsman, and the aggregate of the scores of a team's batsmen constitutes the team's score. A batsman scoring 50 or 100 runs , or any higher multiple of 50 runs, is considered a particular achievement...
as possible while the other team bowls
Bowling (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, bowling is the action of propelling the ball toward the wicket defended by a batsman. A player skilled at bowling is called a bowler; a bowler who is also a competent batsman is known as an all-rounder...
and fields
Fielding (cricket)
Fielding in the sport of cricket is the action of fielders in collecting the ball after it is struck by the batsman, in such a way as to either limit the number of runs that the batsman scores or get the batsman out by catching the ball in flight or running the batsman out.Cricket fielding position...
, trying to dismiss
Dismissal (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, a dismissal occurs when the batsman is out . Colloquially, the fielding team is also said to have snared, bagged or captured a wicket. At this point a batsman must discontinue batting and leave the field permanently for the innings...
the batsmen and thus limit the runs scored by the batting team. A run is scored by the striking batsman hitting the ball with his bat, running to the opposite end of the pitch and touching the crease
Crease (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, the crease is a certain area demarcated by white lines painted or chalked on the field of play.The term crease also refers to any of the lines themselves, particularly the popping crease. Law 9 of the Laws of Cricket governs the size and position of the crease markings...
there without being dismissed. The teams switch between batting and fielding at the end of an innings
Innings
An inning, or innings, is a fixed-length segment of a game in any of a variety of sports – most notably cricket and baseball during which one team attempts to score while the other team attempts to prevent the first from scoring. In cricket, the term innings is both singular and plural and is...
.
In professional cricket the length of a game ranges from 20 overs
Twenty20
Twenty20 is a form of cricket, originally introduced in England for professional inter-county competition by the England and Wales Cricket Board , in 2003. A Twenty20 game involves two teams, each has a single innings, batting for a maximum of 20 overs. Twenty20 cricket is also known as T20 cricket...
of six bowling deliveries per side to Test cricket
Test cricket
Test cricket is the longest form of the sport of cricket. Test matches are played between national representative teams with "Test status", as determined by the International Cricket Council , with four innings played between two teams of 11 players over a period of up to a maximum five days...
played over five days. The Laws of Cricket
Laws of cricket
The laws of cricket are a set of rules established by the Marylebone Cricket Club which describe the laws of cricket worldwide, to ensure uniformity and fairness. There are currently 42 laws, which outline all aspects of how the game is played from how a team wins a game, how a batsman is...
are maintained by the International Cricket Council
International Cricket Council
The International Cricket Council is the international governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1909 by representatives from England, Australia and South Africa, renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1965, and took up its current name in 1989.The...
(ICC) and the Marylebone Cricket Club
Marylebone Cricket Club
Marylebone Cricket Club is a cricket club in London founded in 1787. Its influence and longevity now witness it as a private members' club dedicated to the development of cricket. It owns, and is based at, Lord's Cricket Ground in St John's Wood, London NW8. MCC was formerly the governing body of...
(MCC) with additional Standard Playing Conditions for Test matches and One Day Internationals.
Cricket was first played in southern England in the 16th century. By the end of the 18th century, it had developed into the national sport of England. The expansion of the British Empire led to cricket being played overseas and by the mid-19th century the first international matches were being held. The ICC, the game's governing body, has ten full members. The game is played particularly in Australasia
Australasia
Australasia is a region of Oceania comprising Australia, New Zealand, the island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes...
, the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, the West Indies, Southern Africa and England.
History
Early cricket was at some time or another described as "a club striking a ball (like) the ancient games of club-ball, stool-ball, trap-ball, stob-ball". Cricket can definitely be traced back to Tudor times in early 16th-century England. Written evidence exists of a game known as creag being played by Prince EdwardEdward II of England
Edward II , called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England from 1307 until he was deposed by his wife Isabella in January 1327. He was the sixth Plantagenet king, in a line that began with the reign of Henry II...
, the son of Edward I (Longshanks)
Edward I of England
Edward I , also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England from 1272 to 1307. The first son of Henry III, Edward was involved early in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included an outright rebellion by the English barons...
, at Newenden, Kent in 1301 and there has been speculation, but no evidence, that this was a form of cricket.
A number of other words have been suggested as sources for the term "cricket". In the earliest definite reference to the sport in 1598, it is called creckett. Given the strong medieval trade connections between south-east England and the County of Flanders
County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was one of the territories constituting the Low Countries. The county existed from 862 to 1795. It was one of the original secular fiefs of France and for centuries was one of the most affluent regions in Europe....
when the latter belonged to the Duchy of Burgundy
Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy , was heir to an ancient and prestigious reputation and a large division of the lands of the Second Kingdom of Burgundy and in its own right was one of the geographically larger ducal territories in the emergence of Early Modern Europe from Medieval Europe.Even in that...
, the name may have been derived from the Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects which were spoken and written between 1150 and 1500...
krick(-e), meaning a stick (crook); or the Old English
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
cricc or cryce meaning a crutch or staff. In Old French
Old French
Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
, the word criquet seems to have meant a kind of club or stick. In Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson , often referred to as Dr. Johnson, was an English author who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, essayist, moralist, literary critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer...
's Dictionary, he derived cricket from "cryce, Saxon, a stick". Another possible source is the Middle Dutch word krickstoel, meaning a long low stool used for kneeling in church and which resembled the long low wicket
Wicket
In the sport of cricket the word wicket has several distinct meanings:-Definitions of wicket:Most of the time, the wicket is one of the two sets of three stumps and two bails at either end of the pitch...
with two stumps
Stump (cricket)
Stump is a term used in the sport of cricket where it has three different meanings:# part of the wicket# a manner of dismissing a batsman# the end of the day's play .-Part of the wicket:...
used in early cricket. According to Heiner Gillmeister, a European language expert of Bonn University, "cricket" derives from the Middle Dutch phrase for hockey
Hockey
Hockey is a family of sports in which two teams play against each other by trying to maneuver a ball or a puck into the opponent's goal using a hockey stick.-Etymology:...
, met de (krik ket)sen (i.e., "with the stick chase"). Dr Gillmeister believes that not only the name but the sport itself is of Flemish origin.

Guildford
Guildford is the county town of Surrey. England, as well as the seat for the borough of Guildford and the administrative headquarters of the South East England region...
, Surrey, around 1550. The court in Guildford heard on Monday, 17 January 1597 (Julian date, equating to the year 1598 in the Gregorian calendar) from a 59 year-old coroner
Coroner
A coroner is a government official who* Investigates human deaths* Determines cause of death* Issues death certificates* Maintains death records* Responds to deaths in mass disasters* Identifies unknown dead* Other functions depending on local laws...
, John Derrick
John Derrick
John Derrick is a former Welsh cricketer who played for Glamorgan. He also spent some time in New Zealand with Northern Districts....
, who gave witness that when he was a scholar at the "Free School at Guildford", fifty years earlier, "hee and diverse of his fellows did runne and play [on the common land] at creckett and other plaies." It is believed that it was originally a children's game but references around 1610 indicate that adults had started playing it and the earliest reference to inter-parish or village cricket
Village cricket
Village cricket is a term, sometimes pejorative, given to the playing of cricket in rural villages in England. Many villages have their own teams that play at varying levels of the English cricket pyramid....
occurs soon afterwards. In 1624, a player called Jasper Vinall
Jasper Vinall
Jasper Vinall was the first cricketer known to have been killed while playing the game.-Incident:...
was killed when he was struck on the head during a match between two parish teams in Sussex.
During the 17th century, numerous references indicate the growth of cricket in the south-east of England. By the end of the century, it had become an organised activity being played for high stakes and it is believed that the first professionals appeared in the years following the Restoration
English Restoration
The Restoration of the English monarchy began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Interregnum that followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms...
in 1660. A newspaper report survives of "a great cricket match" with eleven players a side that was played for high stakes in Sussex in 1697 and this is the earliest known reference to a cricket match of such importance.
The game underwent major development in the 18th century and became the national sport of England. Betting played a major part in that development with rich patrons forming their own "select XIs". Cricket was prominent in London as early as 1707 and large crowds flocked to matches on the Artillery Ground
Artillery Ground
The Artillery Ground in Finsbury is one of London's most centrally located cricket grounds, situated just off the City Road immediately north of the City of London...
in Finsbury. The single wicket
Single Wicket
Single wicket cricket is a form of cricket played between two individuals, who take turns to bat and bowl against each other. The one bowling is assisted by a team of fielders, who remain as fielders at the change of innings. The winner is the one who scores more runs...
form of the sport attracted huge crowds and wagers to match. Bowling evolved around 1760 when bowlers began to pitch the ball instead of rolling or skimming it towards the batsman. This caused a revolution in bat design because, to deal with the bouncing ball, it was necessary to introduce the modern straight bat in place of the old "hockey stick" shape. The Hambledon Club
Hambledon Club
The Hambledon Club was a social club that is famous for its organisation of 18th century cricket matches. By the late 1770s it was the foremost cricket club in England.-Foundation:...
was founded in the 1760s and, for the next 20 years until the formation of MCC
Marylebone Cricket Club
Marylebone Cricket Club is a cricket club in London founded in 1787. Its influence and longevity now witness it as a private members' club dedicated to the development of cricket. It owns, and is based at, Lord's Cricket Ground in St John's Wood, London NW8. MCC was formerly the governing body of...
and the opening of Lord's Old Ground
Lord's Old Ground
Lord's Old Ground was a cricket venue in London that was established by Thomas Lord in 1787. It was used mainly by Marylebone Cricket Club for major cricket matches until 1810, after which a dispute about rent caused Lord to relocate.-Matches:...
in 1787, Hambledon was both the game's greatest club and its focal point. MCC quickly became the sport's premier club and the custodian of the Laws of Cricket
Laws of cricket
The laws of cricket are a set of rules established by the Marylebone Cricket Club which describe the laws of cricket worldwide, to ensure uniformity and fairness. There are currently 42 laws, which outline all aspects of how the game is played from how a team wins a game, how a batsman is...
. New Laws introduced in the latter part of the 18th century included the three stump wicket and leg before wicket (lbw).

Underarm bowling
In cricket, underarm bowling is as old as the sport itself. Until the introduction of the roundarm style in the first half of the 19th century, bowling was performed in the same way as in bowls, the ball being delivered with the hand below the waist...
replaced by first roundarm
Roundarm bowling
In cricket, roundarm bowling is a style that was introduced in the first quarter of the 19th century and had largely superseded underarm bowling by the 1830s. Using a roundarm action, the bowler has his arm extended at about 90 degrees from his body at the point where he releases the ball...
and then overarm bowling
Overarm bowling
In cricket, overarm bowling refers to a delivery in which the bowler's hand is above shoulder height. This is in contrast to a roundarm delivery, where the hand is between shoulder height and waist height; and an underarm delivery where the bowler's hand is below waist height.After roundarm was...
. Both developments were controversial. Organisation of the game at county level led to the creation of the county clubs, starting with Sussex CCC in 1839, which ultimately formed the official County Championship
County Championship
The County Championship is the domestic first-class cricket competition in England and Wales...
in 1890. Meanwhile, the British Empire had been instrumental in spreading the game overseas and by the middle of the 19th century it had become well established in India, North America, the Caribbean, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand. In 1844, the first international cricket match
United States v Canada (1844)
The Canadian cricket team in the United States in 1844 was the first international team to travel to another country and the match between the two national sides that year, billed as "United States of America versus the British Empire's Canadian Province", was the first official international...
took place between the United States and Canada (although neither has ever been ranked as a Test-playing nation).
In 1859, a team of England players went on the first overseas tour (to North America). The first Australian team to tour overseas was a team of Aboriginal
Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are the original inhabitants of the Australian continent and nearby islands. The Aboriginal Indigenous Australians migrated from the Indian continent around 75,000 to 100,000 years ago....
stockmen who travelled to England in 1868 to play matches against county teams. In 1862, an English team made the first tour of Australia and in 1876–77, an England team took part in the first-ever Test match
Test cricket
Test cricket is the longest form of the sport of cricket. Test matches are played between national representative teams with "Test status", as determined by the International Cricket Council , with four innings played between two teams of 11 players over a period of up to a maximum five days...
at the Melbourne Cricket Ground
Melbourne Cricket Ground
The Melbourne Cricket Ground is an Australian sports stadium located in Yarra Park, Melbourne and is home to the Melbourne Cricket Club. It is the tenth largest stadium in the world, the largest in Australia, the largest stadium for playing cricket, and holds the world record for the highest light...
against Australia.
W G Grace started his long career in 1865; his career is often said to have revolutionised the sport. The rivalry between England and Australia gave birth to The Ashes
The Ashes
The Ashes is a Test cricket series played between England and Australia. It is one of the most celebrated rivalries in international cricket and dates back to 1882. It is currently played biennially, alternately in the United Kingdom and Australia. Cricket being a summer sport, and the venues...
in 1882 and this has remained Test cricket's most famous contest . Test cricket began to expand in 1888–89 when South Africa played England. The last two decades before the First World War
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
have been called the "Golden Age of cricket
Golden Age of cricket
The Golden Age of Cricket is a term that has often been applied in cricket literature to the period in English, Australian, and American cricket from the formation of the official County Championship in the 1890 season to the outbreak of World War I, which occurred just before the scheduled end of...
". It is a nostalgic name prompted by the collective sense of loss resulting from the war, but the period did produce some great players and memorable matches, especially as organised competition at county and Test level developed.
The inter-war years were dominated by one player: Australia's Don Bradman, statistically the greatest batsman of all time. It was the determination of the England team to overcome his skill that brought about the infamous Bodyline
Bodyline
Bodyline, also known as fast leg theory bowling, was a cricketing tactic devised by the English cricket team for their 1932–33 Ashes tour of Australia, specifically to combat the extraordinary batting skill of Australia's Don Bradman...
series in 1932–33, particularly from the accurate short-pitched bowling of Harold Larwood
Harold Larwood
Harold Larwood was an English cricket player, an extremely accurate fast bowler best known for his key role as the implementer of fast leg theory in the infamous "bodyline" Ashes Test series of 1932–33....
. Test cricket continued to expand during the 20th century with the addition of the West Indies, India, and New Zealand before the Second World War
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
and then Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh in the post-war period. However, South Africa was banned from international cricket from 1970 to 1992 because of its government's apartheid policy.
Cricket entered a new era in 1963 when English counties introduced the limited overs variant. As it was sure to produce a result, limited overs cricket was lucrative and the number of matches increased. The first Limited Overs International was played in 1971. The governing International Cricket Council
International Cricket Council
The International Cricket Council is the international governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1909 by representatives from England, Australia and South Africa, renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1965, and took up its current name in 1989.The...
(ICC) saw its potential and staged the first limited overs Cricket World Cup
Cricket World Cup
The ICC Cricket World Cup is the premier international championship of men's One Day International cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council , with preliminary qualification rounds leading up to a finals tournament which is held every four years...
in 1975. In the 21st century, a new limited overs form, Twenty20
Twenty20
Twenty20 is a form of cricket, originally introduced in England for professional inter-county competition by the England and Wales Cricket Board , in 2003. A Twenty20 game involves two teams, each has a single innings, batting for a maximum of 20 overs. Twenty20 cricket is also known as T20 cricket...
, has made an immediate impact.
Rules and game-play

Summary
A cricket match is played between two teams of eleven players each on a grassyLawn
A lawn is an area of aesthetic and recreational land planted with grasses or other durable plants, which usually are maintained at a low and consistent height. Low ornamental meadows in natural landscaping styles are a contemporary option of a lawn...
field
Cricket field
A cricket field consists of a large circular or oval-shaped grassy ground on which the game of cricket is played. There are no fixed dimensions for the field but its diameter usually varies between 450 feet to 500 feet...
, typically 137–150 m (149.8–164 yd) in diameter. The Laws of Cricket do not specify the size or shape of the field but it is often oval.
A cricket match is divided into periods called innings. During an innings (innings ends with 's' in both singular and plural form), one team plays defense (the fielding team) and the other offense (the batting team). The two teams switch between fielding and batting after each innings. All eleven members of the fielding team take the field, but only two members of the batting team (two batsmen) are on the field at any given time.
The key action takes place in the pitch
Cricket pitch
In the game of cricket, the cricket pitch consists of the central strip of the cricket field between the wickets - 1 chain or 22 yards long and 10 feet wide. The surface is very flat and normally covered with extremely short grass though this grass is soon removed by wear at the ends of the...
, a rectangular strip in the centre of the field. The two batsmen face each other at opposite ends of the pitch. The fielding team's eleven members stand outside the pitch, spread out across the field.
Behind each batsman is a target called a wicket. One designated member of the fielding team, called the bowler, is given a ball, and attempts to throw (bowl) the ball from one end of the pitch to the wicket behind the batsman on the other side of the pitch. The batsman tries to prevent the ball from hitting the wicket by striking the ball with a bat. If the bowler succeeds in hitting the wicket, or if the ball, after being struck by the batsman, is caught by the fielding team before it touches the ground, the batsman is dismissed. A dismissed batsman must leave the field, to be replaced by another batsman from the batting team.
If the batsman is successful in striking the ball and the ball isn't caught before it hits the ground, the two batsmen may then try to score points (runs) for their team by running across the pitch, switching positions. Each switch of positions is worth one run. The batsmen may attempt multiple runs or they may attempt no runs. By attempting runs, the batsmen risk dismissal, which can happen if the fielding team retrieves the ball and hits a wicket with the ball before a batsman has reached that end of the pitch.
If the batsman hits the bowled ball over the field boundary without the ball touching the field, the batting team scores six runs and may not attempt more. If the ball touches the ground and then reaches the boundary, the batting team scores four runs and may not attempt more. When the batsmen have finished attempting their runs, the ball is returned to the bowler to be bowled again. The bowler continues to bowl toward the same wicket, regardless of any switch of the batsmen's positions.
After a bowler has bowled six times (an over), another member of the fielding team is designated as the new bowler. The new bowler bowls to the opposite wicket, and play continues. Fielding team members may bowl multiple times during an innings, but may not bowl two overs in succession.
The innings is complete when 10 of the 11 members of the batting team have been dismissed or a set number of overs has been played. The number of innings and the number of overs per innings vary depending on the match.
Objectives
The objective of each team is to score more runsRun (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, a run is the basic unit of scoring. Runs are scored by a batsman, and the aggregate of the scores of a team's batsmen constitutes the team's score. A batsman scoring 50 or 100 runs , or any higher multiple of 50 runs, is considered a particular achievement...
than the other team and to completely dismiss
Dismissal (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, a dismissal occurs when the batsman is out . Colloquially, the fielding team is also said to have snared, bagged or captured a wicket. At this point a batsman must discontinue batting and leave the field permanently for the innings...
the other team. In limited overs cricket, winning the game is achieved by scoring the most runs, even if the opposition has not been completely dismissed. In Test cricket, it is necessary to score the most runs and dismiss the opposition twice in order to win the match, which would otherwise be drawn.
Pitch, wickets and creases

Wicket
In the sport of cricket the word wicket has several distinct meanings:-Definitions of wicket:Most of the time, the wicket is one of the two sets of three stumps and two bails at either end of the pitch...
s. These serve as a target for the bowling
Bowling (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, bowling is the action of propelling the ball toward the wicket defended by a batsman. A player skilled at bowling is called a bowler; a bowler who is also a competent batsman is known as an all-rounder...
(aka fielding
Fielding (cricket)
Fielding in the sport of cricket is the action of fielders in collecting the ball after it is struck by the batsman, in such a way as to either limit the number of runs that the batsman scores or get the batsman out by catching the ball in flight or running the batsman out.Cricket fielding position...
) side and are defended by the batting
Batting (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, batting is the act or skill of hitting the cricket ball with a cricket bat to score runs or prevent the loss of one's wicket. A player who is currently batting is denoted as a batsman, while the act of hitting the ball is called a shot or stroke...
side which seeks to accumulate runs. The pitch
Cricket pitch
In the game of cricket, the cricket pitch consists of the central strip of the cricket field between the wickets - 1 chain or 22 yards long and 10 feet wide. The surface is very flat and normally covered with extremely short grass though this grass is soon removed by wear at the ends of the...
is 22 yards (20.1 m) or one chain in length between the wickets and is 10 feet (3 m) wide. It is a flat surface and has very short grass that tends to be worn away as the game progresses. The "condition" of the pitch has a significant bearing on the match and team tactics are always determined with the state of the pitch, both current and anticipated, as a deciding factor.
Each wicket consists of three wooden stumps
Stump (cricket)
Stump is a term used in the sport of cricket where it has three different meanings:# part of the wicket# a manner of dismissing a batsman# the end of the day's play .-Part of the wicket:...
placed in a straight line and surmounted by two wooden crosspieces called bails
Bail (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, a bail is one of the two smaller sticks placed on top of the three stumps to form a wicket. The bails are used to determine when the wicket is broken, which in turn is one of the critical factors in determining whether a batsman is out bowled, stumped, run out or hit wicket...
; the total height of the wicket including bails is 28.5 inches (72.4 cm) and the combined width of the three stumps is 9 inches (22.9 cm).


When bowling the ball, the bowler's back foot in his "delivery stride" must land within the two return creases while his front foot must land on or behind the popping crease. If the bowler breaks this rule, the umpire calls "No ball".
The importance of the popping crease to the batsman is that it marks the limit of his safe territory for he can be stumped or run out (see Dismissals below) if the wicket is broken while he is "out of his ground".
Bat and ball
The essence of the sport is that a bowler delivers the ball from his end of the pitch towards the batsman who, armed with a bat is "on strike" at the other end.The bat
Cricket bat
A cricket bat is a specialised piece of equipment used by batsmen in the sport of cricket to hit the ball. It is usually made of willow wood. Its use is first mentioned in 1624....
is made of wood (usually White Willow
White Willow
Salix alba is a species of willow native to Europe and western and central Asia. The name derives from the white tone to the undersides of the leaves....
) and has the shape of a blade topped by a cylindrical handle. The blade must not be more than 4.25 inches (10.8 cm) wide and the total length of the bat not more than 38 inches (96.5 cm).
The ball
Cricket ball
A cricket ball is a hard, solid leather ball used to play cricket. Constructed of cork and leather, a cricket ball is heavily regulated by cricket law at first class level...
is a hard leather-seamed spheroid
Spheroid
A spheroid, or ellipsoid of revolution is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters....
with a circumference of 9 inches (22.9 cm). The hardness of the ball, which can be delivered at speeds of more than 90 miles per hour (40.2 m/s), is a matter for concern and batsmen wear protective clothing including pads (designed to protect the knees and shins), batting gloves
Batting gloves
Batting gloves are a component in baseball sportswear. The glove covers one or both hands of a batter, providing comfort, warmth, improved grip, and shock absorption when hitting the ball...
for the hands, a helmet
Helmet (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, batsmen often wear a helmet to protect themselves from injury by the cricket ball, which is very hard and can be bowled to them at speeds over ....
for the head and a box inside the trousers (to protect the crotch
Crotch
The term crotch may be used to describe the region of an object where it splits into two or more limbs. This can include trees, animals, buildings, in wiring diagrams, etc....
area). Some batsmen wear additional padding inside their shirts and trousers such as thigh pads, arm pads, rib protectors and shoulder pads.
Umpires and scorers
The game on the field is regulated by two umpiresUmpire (cricket)
In cricket, an umpire is a person who has the authority to make judgements on the cricket field, according to the Laws of Cricket...
, one of whom stands behind the wicket at the bowler's end, the other in a position called "square leg", a position 15–20 metres to the side of the "on strike" batsman. When the bowler delivers the ball, the umpire at the wicket is between the bowler and the non-striker. The umpires confer if there is doubt about playing conditions and can postpone the match by taking the players off the field if necessary, for example rain or deterioration of the light.

Third umpire
In international cricket matches the third umpire is an off-field umpire who makes the final decision in questions referred to him by the two on-field umpires. Television replays are available to the third umpire to assist him in coming to a decision...
who can make decisions on certain incidents with the aid of video evidence. The third umpire is mandatory under the playing conditions for Test matches and limited overs internationals played between two ICC full members. These matches also have a match referee whose job is to ensure that play is within the Laws of cricket
Laws of cricket
The laws of cricket are a set of rules established by the Marylebone Cricket Club which describe the laws of cricket worldwide, to ensure uniformity and fairness. There are currently 42 laws, which outline all aspects of how the game is played from how a team wins a game, how a batsman is...
and the spirit of the game.
Off the field, the match details including runs and dismissals are recorded by two official scorer
Scorer
A scorer in the sport of cricket is someone appointed to record all runs scored, all wickets taken and, where appropriate, number of overs bowled. In professional games, in compliance with the Laws of Cricket, two scorers are appointed, most often one provided by each team.The scorers have no say...
s, one representing each team. The scorers are directed by the hand signals of an umpire. For example, the umpire raises a forefinger to signal that the batsman is out (has been dismissed); he raises both arms above his head if the batsman has hit the ball for six runs. The scorers are required by the Laws of cricket to record all runs scored, wickets taken and overs bowled. In practice, they accumulate much additional data such as bowling analyses and run rates.
Innings
The innings (ending with 's' in both singular and plural form) is the term used for the collective performance of the batting side. In theory, all eleven members of the batting side take a turn to bat but, for various reasons, an innings can end before they all do so.Depending on the type of match being played, each team has one or two innings apiece. The term "innings" is also sometimes used to describe an individual batsman's contribution ("he played a fine innings").
The main aim of the bowler, supported by his fielders, is to dismiss the batsman. A batsman when dismissed is said to be "out" and that means he must leave the field of play and be replaced by the next batsman on his team. When ten batsmen have been dismissed (i.e., are out), then the whole team is dismissed and the innings is over. The last batsman, the one who has not been dismissed, is not allowed to continue alone as there must always be two batsmen "in". This batsman is termed "not out".
An innings can end early for three reasons: because the batting side's captain has chosen to "declare" the innings closed (which is a tactical decision), or because the batting side has achieved its target and won the game, or because the game has ended prematurely due to bad weather or running out of time. In each of these cases the team's innings ends with two "not out" batsmen, unless the innings is declared closed at the fall of a wicket and the next batsman has not joined in the play.
In limited overs cricket, there might be two batsmen still "not out" when the last of the allotted overs has been bowled.
Overs
The bowler bowls the ball in sets of six deliveries (or "balls") and each set of six balls is called an overOver (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, an over is a set of six consecutive balls bowled in succession. An over is normally bowled by a single bowler. However, in the event of injury preventing a bowler from completing an over, it is completed by a teammate....
. This name came about because the umpire calls "Over!" when six balls have been bowled. At this point, another bowler is deployed at the other end, and the fielding side changes ends while the batsmen do not. A bowler cannot bowl two successive overs, although a bowler can bowl unchanged at the same end for several overs. The batsmen do not change ends and so the one who was non-striker is now the striker and vice-versa. The umpires also change positions so that the one who was at square leg now stands behind the wicket at the non-striker's end and vice-versa.
Team structure
A team consists of eleven players. Depending on his or her primary skills, a player may be classified as a specialist batsman or bowler. A well-balanced team usually has five or six specialist batsmen and four or five specialist bowlers. Teams nearly always include a specialist wicket-keeperWicket-keeper
The wicket-keeper in the sport of cricket is the player on the fielding side who stands behind the wicket or stumps being guarded by the batsman currently on strike...
because of the importance of this fielding position. Each team is headed by a captain
Captain (cricket)
The captain of a cricket team often referred to as the skipper is the appointed leader, having several additional roles and responsibilities over and above those of a regular player...
who is responsible for making tactical decisions such as determining the batting order, the placement of fielders and the rotation of bowlers.
A player who excels in both batting and bowling is known as an all-rounder
All-rounder
An all-rounder is a cricketer who regularly performs well at both batting and bowling. Although all bowlers must bat and quite a few batsmen do bowl occasionally, most players are skilled in only one of the two disciplines and are considered specialists...
. One who excels as a batsman and wicket-keeper is known as a "wicket-keeper/batsman", sometimes regarded as a type of all-rounder. True all-rounders are rare as most players focus on either batting or bowling skills.
Bowling
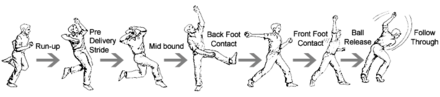
The fastest bowlers can deliver the ball at a speed of over 90 miles per hour (40.2 m/s) and they sometimes rely on sheer speed to try and defeat the batsman, who is forced to react very quickly. Other fast bowlers rely on a mixture of speed and guile. Some fast bowlers make use of the seam of the ball so that it "curves" or "swings" in flight. This type of delivery can deceive a batsman into mistiming his shot so that the ball touches the edge of the bat and can then be "caught behind" by the wicketkeeper or a slip fielder.
At the other end of the bowling scale is the "spinner" who bowls at a relatively slow pace and relies entirely on guile to deceive the batsman. A spinner will often "buy his wicket" by "tossing one up" (in a slower, higher parabolic
Parabolic trajectory
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics a parabolic trajectory is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity equal to 1. When moving away from the source it is called an escape orbit, otherwise a capture orbit...
path) to lure the batsman into making a poor shot. The batsman has to be very wary of such deliveries as they are often "flighted" or spun so that the ball will not behave quite as he expects and he could be "trapped" into getting himself out.
In between the pacemen and the spinners are the "medium pacers" who rely on persistent accuracy to try and contain the rate of scoring and wear down the batsman's concentration.
All bowlers are classified according to their looks or style. The classifications
Types of bowlers in cricket
In the sport of cricket there are two broad categories of bowlers: pace bowlers and spin bowlers. Pace bowlers rely mostly on the speed of the ball to dismiss batsmen, whereas spin bowlers rely on the rotation of the ball.-Pace bowlers:...
, as with much cricket terminology, can be very confusing. Hence, a bowler could be classified as LF, meaning he is a left arm fast bowler; or as LBG, meaning he is a right arm spin bowler who bowls deliveries that are called a "leg break
Leg break
A leg break is a type of delivery in the sport of cricket. A delivery of a right-handed leg spin bowler. Leg breaks are also colloquially known as leggies or wrist spinners, as the wrist is the body part which is primarily used to impart spin on the ball, as opposed to the fingers in the case of...
" and a "Googly
Googly
In cricket, a googly is a type of delivery bowled by a right-arm leg spin bowler. It is occasionally referred to as a Bosie , an eponym in honour of its inventor Bernard Bosanquet.- Explanation :...
".
During the bowling action the elbow may be held at any angle and may bend further, but may not straighten out. If the elbow straightens illegally then the square-leg umpire may call no-ball: this is known as "throwing" or "chucking", and can be difficult to detect. The current laws allow a bowler to straighten his arm 15 degrees or less.
Fielding

Wicket-keeper
The wicket-keeper in the sport of cricket is the player on the fielding side who stands behind the wicket or stumps being guarded by the batsman currently on strike...
aka "keeper" who operates behind the wicket being defended by the batsman on strike. Wicket-keeping is normally a specialist occupation and his primary job is to gather deliveries that the batsman does not hit, so that the batsmen cannot run byes. He wears special gloves (he is the only fielder allowed to do so), a box over the groin, and pads to cover his lower legs. Owing to his position directly behind the striker, the wicket-keeper has a good chance of getting a batsman out caught off a fine edge from the bat. He is the only player who can get a batsman out stumped
Stump (cricket)
Stump is a term used in the sport of cricket where it has three different meanings:# part of the wicket# a manner of dismissing a batsman# the end of the day's play .-Part of the wicket:...
.
Apart from the one currently bowling, the other nine fielders are tactically deployed by the team captain in chosen positions around the field. These positions are not fixed but they are known by specific and sometimes colourful names such as "slip", "third man", "silly mid on" and "long leg". There are always many unprotected areas.
The captain is the most important member of the fielding side as he determines all the tactics including who should bowl (and how); and he is responsible for "setting the field", though usually in consultation with the bowler.
In all forms of cricket, if a fielder gets injured or becomes ill during a match, a substitute
Substitute (cricket)
A substitute in the sport of cricket is a replacement player that the umpires allow when a player has been injured or become ill after the nomination of the players at the start of the game...
is allowed to field instead of him. The substitute cannot bowl, act as a captain or keep wicket. The substitute leaves the field when the injured player is fit to return.
Batting

Batsmen come in to bat in a batting order
Batting order (cricket)
In cricket, the batting order is the sequence in which batsmen play through their team's innings, there always being two batsmen taking part at any one time...
, decided by the team captain. The first two batsmen – the "openers" – usually face the hostile bowling from fresh fast bowlers with a new ball. The top batting positions are usually given to the most competent batsmen in the team, and the non-batsmen typically bat last. The pre-announced batting order is not mandatory and when a wicket falls any player who has not yet batted may be sent in next.
If a batsman "retires" (usually due to injury) and cannot return, he is actually "not out" and his retirement does not count as a dismissal, though in effect he has been dismissed because his innings is over. Substitute batsmen are not allowed.
A skilled batsman can use a wide array of "shots" or "strokes" in both defensive and attacking mode. The idea is to hit the ball to best effect with the flat surface of the bat's blade. If the ball touches the side of the bat it is called an "edge". Batsmen do not always seek to hit the ball as hard as possible, and a good player can score runs just by making a deft stroke with a turn of the wrists or by simply "blocking" the ball but directing it away from fielders so that he has time to take a run.
There is a wide variety of shots played in cricket. The batsman's repertoire includes strokes named according to the style of swing and the direction aimed: e.g., "cut", "drive", "hook", "pull".
Note that a batsman does not have to play a shot and can "leave" the ball to go through to the wicketkeeper, providing he thinks it will not hit his wicket. Equally, he does not have to attempt a run when he hits the ball with his bat. He can deliberately use his leg to block the ball and thereby "pad it away" but this is risky because of the leg before wicket
Leg before wicket
In the sport of cricket, leg before wicket is one of the ways in which a batsman can be dismissed. An umpire will rule a batsman out LBW under a series of circumstances which primarily include the ball striking the batsman's body when it would otherwise have continued on to hit the batsman's...
rule.
In the event of an injured batsman being fit to bat but not to run, the umpires and the fielding captain may allow another member of the batting side to be a runner
Runner (cricket)
In cricket, a runner is a team member who runs between the wickets for an injured batsman.When a runner is used, the batsman stands in position and plays shots as normal, but does not attempt to run between the wickets: the runner runs for him...
. The runner's only task is to run between the wickets instead of the injured batsman. The runner is required to wear and carry exactly the same equipment as the incapacitated batsman. It is possible for both batsmen to have runners.
Runs

Run (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, a run is the basic unit of scoring. Runs are scored by a batsman, and the aggregate of the scores of a team's batsmen constitutes the team's score. A batsman scoring 50 or 100 runs , or any higher multiple of 50 runs, is considered a particular achievement...
by hitting the ball with his bat so that he and his partner have time to run from one end of the pitch to the other before the fielding side can return the ball. To register a run, both runners must touch the ground behind the crease with either their bats or their bodies (the batsmen carry their bats as they run). Each completed run increments the score.
More than one run can be scored from a single hit; but, while hits worth one to three runs are common, the size of the field is such that it is usually difficult to run four or more. To compensate for this, hits that reach the boundary of the field are automatically awarded four runs if the ball touches the ground en route to the boundary or six runs if the ball clears the boundary on the full. The batsmen do not need to run if the ball reaches or crosses the boundary.

The decision to attempt a run is ideally made by the batsman who has the better view of the ball's progress, and this is communicated by calling: "yes", "no" and "wait" are often heard.
Running is a calculated risk because if a fielder breaks the wicket with the ball while the nearest batsman is out of his ground (i.e., he does not have part of his body or bat in contact with the ground behind the popping crease), the batsman is run out
Run out
Run out is a method of dismissal in the sport of cricket. It is governed by Law 38 of the Laws of cricket.-The rules:A batsman is out Run out if at any time while the ball is in play no part of his bat or person is grounded behind the popping crease and his wicket is fairly put down by the opposing...
.
A team's score is reported in terms of the number of runs scored and the number of batsmen that have been dismissed. For example, if five batsmen are out and the team has scored 224 runs, they are said to have scored 224 for the loss of 5 wickets (commonly shortened to "224 for five" and written 224/5 or, in Australia, "five for 224" and 5/224).
Extras
Additional runs can be gained by the batting team as extrasExtra (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, an extra is a run scored by a means other than a batsman hitting the ball.Other than runs scored off the bat from a no ball, a batsman is not given credit for extras and the extras are tallied separately on the scorecard and count only towards the team's score...
(called "sundries" in Australia) due to errors made by the fielding side. This is achieved in four ways:
- No ball: a penalty of one extra that is conceded by the bowler if he breaks the rules of bowling either by (a) using an inappropriate arm actionThrowing (cricket)In the sport of cricket, throwing, commonly referred to as chucking, is an illegal bowling action which occurs when a bowler straightens their arm when delivering the ball. The Laws of Cricket specify that a bowler's arm must be fully extended and rotated about the shoulder to impart velocity to...
; (b) overstepping the popping crease; (c) having a foot outside the return crease. In addition, the bowler has to re-bowl the ball. In limited overs matches, a no ball is called if the bowling team's field setting fails to comply with the restrictions. In shorter formats of the game (20–20, ODI) the free hit rule has been introduced. The ball following a front foot no-ball will be a free-hit for the batsman, whereby he is safe from losing his wicket except for being run-out. - Wide: a penalty of one extra that is conceded by the bowler if he bowls so that the ball is out of the batsman's reach; as with a no ball, a wide must be re-bowled.
- Bye: extra(s) awarded if the batsman misses the ball and it goes past the wicketkeeper to give the batsmen time to run in the conventional way (note that one mark of a good wicketkeeper is one who restricts the tally of byes to a minimum).
- Leg bye: extra(s) awarded if the ball hits the batsman's body, but not his bat, while attempting a legitimate shot, and it goes away from the fielders to give the batsmen time to run in the conventional way.
When the bowler has bowled a no ball or a wide, his team incurs an additional penalty because that ball (i.e., delivery) has to be bowled again and hence the batting side has the opportunity to score more runs from this extra ball. The batsmen have to run (i.e., unless the ball goes to the boundary for four) to claim byes and leg byes but these only count towards the team total, not to the striker's individual total for which runs must be scored off the bat.
Dismissals (outs)
There are ten ways in which a batsman can be dismissed and some are so unusual that only a few instances of them exist in the whole history of the game. The common forms of dismissal are "bowled", "caught", "leg before wicket" (lbw), "run out", and "stumped". The unusual methods are "hit wicket", "hit the ball twice", "obstructed the field", "handled the ball" and "timed out".Before the umpire will award a dismissal and declare the batsman to be out, a member of the fielding side (generally the bowler) must "appeal". This is invariably done by asking (or shouting) the term "Howzat?" which means, simply enough, "How is that?" If the umpire agrees with the appeal, he will raise a forefinger and say "Out!". Otherwise he will shake his head and say "Not out". Appeals are particularly loud when the circumstances of the claimed dismissal are unclear, as is always the case with lbw and often with run outs and stumpings.
- BowledBowledBowled is a method of dismissing a batsman in the sport of cricket. This method of dismissal is covered by Law 30 of the Laws of cricket.A batsman is out bowled if his wicket is put down by a ball delivered by the bowler...
: the bowler has hit the wicket with the ball and the wicket has "broken" with at least one bail being dislodged (note that if the ball hits the wicket without dislodging a bail it is not out). - Caught: the batsman has hit the ball with his bat, or with his hand which was holding the bat, and the ball has been caught before it has touched the ground by a member of the fielding side.
- Leg before wicketLeg before wicketIn the sport of cricket, leg before wicket is one of the ways in which a batsman can be dismissed. An umpire will rule a batsman out LBW under a series of circumstances which primarily include the ball striking the batsman's body when it would otherwise have continued on to hit the batsman's...
(lbw): first and foremost, the ball must, in the opinion of the on-field umpire, be going on to hit the stumps if the ball had not hit the pad of the batsman first. If the batsman plays an attempted shot to the delivery, then the ball must hit the batsman's pad in line with the stumps and be going on to hit the stumps for the batsman to be given out. If the batsman does not attempt to play a shot, then the ball does not have to hit the pad in line with the stumps but it still must be going on to hit the stumps. If the ball pitches outside the leg stump, then the batsman cannot be given out under any circumstances. - Run outRun outRun out is a method of dismissal in the sport of cricket. It is governed by Law 38 of the Laws of cricket.-The rules:A batsman is out Run out if at any time while the ball is in play no part of his bat or person is grounded behind the popping crease and his wicket is fairly put down by the opposing...
: a member of the fielding side has broken or "put down" the wicket with the ball while a batsman was out of his ground; this usually occurs by means of an accurate throw to the wicket while the batsmen are attempting a run, although a batsman can be given out Run out even when he is not attempting a run; he merely needs to be out of his ground. - Stumped is similar except that it is done by the wicketkeeper after the batsman has missed the bowled ball and has stepped out of his ground, and is not attempting a run.
- Hit wicketHit wicketHit wicket is a method of dismissal in the sport of cricket. This method of dismissal is governed by Law 35 of the laws of cricket. The striker is out "hit wicket" if, after the bowler has entered his delivery stride and while the ball is in play, his wicket is put down by his bat or his person...
: a batsman is out hit wicket, if he dislodges one or both bails with his bat, person, clothing or equipment in the act of receiving a ball, or in setting off for a run having just received a ball. - Hit the ball twiceHit the ball twiceHit the ball twice, or "double-hit", is a method of dismissal in the sport of cricket.-Definition:Law 34 of the Laws of cricket states:Law 34 1...
is very unusual and was introduced as a safety measure to counter dangerous play and protect the fielders. The batsman may legally play the ball a second time only to stop the ball hitting the wicket after he has already played it. - Obstructing the fieldObstructing the fieldObstructing the field is a rare method of dismissal in the sport of cricket.-Definition:Law 37 of the Laws of cricket provides that:"Either batsman is out Obstructing the field if he wilfully obstructs or distracts the opposing side by word or action...
: another unusual dismissal which tends to involve a batsman deliberately getting in the way of a fielder. - Handled the ballHandled the ballHandled the ball is a method of dismissal in the sport of cricket.-Definition:Law 33 of the Laws of cricket provides that:"Either batsman is out Handled the ball if he wilfully touches the ball while in play with a hand or hands not holding the bat unless he does so with the consent of the opposing...
: a batsman must not deliberately touch the ball with his hand, for example to protect his wicket. Note that the batsman's hand or glove counts as part of the bat while the hand is holding the bat, so batsmen are frequently caught off their gloves. - Timed outTimed outTimed out is a method of dismissal in the sport of cricket. It occurs when an incoming batsman is not ready to play within three minutes of the previous batsman being out...
usually means that the next batsman did not arrive at the wicket within three minutes of the previous one being dismissed.
In the vast majority of cases, it is the striker who is out when a dismissal occurs. If the non-striker is dismissed it is usually by being run out, but he could also be dismissed for obstructing the field, handling the ball or being timed out.
A batsman may leave the field without being dismissed. If injured or taken ill the batsman may temporarily retire, and be replaced by the next batsman. This is recorded as retired hurt
Substitute (cricket)
A substitute in the sport of cricket is a replacement player that the umpires allow when a player has been injured or become ill after the nomination of the players at the start of the game...
or retired ill
Substitute (cricket)
A substitute in the sport of cricket is a replacement player that the umpires allow when a player has been injured or become ill after the nomination of the players at the start of the game...
. The retiring batsman is not out, and may resume the innings later. An unimpaired batsman may retire, and this is treated as being dismissed retired out
Retired out
In cricket, a batsman retires out if he retires without the umpire's permission, and does not have the permission of the opposing captain to resume his innings. This occasionally happens in friendly or practice matches, for instance English county sides against University Centres of Cricketing...
; no player is credited with the dismissal. Batsmen cannot be out bowled, caught, leg before wicket, stumped or hit wicket off a no ball. They cannot be out bowled, caught, leg before wicket, or hit the ball twice off a wide. Some of these modes of dismissal can occur without the bowler bowling a delivery. The batsman who is not on strike may be run out by the bowler if he leaves his crease before the bowler bowls, and a batsman can be out obstructing the field or retired out at any time. Timed out is, by its nature, a dismissal without a delivery. With all other modes of dismissal, only one batsman can be dismissed per ball bowled.
Innings closed
An innings is closed when:- Ten of the eleven batsmen are out (have been dismissed); in this case, the team is said to be "all out"
- The team has only one batsman left who can bat, one or more of the remaining players being unavailable owing to injury, illness or absence; again, the team is said to be "all out"
- The team batting last reaches the score required to win the match
- The predetermined number of overs has been bowled (in a one-day match only, commonly 50 overs; or 20 in Twenty20Twenty20Twenty20 is a form of cricket, originally introduced in England for professional inter-county competition by the England and Wales Cricket Board , in 2003. A Twenty20 game involves two teams, each has a single innings, batting for a maximum of 20 overs. Twenty20 cricket is also known as T20 cricket...
) - A captain declaresDeclaration and forfeitureIn the sport of cricket a declaration occurs when a captain declares his team's innings closed and a forfeiture is when a captain chooses to forfeit an innings. Declaration and forfeiture are covered in Law 14 of the Laws of cricket...
his team's innings closed while at least two of his batsmen are not out (this does not apply in one-day limited over matches)
Results
If the team that bats last is all out having scored fewer runs than their opponents, the team is said to have "lost by n runs" (where n is the difference between the number of runs scored by the teams). If the team that bats last scores enough runs to win, it is said to have "won by n wickets", where n is the number of wickets left to fall. For instance a team that passes its opponents' score having only lost six wickets would have won "by four wickets".In a two-innings-a-side match, one team's combined first and second innings total may be less than the other side's first innings total. The team with the greater score is then said to have won by an innings and n runs, and does not need to bat again: n is the difference between the two teams' aggregate scores.
If the team batting last is all out, and both sides have scored the same number of runs, then the match is a tie; this result is quite rare in matches of two innings a side. In the traditional form of the game, if the time allotted for the match expires before either side can win, then the game is declared a draw.
If the match has only a single innings per side, then a maximum number of deliveries for each innings is often imposed. Such a match is called a "limited overs" or "one-day" match, and the side scoring more runs wins regardless of the number of wickets lost, so that a draw cannot occur. If this kind of match is temporarily interrupted by bad weather, then a complex mathematical formula, known as the Duckworth-Lewis method
Duckworth-Lewis method
In the sport of cricket, the Duckworth–Lewis method is a mathematical formulation designed to calculate the target score for the team batting second in a one-day cricket or Twenty20 cricket match interrupted by weather or other circumstance...
after its developers, is often used to recalculate a new target score. A one-day match can also be declared a "no-result" if fewer than a previously agreed number of overs have been bowled by either team, in circumstances that make normal resumption of play impossible; for example, wet weather.
Individual focus
For a team sport, cricket places individual players under unusual scrutiny and pressure. Bowler, Batsman, and fielder all act essentially independent of each other. While team managements can signal bowler or batsman to pursue certain tactics, the execution of the play itself is a series of solitary acts. Cricket is more similar to baseballBaseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each. The aim is to score runs by hitting a thrown ball with a bat and touching a series of four bases arranged at the corners of a ninety-foot diamond...
than many other team sports in this regard: while the individual focus in cricket is slightly mitigated by the importance of the batting partnership
Partnership (cricket)
In the sport of cricket, two batsmen always bat in partnership, although only one is on strike at any time. The partnership between two batsmen will come to an end when one of them is dismissed or retires, or the innings comes to a close In the sport of cricket, two batsmen always bat in...
and the practicalities of running, it is enhanced by the fact that a batsman may occupy the wicket
Wicket
In the sport of cricket the word wicket has several distinct meanings:-Definitions of wicket:Most of the time, the wicket is one of the two sets of three stumps and two bails at either end of the pitch...
for a long time.
Spirit of the Game
Cricket is a unique game where in addition to the laws, the players have to abide by the "Spirit of the Game". The standard of sportsmanship has historically been considered so high that the phrase "it's just not cricket" was coined in the 19th Century to describe unfair or underhanded behaviour in any walk of life. In the last few decades though, cricket has become increasingly fast-paced and competitive, increasing the use of appealing and sledgingSledging (cricket)
Sledging is a term used in cricket to describe the practice whereby some players seek to gain an advantage by insulting or verbally intimidating the opposing player. The purpose is to try to weaken the opponent's concentration, thereby causing him to make mistakes or underperform...
, although players are still expected to abide by the umpires' rulings without argument, and for the most part they do. Even in the modern game fielders are known to signal to the umpire that a boundary was hit, despite what could have been considered a spectacular save (though they might be found out by the TV replays anyway). In addition to this, some cricket batsmen, like Sachin Tendulkar
Sachin Tendulkar
Sachin Ramesh Tendulkar is an Indian cricketer widely regarded as one of the greatest batsmen in the history of cricket. He is the leading run-scorer and century maker in Test and one-day international cricket. He is the only male player to score a double century in the history of ODI cricket...
and Adam Gilchrist
Adam Gilchrist
Adam Craig Gilchrist AM , nicknamed "Gilly" or "Churchy", is an Australian international cricketer who currently captains Kings XI Punjab and recently captained Middlesex. He is an attacking left-handed batsman and record-breaking wicket-keeper, who redefined the role for the Australian national...
have been known to "walk" when they think they are out even if the umpire does not declare them out. This is a high level of sportsmanship, as a batsman can easily take advantage of incorrect umpiring decisions.
Influence of weather
Cricket is a sport played predominantly in the drier periods of the year. But, even so, the weather is a major factor in all cricket matches.A scheduled game of cricket cannot be played in wet weather. Dampness affects the bounce of the ball on the wicket and is a risk to all players involved in the game. Many grounds have facilities to cover the cricket pitch (or the wicket). Covers can be in the form of sheets being laid over the wicket to elevated covers on wheels (using the same concept as an umbrella) to even hover covers which form an airtight seal around the wicket. However, most grounds do not have the facilities to cover the outfield. This means that in the event of heavy bouts of bad weather, games may be cancelled, abandoned or suspended due to an unsafe outfield.
Another factor in cricket is the amount of light available. At grounds without floodlights (or in game formats which disallow the use of floodlights), umpires can stop play in the event of bad light as it becomes too difficult for the batsmen to be able to see the ball coming at them, (and in extreme cases, members of the fielding team).
On the other hand, in instances of good light, batsmen can utilize sight-screens which enable batsmen to have a white background against which they can pick out the red ball (or black background for white ball) with greater ease.
The umpires always have the final decision on weather related issues.
Uniqueness of each field
Unlike those of most sports, cricket playing fields can vary significantly in size and shape. While the dimensions of the pitch and infield are specifically regulated, the Laws of Cricket do not specify the size or shape of the field. The field boundariesBoundary (cricket)
Boundary has two distinct meanings in the sport of cricket:# the edge or boundary of the playing field, and# a manner of scoring runs.-Edge of the field:...
are sometimes painted and sometimes marked by a rope. Pitch and outfield variations can have a significant effect on how balls behave and are fielded as well as on batting. Pitches vary in consistency, and thus in the amount of bounce, spin, and seam movement available to the bowler. Hard pitches are usually good to bat on because of high but even bounce. Dry pitches tend to deteriorate for batting as cracks often appear, and when this happens to the pitch, spinners can play a major role. Damp pitches, or pitches covered in grass (termed "green" pitches), allow good fast bowlers to extract extra bounce. Such pitches tend to offer help to fast bowlers throughout the match, but become better for batting as the game goes on. While players of other outdoor sports deal with similar variations of field surface and stadium covering, the size and shape of their fields are much more standardized. Other local factors, such as altitude and climate, can also significantly affect play. These physical variations create a distinctive set of playing conditions at each ground. A given ground may acquire a reputation as batsman friendly or bowler friendly if one or the other discipline notably benefits from its unique mix of elements. The absence of a standardized field affects not only how particular games play out, but the nature of team makeup and players' statistical records.
Types of matches
Cricket is a multi-faceted sport which, in very broad terms, can be divided into major cricket and minor cricket based on playing standards. A more pertinent division, particularly in terms of major cricket, is between matches in which the teams have two innings apiece and those in which they have a single innings each. The former, known as first-class cricketFirst-class cricket
First-class cricket is a class of cricket that consists of matches of three or more days' scheduled duration, that are between two sides of eleven players and are officially adjudged first-class by virtue of the standard of the competing teams...
, has a duration of three to five days (there have been examples of "timeless" matches too); the latter, known as limited overs cricket because each team bowls a limit of typically 50 or 20 overs, has a planned duration of one day only (a match can be extended if necessary due to bad weather, etc.).
Typically, two-innings matches have at least six hours of playing time
Playing time (cricket)
Games in the sport of cricket are played over a number of hours or days, making it one of the sports with the longest playing time, though sailing, yachting, road cycling and rallying are sometimes longer. Typically, first-class cricket matches are played over three to five days with at least six...
each day. Limited overs matches often last six hours or more. There are usually formal intervals on each day for lunch and tea with brief informal breaks for drinks. There is also a short interval between innings. Historically, a form of cricket known as single wicket
Single Wicket
Single wicket cricket is a form of cricket played between two individuals, who take turns to bat and bowl against each other. The one bowling is assisted by a team of fielders, who remain as fielders at the change of innings. The winner is the one who scores more runs...
had been extremely successful and many of these contests in the 18th and 19th centuries qualify as major cricket matches. In this form, although each team may have from one to six players, there is only one batsman at a time and he must face every delivery bowled while his innings lasts. Single wicket has rarely been played since limited overs cricket began.
Test cricket

Test cricket
Test cricket is the longest form of the sport of cricket. Test matches are played between national representative teams with "Test status", as determined by the International Cricket Council , with four innings played between two teams of 11 players over a period of up to a maximum five days...
is the highest standard of first-class cricket. A Test match is an international fixture between teams representing those countries that are Full Members of the ICC.
Although the term "Test match" was not coined until much later, Test cricket is deemed to have begun with two matches between Australia and England in the 1876–77 Australian season. Subsequently, eight other national teams have achieved Test status: South Africa (1889), West Indies (1928), New Zealand (1929), India (1932), Pakistan (1952), Sri Lanka (1982), Zimbabwe (1992) and Bangladesh (2000). Zimbabwe suspended its Test status in 2006 due to its inability to compete against other Test teams, and returned in 2011.
Welsh players are eligible to play for England, which is in effect an England and Wales team. The West Indies team comprises players from numerous states in the Caribbean, notably Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, Trinidad & Tobago, the Leeward Islands and the Windward Islands.
Test matches between two teams are usually played in a group of matches called a "series". Matches last up to five days and a series normally consists of three to five matches. Test matches that are not finished within the allotted time are drawn. In the case of Test
Test cricket
Test cricket is the longest form of the sport of cricket. Test matches are played between national representative teams with "Test status", as determined by the International Cricket Council , with four innings played between two teams of 11 players over a period of up to a maximum five days...
and first-class cricket
First-class cricket
First-class cricket is a class of cricket that consists of matches of three or more days' scheduled duration, that are between two sides of eleven players and are officially adjudged first-class by virtue of the standard of the competing teams...
: the possibility of a draw often encourages a team that is batting last and well behind to bat defensively, giving up any faint chance at a win to avoid a loss.
Since 1882, most Test series between England and Australia have been played for a trophy known as The Ashes
The Ashes
The Ashes is a Test cricket series played between England and Australia. It is one of the most celebrated rivalries in international cricket and dates back to 1882. It is currently played biennially, alternately in the United Kingdom and Australia. Cricket being a summer sport, and the venues...
. Some other bilateral series have individual trophies too: for example, the Wisden Trophy
Wisden Trophy
The Wisden Trophy is awarded to the winner of the Test cricket series played between England and the West Indies. It was first awarded in 1963 to commemorate the hundredth edition of Wisden Cricketers' Almanack. Series are played in accordance with the International Cricket Council's future tours...
is contested by England and West Indies; the Frank Worrell Trophy
Frank Worrell Trophy
The Frank Worrell Trophy is awarded for the winner of the West Indies - Australia Test match series in cricket.The trophy is named after the former West Indies captain Sir Frank Worrell, and was first awarded at the end of the 1960-61 series...
by Australia and West Indies and the Border-Gavaskar Trophy
Border-Gavaskar Trophy
The Border–Gavaskar Trophy is a Test cricket series, played between India and Australia. It has witnessed some of the most competitive Test series played in recent years, with results usually either being a narrow win for one of the sides or a closely fought draw...
between India and Australia.
Limited overs

Cricket World Cup
The ICC Cricket World Cup is the premier international championship of men's One Day International cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council , with preliminary qualification rounds leading up to a finals tournament which is held every four years...
took place in England. Limited overs cricket has seen various innovations including the use of multi-coloured kit and floodlit matches using a white ball.
A "one day match", named so because each match is scheduled for completion in a single day, is the common form of limited overs cricket played on an international level. In practice, matches sometimes continue on a second day if they have been interrupted or postponed by bad weather. The main objective of a limited overs match is to produce a definite result and so a conventional draw is not possible, but matches can be undecided if the scores are tied or if bad weather prevents a result. Each team plays one innings only and faces a limited number of overs, usually a maximum of 50. The Cricket World Cup
Cricket World Cup
The ICC Cricket World Cup is the premier international championship of men's One Day International cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council , with preliminary qualification rounds leading up to a finals tournament which is held every four years...
is held in one day format and the last World Cup
2011 Cricket World Cup
The 2011 ICC Cricket World Cup was the tenth Cricket World Cup. It was played in India, Sri Lanka, and Bangladesh. It was Bangladesh's first time co-hosting a World Cup...
in 2011 was won by the co-hosts, India. The next World Cup
2015 Cricket World Cup
The 2015 ICC Cricket World Cup will be the 11th ICC Cricket World Cup, and will be jointly hosted by Australia and New Zealand. The location of the games will be evenly split, with the location of the final yet to be decided....
will hosted by Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
and New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
in 2015.
Twenty20
Twenty20
Twenty20 is a form of cricket, originally introduced in England for professional inter-county competition by the England and Wales Cricket Board , in 2003. A Twenty20 game involves two teams, each has a single innings, batting for a maximum of 20 overs. Twenty20 cricket is also known as T20 cricket...
is a new variant of limited overs itself with the purpose being to complete the match within about three hours, usually in an evening session. The original idea, when the concept was introduced in England in 2003, was to provide workers with an evening entertainment. It was commercially successful and has been adopted internationally. The inaugural Twenty20 World Championship was held in 2007 and won by India. 2009's Twenty20 World Championship
ICC World Twenty20
The ICC World Twenty20 or ICC World T20 also referred to as the T20 World Cup is the international championship of Twenty20 cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council...
was staged in England and won by Pakistan. The next Twenty20 World Championship will be held in the West Indies. After the inaugural ICC World Twenty20
ICC World Twenty20
The ICC World Twenty20 or ICC World T20 also referred to as the T20 World Cup is the international championship of Twenty20 cricket. The event is organised by the sport's governing body, the International Cricket Council...
many domestic Twenty20 leagues were born. First of them was Indian Cricket League
Indian Cricket League
The Indian Cricket League was a private cricket league funded by Zee Entertainment Enterprises that operated between 2007 and 2009 in India...
which is a rebel league since it is unauthorized by BCCI
Board of Control for Cricket in India
The Board of Control for Cricket in India , headquartered at Mumbai, is the national governing body for all cricket in India. It's not the apex governing body in India. The board was formed in December 1928 as BCCI replaced Calcutta Cricket Club. BCCI is a society, registered under the Tamil Nadu...
and led to form an official league called the Indian Premier League
Indian Premier League
The Indian Premier League is a professional league for Twenty20 cricket competition in India. It was initiated by the Board of Control for Cricket in India , headquartered in Mumbai, and is supervised by BCCI Vice President Rajeev Shukla, who serves as the league's Chairman and Commissioner...
. Both these leagues are cash rich and attracted players and audience around the globe. Recently Twenty20 Champions League
Twenty20 Champions League
The Champions League Twenty20 is an international Twenty20 cricket competition between club teams from India, Australia, England, South Africa, Sri Lanka, New Zealand and West Indies...
was formed as a tournament for domestic clubs of various countries.
National championships

First-class cricket
First-class cricket is a class of cricket that consists of matches of three or more days' scheduled duration, that are between two sides of eleven players and are officially adjudged first-class by virtue of the standard of the competing teams...
includes Test cricket but the term is generally used to refer to the highest level of domestic cricket in those countries with full ICC membership, although there are exceptions to this. First-class cricket in England is played for the most part by the 18 county clubs which contest the County Championship
County Championship
The County Championship is the domestic first-class cricket competition in England and Wales...
. The concept of a champion county has existed since the 18th century but the official competition was not established until 1890. The most successful club has been Yorkshire County Cricket Club
Yorkshire County Cricket Club
Yorkshire County Cricket Club represents the historic county of Yorkshire as one of the 18 major county clubs which make up the English and Welsh domestic cricket structure....
with 30 official titles.
Australia established its national first-class championship in 1892–93 when the Sheffield Shield was introduced. In Australia, the first-class teams represent the various states. New South Wales has won the maximum number of titles with 45 to 2008.
National championship trophies to be established elsewhere included the Ranji Trophy
Ranji Trophy
The Ranji Trophy is a domestic first-class cricket championship played in India between different city and state sides, equivalent to the County Championship in England and the Sheffield Shield in Australia...
(India), Plunket Shield (New Zealand), Currie Cup
Currie Cup
The Currie Cup tournament is South Africa's premier domestic rugby union competition, played each winter and spring , featuring teams representing either entire provinces or substantial regions within provinces...
(South Africa) and Shell Shield (West Indies). Some of these competitions have been updated and renamed in recent years.
Domestic limited overs competitions began with England's Gillette Cup knockout in 1963. Countries usually stage seasonal limited overs competitions in both knockout and league format. In recent years, national Twenty20 competitions have been introduced, usually in knockout form though some incorporate mini-leagues.
Other types of matches
There are numerous variations of the sport played throughout the world that include indoor cricketIndoor cricket
Indoor cricket is a variant of and shares many basic concepts with cricket. The game is most often played between two teams each consisting of eight players, in matches featuring two innings of sixteen 7-ball overs each...
, French cricket
French cricket
French cricket is an informal game derived from the sport of cricket. There is only one batsman, and their objective is to not be dismissed by the other participants - who are fielders, or a bowler if they have possession of the ball - for as long as possible. The objective of the other...
, beach cricket
Beach cricket
Backyard cricket, street cricket, beach cricket, gully cricket, corridor cricket, deef or garden cricket is an informal ad hoc variant of the game of cricket, played by people of both sexes and all ages in gardens, back yards, on the street, in parks, carparks, beaches or any deef arena not...
, Kwik cricket
Kwik cricket
Kwik cricket is a high-speed version of cricket aimed mainly at encouraging children to take part in the main sport....
and all sorts of card games and board games that have been inspired by cricket. In these variants, the rules are often changed to make the game playable with limited resources or to render it more convenient and enjoyable for the participants.
Indoor cricket
Indoor cricket
Indoor cricket is a variant of and shares many basic concepts with cricket. The game is most often played between two teams each consisting of eight players, in matches featuring two innings of sixteen 7-ball overs each...
is played in a netted, indoor arena, and is quite formal but many of the outdoor variants are very informal.
Families and teenagers play backyard cricket in suburban yards or driveways, and the cities of India and Pakistan play host to countless games of "Gully Cricket" or "tapeball" in their long narrow streets. Sometimes the rules are improvised: e.g. it may be agreed that fielders can catch the ball with one hand after one bounce and claim a wicket; or if only a few people are available then everyone may field while the players take it in turns to bat and bowl. Tennis balls and homemade bats are often used, and a variety of objects may serve as wickets: for example, the batter's legs as in French cricket
French cricket
French cricket is an informal game derived from the sport of cricket. There is only one batsman, and their objective is to not be dismissed by the other participants - who are fielders, or a bowler if they have possession of the ball - for as long as possible. The objective of the other...
, which did not in fact originate in France, and is usually played by small children.
In Kwik cricket
Kwik cricket
Kwik cricket is a high-speed version of cricket aimed mainly at encouraging children to take part in the main sport....
, the bowler does not have to wait for the batsman to be ready before a delivery, leading to a faster, more exhausting game designed to appeal to children, which is often used PE lessons at English schools. Another modification to increase the pace of the game is the "Tip and Run", "Tipity" Run, "Tipsy Run" or "Tippy-Go" rule, in which the batter must run when the ball touches the bat, even if it the contact is unintentional or minor. This rule, seen only in impromptu games, speeds the match up by removing the batsman's right to block the ball.
In Samoa a form of cricket called Kilikiti
Kilikiti
Kilikiti is one of several forms of the game of cricket. Originating in Samoa , it spread throughout Polynesia and can now be found around the world in areas with strong Polynesian populations...
is played in which hockey stick
Hockey stick
A hockey stick is a piece of equipment used in field hockey, ice hockey or roller hockey to move the ball or puck.- Field hockey :Field hockey sticks have an end which varies in shape, often depending on the players position...
-shaped bats are used. In original English cricket, the hockey stick shape was replaced by the modern straight bat in the 1760s after bowlers began to pitch the ball instead of rolling or skimming it. In Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, teams gather over the winter for the annual Ice Cricket
Ice cricket
An international ice cricket tournament has been played on Lake St. Moritz since 1988 and now in Estonia every year since 2004. The inventor of the Estonian version is credited to Jason Barry, a British ex-pat and former Estonian cricket president who was determined to increase the visibility of...
tournament. The game juxtaposes the normal summer pursuit with harsh, wintry conditions. Rules are otherwise similar to those for the six-a-side game.
International structure

The ICC has 104 members: 10 Full Members that play official Test matches, 34 Associate Members, and 60 Affiliate Members. The ICC is responsible for the organisation and governance of cricket's major international tournaments, notably the Cricket World Cup. It also appoints the umpires and referees that officiate at all sanctioned Test matches, One Day International and Twenty20 Internationals. Each nation has a national cricket board which regulates cricket matches played in its country. The cricket board also selects the national squad and organises home and away tours for the national team. In the West Indies these matters are addressed by the West Indies Cricket Board
West Indies Cricket Board
The West Indies Cricket Board is the governing body for professional and amateur cricket in the West Indies...
which consists of members appointed by four national boards and two multi-national boards.
Full Members
Full Members are the governing bodies for cricket in a country or associated countries. Full Members may also represent a geographical area. All Full Members have a right to send one representative team to play official Test matches. Also, all Full Member nations are automatically qualified to play ODIsOne-day International
A One Day International is a form of limited overs cricket, in which a fixed number of overs, usually 50, but in the past 40, 45 or 60 overs, are played between two teams with international status. The Cricket World Cup is played in this format...
and Twenty20 International
Twenty20 International
A Twenty20 International is a form of cricket which is played over 20 overs per side between two national cricket teams. The game is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket...
s. West Indies cricket team does not represent one country instead an amalgamation of over 20 countries from the Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
. The English Cricket team represents both England and Wales.
| Nation | Governing body | Member since | Current Test ICC Test Championship The ICC Test Championship is an international competition run by the International Cricket Council in the sport of cricket for the 10 teams that play Test cricket... Rankings |
Current ODI ICC ODI Championship The ICC ODI Championship is an international One Day International cricket competition run by the International Cricket Council. The competition is notional in that it is simply a ranking scheme overlaid on the regular ODI match schedule. After every ODI match, the two teams involved receive points... Rankings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cricket Australia Cricket Australia Cricket Australia, formerly known as the Australian Cricket Board, is the governing body for professional and amateur cricket in Australia. It was originally formed in 1905 as the Australian Board of Control for International Cricket... |
4 | 1 | ||
| Bangladesh Cricket Board Bangladesh Cricket Board Bangladesh Cricket Board , previously known as the Bangladesh Cricket Control Board, is the main governing body of cricket in Bangladesh. The Board has its headquarters in Dhaka, it is responsible for the operation and development of cricket, maintenance of of venues, and selection for the... |
9 | 9 | ||
| England and Wales Cricket Board England and Wales Cricket Board The England and Wales Cricket Board is the governing body of cricket in England and Wales. It was created on 1 January 1997 combining the roles of the Test and County Cricket Board, the National Cricket Association and the Cricket Council... |
1 | 4 | ||
| Board of Control for Cricket in India Board of Control for Cricket in India The Board of Control for Cricket in India , headquartered at Mumbai, is the national governing body for all cricket in India. It's not the apex governing body in India. The board was formed in December 1928 as BCCI replaced Calcutta Cricket Club. BCCI is a society, registered under the Tamil Nadu... |
3 | 5 | ||
| New Zealand Cricket New Zealand Cricket New Zealand Cricket, formerly the New Zealand Cricket Board, is the governing body for professional cricket in New Zealand. Cricket is the most popular and highest profile summer sport in New Zealand.... |
8 | 7 | ||
| Pakistan Cricket Board Pakistan Cricket Board The Pakistan Cricket Board is a sporting organization that is responsible for governing all professional cricket including Test cricket and One Day International matches played in Pakistan... |
6 | 6 | ||
| Cricket South Africa Cricket South Africa Cricket South Africa is the governing body for professional and amateur cricket in South Africa. The board was originally created as the United Cricket Board of South Africa in 1991.-History:... |
A | 2 | 3 | |
| Sri Lanka Cricket Sri Lanka Cricket Sri Lanka Cricket, formerly the Board for Cricket Control in Sri Lanka , is the controlling body for cricket in Sri Lanka. It operates the Sri Lankan cricket team and first-class cricket within Sri Lanka.... |
5 | 2 | ||
| West Indies Cricket Board West Indies Cricket Board The West Indies Cricket Board is the governing body for professional and amateur cricket in the West Indies... |
7 | 8 | ||
| Zimbabwe Cricket Union | 10 |
AResigned May 1961, readmitted 10 July 1991.
Top Associate and Affiliate Members
All the associate and affiliate members are not qualified to play Test CricketTest cricket
Test cricket is the longest form of the sport of cricket. Test matches are played between national representative teams with "Test status", as determined by the International Cricket Council , with four innings played between two teams of 11 players over a period of up to a maximum five days...
, however ICC
International Cricket Council
The International Cricket Council is the international governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1909 by representatives from England, Australia and South Africa, renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1965, and took up its current name in 1989.The...
grants One Day International status to its associate and affiliate members based on their success in the World Cricket League
World Cricket League
The ICC World Cricket League is a series of international one-day cricket tournaments for national teams without Test status, administered by the International Cricket Council. All associate and affiliate members of the ICC are eligible to compete in the league system, which features a promotion...
. The top six teams will be awarded One day international and Twenty20 International
Twenty20 International
A Twenty20 International is a form of cricket which is played over 20 overs per side between two national cricket teams. The game is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket...
status, which will allow the associate and affiliate teams to be eligible to play the full members and play official ODI cricket.
The associate and affiliate teams who currently hold ODI and T20I
Twenty20 International
A Twenty20 International is a form of cricket which is played over 20 overs per side between two national cricket teams. The game is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket...
status:
| Nation | Governing body | Member since | Current ODI ICC ODI Championship The ICC ODI Championship is an international One Day International cricket competition run by the International Cricket Council. The competition is notional in that it is simply a ranking scheme overlaid on the regular ODI match schedule. After every ODI match, the two teams involved receive points... Rankings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan Cricket Board | 14 | ||
| Cricket Canada | 16 | ||
| Cricket Ireland | 11 | ||
| Cricket Kenya Cricket Kenya Cricket Kenya is the official ICC recognised organisation chosen to represent Kenya in terms of cricket issues. They are in charge of overseeing the Kenyan Cricket Team. The current coach is Michael Hesson. Recently Cricket Kenya organized two six team regional tournaments in the T20 and 50 Over... |
13 | ||
| Koninklijke Nederlandse Cricket Bond Koninklijke Nederlandse Cricket Bond The Koninklijke Nederlandse Cricket Bond is the governing body of cricket in the Netherlands. It was formed in 1883 and received a Royal charter in 1958.-See also:*Dutch cricket team*Dutch women's cricket team... |
12 | ||
| Cricket Scotland Cricket Scotland Cricket Scotland, formerly known as the Scottish Cricket Union, is the governing body of the sport of cricket in Scotland. The body is based at the National Cricket Academy, Edinburgh.... |
15 |
Statistics
Organized cricket lends itself to statisticsStatistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
to a greater degree than many other sports. Each play is discrete and has a relatively small number of possible outcomes. At the professional level, statistics for Test cricket, one-day internationals, and first-class cricket are recorded separately. However, since Test matches are a form of first-class cricket, a player's first-class statistics will include his Test match statistics—but not vice versa. The Guide to Cricketers
The Guide to Cricketers
The Guide to Cricketers was a cricket annual edited by Fred Lillywhite between 1849 and his death in 1866. The title varied somewhat but was generally along the lines of The Guide to Cricketers...
was a cricket annual edited by Fred Lillywhite
Fred Lillywhite
Frederick Lillywhite was a sports outfitter and cricketing entrepreneur, who organised the first overseas cricket tour by an English team and published a number of reference works about cricket.-Cricketing dynasty:...
between 1849 and his death in 1866. Wisden Cricketers' Almanack
Wisden Cricketers' Almanack
Wisden Cricketers' Almanack is a cricket reference book published annually in the United Kingdom...
was founded in 1864 by the English cricketer John Wisden
John Wisden
John Wisden was an English cricketer who played 190 first-class cricket matches for three English county cricket teams, Kent, Middlesex and Sussex...
(1826–1884) as a competitor to The Guide to Cricketers. Its annual publication has continued uninterrupted to the present day, making it the longest running sports annual in history.
Certain traditional statistics are familiar to most cricket fans. The basic batting statistics include:
- InningsInningsAn inning, or innings, is a fixed-length segment of a game in any of a variety of sports – most notably cricket and baseball during which one team attempts to score while the other team attempts to prevent the first from scoring. In cricket, the term innings is both singular and plural and is...
(I): The number of innings in which the batsman actually batted. - Not outNot outIn cricket, a batsman will be not out if he comes out to bat in an innings and has not been dismissed by the end of the innings. One may similarly describe a batsman as not out while the innings is still in progress...
s (NO): The number of times the batsman was not out at the conclusion of an innings they batted in.1 - RunsRun (cricket)In the sport of cricket, a run is the basic unit of scoring. Runs are scored by a batsman, and the aggregate of the scores of a team's batsmen constitutes the team's score. A batsman scoring 50 or 100 runs , or any higher multiple of 50 runs, is considered a particular achievement...
(R): The number of runs scored. - Highest Score (HS/Best): The highest score ever made by the batsman.
- Batting AverageBatting averageBatting average is a statistic in both cricket and baseball that measures the performance of cricket batsmen and baseball hitters. The two statistics are related in that baseball averages are directly descended from the concept of cricket averages.- Cricket :...
(Ave): The total number of runs divided by the total number of innings in which the batsman was out. Ave = Runs/[I - NO] (also Avge or Avg.) - CenturiesCentury (cricket)In the sport of cricket, a batsman reaches his century when he scores 100 or more runs in a single innings. The term is also included in "century partnership" which occurs when two batsmen add 100 runs to the team total when they are batting together. A century is regarded as a landmark score for...
(100): The number of innings in which the batsman scored one hundred runs or more. - Half-centuries (50): The number of innings in which the batsman scored fifty to ninety-nine runs (centuries do not count as half-centuries as well).
- Balls Faced (BF): The total number of balls received, including no balls but not including wides.
- Strike RateStrike rateStrike rate refers to two different statistics in the sport of cricket. Batting strike rate is a measure of how frequently a batsman achieves the primary goal of batting, namely scoring runs. Bowling strike rate is a measure of how frequently a bowler achieves the primary goal of bowling, namely...
(SR): The number of runs scored per 100 balls faced. (SR = [100 * Runs]/BF) - Run Rate (RR): Is the number of runs a batsman (or the batting side) scores in an over of six balls.
The basic bowling statistics include:
- OverOver (cricket)In the sport of cricket, an over is a set of six consecutive balls bowled in succession. An over is normally bowled by a single bowler. However, in the event of injury preventing a bowler from completing an over, it is completed by a teammate....
s (O): The number of overs bowled. - Balls (B): The number of balls bowled. Overs is more traditional, but balls is a more useful statistic because the number of balls per over has varied historically.
- Maiden OversOver (cricket)In the sport of cricket, an over is a set of six consecutive balls bowled in succession. An over is normally bowled by a single bowler. However, in the event of injury preventing a bowler from completing an over, it is completed by a teammate....
(M): The number of maiden overs (overs in which the bowler conceded zero runs) bowled. - RunsRun (cricket)In the sport of cricket, a run is the basic unit of scoring. Runs are scored by a batsman, and the aggregate of the scores of a team's batsmen constitutes the team's score. A batsman scoring 50 or 100 runs , or any higher multiple of 50 runs, is considered a particular achievement...
(R): The number of runs conceded. - WicketWicketIn the sport of cricket the word wicket has several distinct meanings:-Definitions of wicket:Most of the time, the wicket is one of the two sets of three stumps and two bails at either end of the pitch...
s (W): The number of wickets taken. - No ballNo ballIn the sport of cricket a no ball is a penalty against the fielding team, usually as a result of an illegal delivery by the bowler. The delivery of a no ball results in one run to be added to the batting team's score, and an additional ball must be bowled...
s (Nb): The number of no balls bowled. - Wides (Wd): The number of wides bowled.
- Bowling AverageBowling averageBowling average is a statistic measuring the performance of bowlers in the sport of cricket.A bowler's bowling average is defined as the total number of runs conceded by the bowlers divided by the number of wickets taken by the bowler, so the lower the average the better. It is similar to earned...
(Ave): The average number of runs conceded per wicket. (Ave = Runs/W) - 'Economy Rate (Econ): The average number of runs conceded per overOver (cricket)In the sport of cricket, an over is a set of six consecutive balls bowled in succession. An over is normally bowled by a single bowler. However, in the event of injury preventing a bowler from completing an over, it is completed by a teammate....
. (Econ = Runs/overs bowled).
In popular culture
Cricket has had a broad impact on popular culture, both in the Commonwealth of NationsCommonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
and elsewhere. Cricket has had an influence on the lexicon of these nations, especially the English language, with such phrases as "that's not cricket" (unfair), "had a good innings", "sticky wicket", and "bowled over". There have been many cricket films. The term "Bradmanesque" from Don Bradman's name has become a generic term for outstanding excellence, both within cricket and in the wider world. The amateur game has also been spread further afield by expatriates from the Test-playing nations. In the late 19th century, a former cricket player, English-born Henry Chadwick of Brooklyn
Brooklyn
Brooklyn is the most populous of New York City's five boroughs, with nearly 2.6 million residents, and the second-largest in area. Since 1896, Brooklyn has had the same boundaries as Kings County, which is now the most populous county in New York State and the second-most densely populated...
, New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, was responsible for the "development of the box score
Box score (baseball)
In baseball, the statistical summary of a game is reported in a box score. An abbreviated version of the box score, duplicated from the field scoreboard, is the line score...
, tabular standings, the annual baseball guide, the batting average
Batting average
Batting average is a statistic in both cricket and baseball that measures the performance of cricket batsmen and baseball hitters. The two statistics are related in that baseball averages are directly descended from the concept of cricket averages.- Cricket :...
, and most of the common statistics and tables used to describe baseball". The statistical record is so central to the game's "historical essence" that Chadwick came to be known as Father Baseball.
See also
- ICC ODI ChampionshipICC ODI ChampionshipThe ICC ODI Championship is an international One Day International cricket competition run by the International Cricket Council. The competition is notional in that it is simply a ranking scheme overlaid on the regular ODI match schedule. After every ODI match, the two teams involved receive points...
- ICC Player Rankings
- ICC Test ChampionshipICC Test ChampionshipThe ICC Test Championship is an international competition run by the International Cricket Council in the sport of cricket for the 10 teams that play Test cricket...
- List of cricket terms
- Blind CricketBlind cricketBlind cricket is a version of the sport of cricket adapted for blind and partially sighted players. It has governed by the World Blind Cricket Council since 1996...
- Comparison of cricket and baseball
- Outline of cricketOutline of cricketThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cricket:Cricket – a bat-and-ball team sport. Many variations exist, with its most popular form played on an oval-shaped outdoor arena known as a cricket field at the centre of which is a rectangular 22-yard long pitch...
- Women's cricketWomen's cricketWomen's cricket is the form of the team sport of cricket that is played by women.-History:The first recorded match of women's cricket was reported in The Reading Mercury on 26 July 1745, a match contested "between eleven maids of Bramley and eleven maids of Hambledon, all dressed in white." The...
- ICC Cricket World Cup

