
Australasia
Encyclopedia
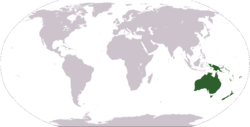

Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
of Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
comprising Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, the island of New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
, and neighbouring island
Island
An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
s in the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses
Charles de Brosses
Charles de Brosses, comte de Tournay, baron de Montfalcon, seigneur de Vezins et de Prevessin was a French writer of the 18th century.-Life:...
in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes (1756). He derived it from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
for "south of Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
" and differentiated the area from Polynesia
Polynesia
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of over 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians and they share many similar traits including language, culture and beliefs...
(to the east) and the southeast Pacific (Magellanica). It is also distinct from Micronesia
Micronesia
Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It is distinct from Melanesia to the south, and Polynesia to the east. The Philippines lie to the west, and Indonesia to the southwest....
(to the northeast). Australasia sits on the Indo-Australian Plate
Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and surrounding ocean, and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and adjacent waters...
, together with India.
Human geography
GeopoliticallyGeopolitics
Geopolitics, from Greek Γη and Πολιτική in broad terms, is a theory that describes the relation between politics and territory whether on local or international scale....
, Australasia is sometimes used as a term for Australia and New Zealand together in the absence of another word limited to those two countries. Sometimes the island of New Guinea (Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands...
and the Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
n part of the island) is encompassed by the term. There are many organisations whose names are prefixed with "(Royal) Australasian Society" that are limited to just Australia and New Zealand.

Tennis
Tennis is a sport usually played between two players or between two teams of two players each . Each player uses a racket that is strung to strike a hollow rubber ball covered with felt over a net into the opponent's court. Tennis is an Olympic sport and is played at all levels of society at all...
between 1905 and 1915, when New Zealand and Australia combined to compete in the Davis Cup
Davis Cup
The Davis Cup is the premier international team event in men's tennis. It is run by the International Tennis Federation and is contested between teams of players from competing countries in a knock-out format. The competition began in 1900 as a challenge between Britain and the United States. By...
international tournament, and at the Olympic Games
Summer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games or the Games of the Olympiad are an international multi-sport event, occurring every four years, organized by the International Olympic Committee. Medals are awarded in each event, with gold medals for first place, silver for second and bronze for third, a tradition that...
of 1908
1908 Summer Olympics
The 1908 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the IV Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event which was held in 1908 in London, England, United Kingdom. These games were originally scheduled to be held in Rome. At the time they were the fifth modern Olympic games...
and 1912
1912 Summer Olympics
The 1912 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the V Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event held in Stockholm, Sweden, between 5 May and 27 July 1912. Twenty-eight nations and 2,407 competitors, including 48 women, competed in 102 events in 14 sports...
.
Ecological geography
From an ecological
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
perspective the Australasia ecozone
Australasia ecozone
The Australasian zone is an ecological region that is coincident, but not synonymous , with the geographic region of Australasia...
is a distinct region with a common geologic and evolutionary history and a great many unique flora
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
and fauna
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
. In this context, Australasia is limited to Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
, and neighbouring islands, including the Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
n islands from Lombok
Lombok
Lombok is an island in West Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. It forms part of the chain of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with the Lombok Strait separating it from Bali to the west and the Alas Strait between it and Sumbawa to the east...
and Sulawesi
Sulawesi
Sulawesi is one of the four larger Sunda Islands of Indonesia and is situated between Borneo and the Maluku Islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger Indonesian populations.- Etymology :The Portuguese were the first to...
eastward. The biological dividing line from the Indomalaya ecozone of tropical Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
is the Wallace Line
Wallace Line
The Wallace Line separates the ecozones of Asia and Wallacea, a transitional zone between Asia and Australia. West of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origin is present...
– Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
and Bali
Bali
Bali is an Indonesian island located in the westernmost end of the Lesser Sunda Islands, lying between Java to the west and Lombok to the east...
lie on the western, Asian side.
Australia, New Zealand, and New Caledonia are all fragments of the ancient supercontinent Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
. These three land masses have been separated from other continents, and from one another, for millions of years. All of Australasia shares the Antarctic flora
Antarctic flora
The Antarctic flora is a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana, and is now found on several separate areas of the Southern Hemisphere, including southern South America, southernmost Africa, New Zealand, Australia and New Caledonia...
, although the northern, tropical islands also share many plants with Southeast Asia.
Australia, New Guinea, and Tasmania are separated from one another by shallow continental shelves
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
, and were linked together when the sea level was lower during the Ice Ages. They share a similar fauna which includes marsupial
Marsupial
Marsupials are an infraclass of mammals, characterized by giving birth to relatively undeveloped young. Close to 70% of the 334 extant species occur in Australia, New Guinea, and nearby islands, with the remaining 100 found in the Americas, primarily in South America, but with thirteen in Central...
and monotreme
Monotreme
Monotremes are mammals that lay eggs instead of giving birth to live young like marsupials and placental mammals...
mammals and ratite
Ratite
A ratite is any of a diverse group of large, flightless birds of Gondwanan origin, most of them now extinct. Unlike other flightless birds, the ratites have no keel on their sternum—hence the name from the Latin ratis...
birds. Eucalypt
Eucalypt
Eucalypts are woody plants belonging to three closely related genera:Eucalyptus, Corymbia and Angophora.In 1995 new evidence, largely genetic, indicated that some prominent Eucalyptus species were actually more closely related to Angophora than to the other eucalypts; they were split off into the...
s are the predominant trees in much of Australia and New Guinea. New Zealand has no native land mammals, but also had ratite birds, including the kiwi
Kiwi
Kiwi are flightless birds endemic to New Zealand, in the genus Apteryx and family Apterygidae.At around the size of a domestic chicken, kiwi are by far the smallest living ratites and lay the largest egg in relation to their body size of any species of bird in the world...
and the extinct moa
Moa
The moa were eleven species of flightless birds endemic to New Zealand. The two largest species, Dinornis robustus and Dinornis novaezelandiae, reached about in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about ....
. The Australasia ecozone includes some nearby island groups, like Wallacea
Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of Indonesian islands separated by deep water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Halmahera, Buru, Seram, and...
, the Bismarck Archipelago
Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea.-History:...
, Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
, and Vanuatu
Vanuatu
Vanuatu , officially the Republic of Vanuatu , is an island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is some east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, west of Fiji, and southeast of the Solomon Islands, near New Guinea.Vanuatu was...
, which were not formerly part of Gondwana, but which share many characteristic plants and animals with Australasia.

