
Critical distance
Encyclopedia
Critical distance is, in audio
physics
, the distance at which the sound pressure level of the direct and the reverberant
sound fields are equal when dealing with a directional source. In other words, the point in space where the combined amplitude
of all the reflected echos are the same as the amplitude of the sound coming directly from the source. This distance is dependent on the geometry and absorption
of the space in which the sound waves propagate, as well as the dimensions and shape of the sound source.
A reverberant room generates a short critical distance and an acoustically dead (anechoic) room generates a longer critical distance.
The calculation of the critical distance:
or:
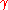 is the degree of bundling of the source,
is the degree of bundling of the source,  the room volume in cubic meters,
the room volume in cubic meters,
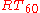 the reverberation time of room in seconds, and
the reverberation time of room in seconds, and 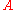 the equivalent absorption surface.
the equivalent absorption surface.
Avoid the words Reverb Radius, Reverberation Radius (omnidirectional source), Hall Radius for Critical Distance.
This distance, called critical distance dc, can be specified as a function of room volume and reverberation time using Sabine's approximation: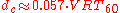
Critical distance dc in m
Room volume V in m3
Reverberation time RT60 in s
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, the distance at which the sound pressure level of the direct and the reverberant
Reverberation
Reverberation is the persistence of sound in a particular space after the original sound is removed. A reverberation, or reverb, is created when a sound is produced in an enclosed space causing a large number of echoes to build up and then slowly decay as the sound is absorbed by the walls and air...
sound fields are equal when dealing with a directional source. In other words, the point in space where the combined amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
of all the reflected echos are the same as the amplitude of the sound coming directly from the source. This distance is dependent on the geometry and absorption
Absorption (acoustics)
Acoustic absorption is that property of any material that changes the acoustic energy of sound waves into another form, often heat, which it to some extent retains, as opposed to that sound energy that material reflects or conducts. Acoustic absorption is represented by the symbol A in calculations...
of the space in which the sound waves propagate, as well as the dimensions and shape of the sound source.
A reverberant room generates a short critical distance and an acoustically dead (anechoic) room generates a longer critical distance.
The calculation of the critical distance:

or:

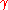 is the degree of bundling of the source,
is the degree of bundling of the source,  the room volume in cubic meters,
the room volume in cubic meters,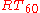 the reverberation time of room in seconds, and
the reverberation time of room in seconds, and  the equivalent absorption surface.
the equivalent absorption surface.Avoid the words Reverb Radius, Reverberation Radius (omnidirectional source), Hall Radius for Critical Distance.
This distance, called critical distance dc, can be specified as a function of room volume and reverberation time using Sabine's approximation:
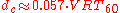
Critical distance dc in m
Room volume V in m3
Reverberation time RT60 in s

