
Reverberation
Encyclopedia
Reverberation is the persistence of sound
in a particular space after the original sound is removed. A reverberation, or reverb, is created when a sound is produced in an enclosed space causing a large number of echoes
to build up and then slowly decay as the sound is absorbed by the walls and air. This is most noticeable when the sound source stops but the reflections
continue, decreasing in amplitude
, until they can no longer be heard. The length of this sound decay, or reverberation time, receives special consideration in the architectural design of large chambers, which need to have specific reverberation times to achieve optimum performance for their intended activity. In comparison to a distinct echo that is 50 to 100 ms after the initial sound, reverberation is many thousands of echoes that arrive in very quick succession (.01 – 1 ms between echoes). As time passes, the volume of the many echoes is reduced until the echoes cannot be heard at all.
below the level of the direct sound. Reverberation time is frequently stated as a single value however it can be measured as a wide band signal (20 Hz to 20kHz) or more precisely in narrow bands (one octave, 1/3 octave, 1/6 octave, etc.). Typically, the reverb time measured in narrow bands will differ depending on the frequency band being measured. It is usually helpful to know what range of frequencies are being described by a reverberation time measurement.
In the late 19th century, Wallace Clement Sabine
started experiments at Harvard University to investigate the impact of absorption on the reverberation time. Using a portable wind chest and organ pipes as a sound source, a stopwatch
and his ears, he measured the time from interruption of the source to inaudibility (roughly 60 dB). He found that the reverberation time is proportional to the dimensions of room and inversely proportional to the amount of absorption present.
The optimum reverberation time for a space in which music is played depends on the type of music that is to be played in the space. Rooms used for speech typically need a shorter reverberation time so that speech can be understood more clearly. If the reflected sound from one syllable
is still heard when the next syllable is spoken, it may be difficult to understand what was said. "Cat", "Cab", and "Cap" may all sound very similar. If on the other hand the reverberation time is too short, tonal balance and loudness may suffer. Reverberation effects are often used in studios
to add depth to sounds. Reverberation changes the perceived harmonic structure of a note, but does not alter the pitch.
Basic factors that affect a room's reverberation time include the size and shape of the enclosure as well as the materials used in the construction of the room. Every object placed within the enclosure can also affect this reverberation time, including people and their belongings.
fashion. He established a relationship between the RT60 of a room, its volume, and its total absorption (in sabins). This is given by the equation:
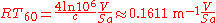 .
.
where is a number that relates to the speed of sound in the room,
is a number that relates to the speed of sound in the room,  is the volume of the room in m³,
is the volume of the room in m³, 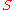 total surface area of room in m²,
total surface area of room in m²,  is the average absorption coefficient of room surfaces, and the product
is the average absorption coefficient of room surfaces, and the product 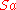 is the total absorption in sabins.
is the total absorption in sabins.
The total absorption in sabins (and hence reverberation time) generally changes depending on frequency (which is defined by the acoustic properties
of the space). The equation does not take into account room shape or losses from the sound travelling through the air (important in larger spaces). Most rooms absorb less sound energy in the lower frequency ranges resulting in longer reverb times at lower frequencies.
The reverberation time RT60 and the volume
V of the room have great influence on the critical distance
dc (conditional equation):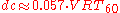
where critical distance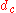 is measured in meters, volume
is measured in meters, volume  is measured in m³, and reverberation time
is measured in m³, and reverberation time 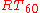 is measured in second
is measured in second
s.
s can carry out this analysis automatically.
Currently several methods exist for measuring reverb time. An impulse can be measured by creating a sufficiently loud noise (which must have a defined cut off point). Impulse noise
sources such as a blank
pistol shot or balloon burst may be used to measure the impulse response of a room.
Alternatively, a random noise signal
such as pink noise
or white noise
may be generated through a loudspeaker, and then turned off. This is known as the interrupted method, and the measured result is known as the interrupted response.
A two port measurement system can also be used to measure noise introduced into a space and compare it to what is subsequently measured in the space. Consider sound reproduced by a loudspeaker into a room. A recording of the sound in the room can be made and compared to what was sent to the loudspeaker. The two signals can be compared mathematically. This two port measurement system utilizes a Fourier transform
to mathematically derive the impulse response of the room. From the impulse response, the reverberation time can be calculated. Using a two port system, allows reverberation time to be measured with signals other than loud impulses. Music or recordings of other sound can be used. This allows measurements to be taken in a room after the audience is present.
Reverberation time is usually stated as a decay time and is measured in seconds. There may or may not be any statement of the frequency band used in the measurement. Decay time is the time it takes the signal to diminish 60 dB below the original sound.
. A loudspeaker
would play the sound, and then a microphone
would pick it up again, including the effects of reverb. Although this is still a common technique, it requires a dedicated soundproofed room, and varying the reverb time is difficult.
, similar to the driver in a loudspeaker, to create vibration in a large plate of sheet metal
. A pickup captures the vibrations as they bounce across the plate, and the result is output as an audio signal. In the late 1950s, Elektro-Mess-Technik
(EMT) introduced the EMT 140; a 600 pounds (272.2 kg) model popular in recording studios, contributing to many hit records such as those recorded by Bill Porter in Nashville's RCA Studio B
. Early units had one pickup for mono output, later models featured two pickups for stereo use. The reverb time can be adjusted by a damping pad, made from framed acoustic tiles. The closer the damping pad, the shorter the reverb time. However, the pad never touches the plate. Some units also featured a remote control.
. Guitar amplifier
s frequently incorporate spring reverbs due to their compact construction and low cost. Spring reverberators were once widely used in semi-professional recording due to their modest cost and small size.
Many musicians have made use of spring reverb units by rocking them back and forth, creating a thundering, crashing sound caused by the springs colliding with each other. The Hammond Organ
included an inbuilt spring reverberator, making this a popular effect when used in a rock band.
algorithms in order to create the reverb effect. Since reverberation is essentially caused by a very large number of echoes, simple reverberation algorithms use multiple feedback delay circuits
to create a large, decaying series of echoes. More advanced digital reverb generators can simulate the time and frequency domain responses of real rooms (based upon room dimensions, absorption and other properties). In real music halls, the direct sound always arrives at the listener's ear first because it follows the shortest path. Shortly after the direct sound, the reverberant sound arrives. The time between the two is called the "pre-delay."
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
in a particular space after the original sound is removed. A reverberation, or reverb, is created when a sound is produced in an enclosed space causing a large number of echoes
Echo (phenomenon)
In audio signal processing and acoustics, an echo is a reflection of sound, arriving at the listener some time after the direct sound. Typical examples are the echo produced by the bottom of a well, by a building, or by the walls of an enclosed room and an empty room. A true echo is a single...
to build up and then slowly decay as the sound is absorbed by the walls and air. This is most noticeable when the sound source stops but the reflections
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
continue, decreasing in amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
, until they can no longer be heard. The length of this sound decay, or reverberation time, receives special consideration in the architectural design of large chambers, which need to have specific reverberation times to achieve optimum performance for their intended activity. In comparison to a distinct echo that is 50 to 100 ms after the initial sound, reverberation is many thousands of echoes that arrive in very quick succession (.01 – 1 ms between echoes). As time passes, the volume of the many echoes is reduced until the echoes cannot be heard at all.
RT60 is the time required for reflections of a direct sound to decay by 60 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
below the level of the direct sound. Reverberation time is frequently stated as a single value however it can be measured as a wide band signal (20 Hz to 20kHz) or more precisely in narrow bands (one octave, 1/3 octave, 1/6 octave, etc.). Typically, the reverb time measured in narrow bands will differ depending on the frequency band being measured. It is usually helpful to know what range of frequencies are being described by a reverberation time measurement.
In the late 19th century, Wallace Clement Sabine
Wallace Clement Sabine
Wallace Clement Sabine was an American physicist who founded the field of architectural acoustics. He graduated from Ohio State University in 1886 at the age of 18 before joining Harvard University for graduate study and remaining as a faculty member...
started experiments at Harvard University to investigate the impact of absorption on the reverberation time. Using a portable wind chest and organ pipes as a sound source, a stopwatch
Stopwatch
A stopwatch is a handheld timepiece designed to measure the amount of time elapsed from a particular time when activated to when the piece is deactivated. A large digital version of a stopwatch designed for viewing at a distance, as in a sports stadium, is called a stopclock.The timing functions...
and his ears, he measured the time from interruption of the source to inaudibility (roughly 60 dB). He found that the reverberation time is proportional to the dimensions of room and inversely proportional to the amount of absorption present.
The optimum reverberation time for a space in which music is played depends on the type of music that is to be played in the space. Rooms used for speech typically need a shorter reverberation time so that speech can be understood more clearly. If the reflected sound from one syllable
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building...
is still heard when the next syllable is spoken, it may be difficult to understand what was said. "Cat", "Cab", and "Cap" may all sound very similar. If on the other hand the reverberation time is too short, tonal balance and loudness may suffer. Reverberation effects are often used in studios
Recording studio
A recording studio is a facility for sound recording and mixing. Ideally both the recording and monitoring spaces are specially designed by an acoustician to achieve optimum acoustic properties...
to add depth to sounds. Reverberation changes the perceived harmonic structure of a note, but does not alter the pitch.
Basic factors that affect a room's reverberation time include the size and shape of the enclosure as well as the materials used in the construction of the room. Every object placed within the enclosure can also affect this reverberation time, including people and their belongings.
Sabine equation
Sabine's reverberation equation was developed in the late 1890s in an empiricalEmpirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
fashion. He established a relationship between the RT60 of a room, its volume, and its total absorption (in sabins). This is given by the equation:
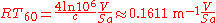 .
.where
 is a number that relates to the speed of sound in the room,
is a number that relates to the speed of sound in the room,  is the volume of the room in m³,
is the volume of the room in m³, 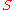 total surface area of room in m²,
total surface area of room in m²,  is the average absorption coefficient of room surfaces, and the product
is the average absorption coefficient of room surfaces, and the product 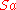 is the total absorption in sabins.
is the total absorption in sabins.The total absorption in sabins (and hence reverberation time) generally changes depending on frequency (which is defined by the acoustic properties
Acoustics
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
of the space). The equation does not take into account room shape or losses from the sound travelling through the air (important in larger spaces). Most rooms absorb less sound energy in the lower frequency ranges resulting in longer reverb times at lower frequencies.
The reverberation time RT60 and the volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
V of the room have great influence on the critical distance
Critical distance
Critical distance is, in audio physics, the distance at which the sound pressure level of the direct and the reverberant sound fields are equal when dealing with a directional source. In other words, the point in space where the combined amplitude of all the reflected echos are the same as the...
dc (conditional equation):
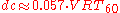
where critical distance
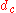 is measured in meters, volume
is measured in meters, volume  is measured in m³, and reverberation time
is measured in m³, and reverberation time 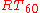 is measured in second
is measured in secondSecond
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
s.
Absorption
The absorption coefficient of a material is a number between 0 and 1 which indicates the proportion of sound which is absorbed by the surface compared to the proportion which is reflected back into the room. A large, fully open window would offer no reflection as any sound reaching it would pass straight out and no sound would be reflected. This would have an absorption coefficient of 1. Conversely, a thick, smooth painted concrete ceiling would be the acoustic equivalent of a mirror, and would have an absorption coefficient very close to 0.Measurement of reverberation time
Historically reverberation time could only be measured using a level recorder (a plotting device which graphs the noise level against time on a ribbon of moving paper). A loud noise is produced, and as the sound dies away the trace on the level recorder will show a distinct slope. Analysis of this slope reveals the measured reverberation time. Some modern digital sound level meterSound level meter
Sound level meters measure sound pressure level and are commonly used in noise pollution studies for the quantification of almost any noise, but especially for industrial, environmental and aircraft noise. However, the reading given by a sound level meter does not correlate well to...
s can carry out this analysis automatically.
Currently several methods exist for measuring reverb time. An impulse can be measured by creating a sufficiently loud noise (which must have a defined cut off point). Impulse noise
Impulse noise (audio)
Impulse noise is a category of noise which includes unwanted, almost instantaneous sharp sounds . Noises of the kind are usually caused by electromagnetic interference, scratches on the recording disks, and ill synchronization in digital recording and communication...
sources such as a blank
Blank (cartridge)
A blank is a type of cartridge for a firearm that contains gunpowder but no bullet or shot. When fired, the blank makes a flash and an explosive sound . Blanks are often used for simulation , training, and for signaling...
pistol shot or balloon burst may be used to measure the impulse response of a room.
Alternatively, a random noise signal
Colors of noise
While noise is by definition derived from a random signal, it can have different characteristic statistical properties corresponding to different mappings from a source of randomness to the concrete noise. Spectral density is such a property, which can be used to distinguish different types of noise...
such as pink noise
Pink noise
Pink noise or 1/ƒ noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density is inversely proportional to the frequency. In pink noise, each octave carries an equal amount of noise power...
or white noise
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
may be generated through a loudspeaker, and then turned off. This is known as the interrupted method, and the measured result is known as the interrupted response.
A two port measurement system can also be used to measure noise introduced into a space and compare it to what is subsequently measured in the space. Consider sound reproduced by a loudspeaker into a room. A recording of the sound in the room can be made and compared to what was sent to the loudspeaker. The two signals can be compared mathematically. This two port measurement system utilizes a Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
to mathematically derive the impulse response of the room. From the impulse response, the reverberation time can be calculated. Using a two port system, allows reverberation time to be measured with signals other than loud impulses. Music or recordings of other sound can be used. This allows measurements to be taken in a room after the audience is present.
Reverberation time is usually stated as a decay time and is measured in seconds. There may or may not be any statement of the frequency band used in the measurement. Decay time is the time it takes the signal to diminish 60 dB below the original sound.
Creating reverberation effects
It is often desirable to create a reverberation effect for recorded or live music. A number of systems have been developed to facilitate or simulate reverberation.Chamber reverberators
The first reverb effects created for recordings used a real physical space as a natural echo chamberEcho chamber
thumb|right|Echo chamber of the Dresden University of Technologythumb|right|Hamilton Mausoleum has a spectacularly long lasting unplanned echoAn echo chamber is a hollow enclosure used to produce echoing sounds, usually for recording purposes...
. A loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
would play the sound, and then a microphone
Microphone
A microphone is an acoustic-to-electric transducer or sensor that converts sound into an electrical signal. In 1877, Emile Berliner invented the first microphone used as a telephone voice transmitter...
would pick it up again, including the effects of reverb. Although this is still a common technique, it requires a dedicated soundproofed room, and varying the reverb time is difficult.
Plate reverberators
A plate reverb system uses an electromechanical transducerTransducer
A transducer is a device that converts one type of energy to another. Energy types include electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic , chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a...
, similar to the driver in a loudspeaker, to create vibration in a large plate of sheet metal
Sheet metal
Sheet metal is simply metal formed into thin and flat pieces. It is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and can be cut and bent into a variety of different shapes. Countless everyday objects are constructed of the material...
. A pickup captures the vibrations as they bounce across the plate, and the result is output as an audio signal. In the late 1950s, Elektro-Mess-Technik
Elektro-Mess-Technik
Elektro-Mess-Technik is a manufacturer of phonograph turntables and professional audio equipment, including a well-regarded line of artificial reverberation devices beginning with the EMT 140 plate reverb. The company was founded by Wilhelm Franz....
(EMT) introduced the EMT 140; a 600 pounds (272.2 kg) model popular in recording studios, contributing to many hit records such as those recorded by Bill Porter in Nashville's RCA Studio B
RCA Studio B
RCA Studio B is a noted recording studio in Nashville, Tennessee. Situated at 30 Music Square W and originally known simply as RCA Studios, it became famous in the 1960s for being a part of what many refer to as the Nashville Sound...
. Early units had one pickup for mono output, later models featured two pickups for stereo use. The reverb time can be adjusted by a damping pad, made from framed acoustic tiles. The closer the damping pad, the shorter the reverb time. However, the pad never touches the plate. Some units also featured a remote control.
Spring reverberators
A spring reverb system uses a transducer at one end of a spring and a pickup at the other, similar to those used in plate reverbs, to create and capture vibrations within a metal springSpring (device)
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened stock, while larger ones are made from annealed steel and hardened after fabrication...
. Guitar amplifier
Guitar amplifier
A guitar amplifier is an electronic amplifier designed to make the signal of an electric or acoustic guitar louder so that it will produce sound through a loudspeaker...
s frequently incorporate spring reverbs due to their compact construction and low cost. Spring reverberators were once widely used in semi-professional recording due to their modest cost and small size.
Many musicians have made use of spring reverb units by rocking them back and forth, creating a thundering, crashing sound caused by the springs colliding with each other. The Hammond Organ
Hammond organ
The Hammond organ is an electric organ invented by Laurens Hammond in 1934 and manufactured by the Hammond Organ Company. While the Hammond organ was originally sold to churches as a lower-cost alternative to the wind-driven pipe organ, in the 1960s and 1970s it became a standard keyboard...
included an inbuilt spring reverberator, making this a popular effect when used in a rock band.
Digital reverberators
Digital reverberators use various signal processingDigital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
algorithms in order to create the reverb effect. Since reverberation is essentially caused by a very large number of echoes, simple reverberation algorithms use multiple feedback delay circuits
Delay (audio effect)
Delay is an audio effect which records an input signal to an audio storage medium, and then plays it back after a period of time. The delayed signal may either be played back multiple times, or played back into the recording again, to create the sound of a repeating, decaying echo.-Early delay...
to create a large, decaying series of echoes. More advanced digital reverb generators can simulate the time and frequency domain responses of real rooms (based upon room dimensions, absorption and other properties). In real music halls, the direct sound always arrives at the listener's ear first because it follows the shortest path. Shortly after the direct sound, the reverberant sound arrives. The time between the two is called the "pre-delay."
See also
- Acoustic resonanceAcoustic resonanceAcoustic resonance is the tendency of an acoustic system to absorb more energy when it is forced or driven at a frequency that matches one of its own natural frequencies of vibration than it does at other frequencies....
- Audio mixingAudio mixing (recorded music)In audio recording, audio mixing is the process by which multiple recorded sounds are combined into one or more channels, most commonly two-channel stereo. In the process, the source signals' level, frequency content, dynamics, and panoramic position are manipulated and effects such as reverb may...
- Exponential decay
- Reverberation roomReverberation roomA reverberation chamber or room is a room designed to create a diffuse or random incidence sound field . Reverberation chambers tend to be large rooms and have very hard exposed surfaces...

