
Cue validity
Encyclopedia
Cue validity is the conditional probability
that an object falls in a particular category given a particular feature or cue. The term was popularized by , and especially by Eleanor Rosch
in her investigations of the acquisition of so-called basic categories .
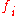 with respect to category
with respect to category 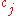 has been defined in the following ways:
has been defined in the following ways:
For the definitions based on probability, a high cue validity for a given feature means that the feature or attribute is more diagnostic of the class membership than a feature with low cue validity. Thus, a high-cue validity feature is one which conveys more information about the category or class variable, and may thus be considered as more useful for identifying objects as belonging to that category. Thus, high cue validity expresses high feature informativeness. For the definitions based on linear correlation, the expression of "informativeness" captured by the cue validity measure is not the full expression of the feature's informativeness (as in mutual information
, for example), but only that portion of its informativeness that is expressed in a linear relationship. For some purposes, a bilateral measure such as the mutual information
or category utility
is more appropriate than the cue validity.
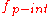 , and which adopts the value 1 if the number is actually a positive integer
, and which adopts the value 1 if the number is actually a positive integer
. Then we can inquire what the validity of this cue is with regard to the following classes: {
In perception
, "cue validity" is often short for ecological validity
of a perceptual cue, and is defined as a correlation rather than a probability (see above). In this definition, an uninformative perceptual cue has an ecological validity of 0 rather than 0.5.
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
that an object falls in a particular category given a particular feature or cue. The term was popularized by , and especially by Eleanor Rosch
Eleanor Rosch
Eleanor Rosch is a professor of psychology at the University of California, Berkeley, specializing in cognitive psychology and primarily known for her work on categorization, in particular her prototype theory, which has profoundly influenced the field of cognitive psychology...
in her investigations of the acquisition of so-called basic categories .
Definition of cue validity
Formally, the cue validity of a feature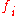 with respect to category
with respect to category 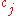 has been defined in the following ways:
has been defined in the following ways:
- As the conditional probability
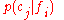 ; see , , .
; see , , . - As the deviation of the conditional probability from the category base rate,
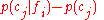 ; see , .
; see , . - As a function of the linear correlation; see , , , .
- Other definitions; see , .
For the definitions based on probability, a high cue validity for a given feature means that the feature or attribute is more diagnostic of the class membership than a feature with low cue validity. Thus, a high-cue validity feature is one which conveys more information about the category or class variable, and may thus be considered as more useful for identifying objects as belonging to that category. Thus, high cue validity expresses high feature informativeness. For the definitions based on linear correlation, the expression of "informativeness" captured by the cue validity measure is not the full expression of the feature's informativeness (as in mutual information
Mutual information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information of two random variables is a quantity that measures the mutual dependence of the two random variables...
, for example), but only that portion of its informativeness that is expressed in a linear relationship. For some purposes, a bilateral measure such as the mutual information
Mutual information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information of two random variables is a quantity that measures the mutual dependence of the two random variables...
or category utility
Category utility
Category utility is a measure of "category goodness" defined in and . It was intended to supersede more limited measures of category goodness such as "cue validity" and "collocation index"...
is more appropriate than the cue validity.
Examples
As an example, let us consider the domain of "numbers" and allow that every number has an attribute (i.e., a cue) named "is_positive_integer", which we call  , and which adopts the value 1 if the number is actually a positive integer
, and which adopts the value 1 if the number is actually a positive integerInteger
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
. Then we can inquire what the validity of this cue is with regard to the following classes: {
rational number, irrational number, even integer}:
- If we know that a number is a positive integer we know that it is a rational numberRational numberIn mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction a/b of two integers, with the denominator b not equal to zero. Since b may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number...
. Thus,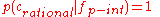 , the cue validity for
, the cue validity for is_positive_integeras a cue for the categoryrational numberis 1. - If we know that a number is a positive integer then we know that it is not an irrational numberIrrational numberIn mathematics, an irrational number is any real number that cannot be expressed as a ratio a/b, where a and b are integers, with b non-zero, and is therefore not a rational number....
. Thus,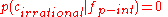 , the cue validity for
, the cue validity for is_positive_integeras a cue for the categoryirrational numberis 0. - If we know only that a number is a positive integer, then its chances of being even or odd are 50-50 (there being the same number of even and odd integers). Thus,
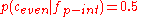 , the cue validity for
, the cue validity for is_positive_integeras a cue for the categoryeven integeris 0.5, meaning that the attributeis_positive_integeris entirely uninformative about the number's membership in the classeven integer.
In perception
Perception
Perception is the process of attaining awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information. All perception involves signals in the nervous system, which in turn result from physical stimulation of the sense organs...
, "cue validity" is often short for ecological validity
Ecological validity (perception)
The ecological validity of a sensory cue in perception is the correlation between the cue and a property of the world . For example, the color of a banana is a cue that indicates whether the banana is ripe...
of a perceptual cue, and is defined as a correlation rather than a probability (see above). In this definition, an uninformative perceptual cue has an ecological validity of 0 rather than 0.5.

