Cyclobutane
Encyclopedia
Cyclobutane is an organic compound
with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commercial or biological significance, but more complex derivatives are important in biology and biotechnology.
atom
s are significantly strained
and as such have lower bond energies
than related linear or unstrained hydrocarbons, e.g. butane
or cyclohexane
. As such, cyclobutane is unstable above about 500 °C.
The four carbon atoms in cyclobutane are not coplanar, instead the ring typically adopts a folded or "puckered" conformation. One of the carbon atoms makes a 25° angle with the plane formed by the other three carbons. In this way some of the eclipsing interactions are reduced. The conformation is also known as a "butterfly". Equivalent puckered conformations interconvert:
Despite inherent strain the cyclobutane motif is indeed found in nature. One unusual example is pentacycloanammoxic acid, which is a ladderane
composed of 5 fused cyclobutane units. The estimated strain in this compound is 3 times that of cyclobutane. The compound is found in bacteria performing the anammox
process where it forms part of a tight and very dense membrane believed to protect the organism from toxic hydroxylamine
and hydrazine
involved in the production of nitrogen and water from nitrite
ions and ammonia
. Some related fenestrane
s are also found in nature.
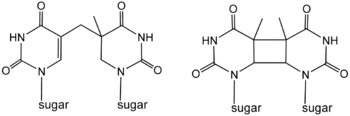
Cyclobutane photodimers ("CPD's") are formed by photochemical reactions that result in the coupling of the C=C double bonds of pyrimidines. T-T dimers thymine dimers formed in between two thymines are the most abundant of the CPD's. CPD's are readily repaired by nucleotide excision repair
enzymes. In most organisms they can also be repaired by photolyases, a light-dependent family of enzymes. Xeroderma pigmentosum
is a genetic disease where this damage can not be repaired, resulting in skin discolouration and tumours induced by exposure to UV light.
Carboplatin
is a popular anticancer drug that is derived from cyclobutane-1,1-carboxylic acid.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commercial or biological significance, but more complex derivatives are important in biology and biotechnology.
Structure
The bond angles between carbonCarbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s are significantly strained
Angle strain
Angle strain, also called Baeyer strain in cyclic molecules, is the resistance associated with bond angle compression or bond angle expansion. It occurs when bond angles deviate from the ideal bond angles to achieve maximum bond strength in a specific chemical conformation...
and as such have lower bond energies
Bond energy
In chemistry, bond energy is the measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. It is the heat required to break one Mole of molecules into their individual atoms. For example, the carbon-hydrogen bond energy in methane E is the enthalpy change involved with breaking up one molecule of methane into...
than related linear or unstrained hydrocarbons, e.g. butane
Butane
Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or...
or cyclohexane
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry, and also as a raw material for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, both of which being intermediates used in the production of nylon...
. As such, cyclobutane is unstable above about 500 °C.
The four carbon atoms in cyclobutane are not coplanar, instead the ring typically adopts a folded or "puckered" conformation. One of the carbon atoms makes a 25° angle with the plane formed by the other three carbons. In this way some of the eclipsing interactions are reduced. The conformation is also known as a "butterfly". Equivalent puckered conformations interconvert:
Cyclobutanes in biology and biotechnology
Despite inherent strain the cyclobutane motif is indeed found in nature. One unusual example is pentacycloanammoxic acid, which is a ladderane
Ladderane
A ladderane is an organic molecule containing two or more fused rings of cyclobutane. The name is a portmanteau because the serial cyclobutane rings look like a ladder and are singly bonded like alkanes. The chemical formula for a ladderane with n rings is C2n+2H2n+6...
composed of 5 fused cyclobutane units. The estimated strain in this compound is 3 times that of cyclobutane. The compound is found in bacteria performing the anammox
Anammox
Anammox, an abbreviation for ANaerobic AMMonium OXidation, is a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle . The bacteria mediating this process were identified in 1991, and at the time were a great surprise for the scientific community...
process where it forms part of a tight and very dense membrane believed to protect the organism from toxic hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula NH2OH. The pure material is a white, unstable crystalline, hygroscopic compound. However, hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is used to prepare oximes, an important functional group. It is also an...
and hydrazine
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually...
involved in the production of nitrogen and water from nitrite
Nitrite
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO2−. The anion is symmetric with equal N-O bond lengths and a O-N-O bond angle of ca. 120°. On protonation the unstable weak acid nitrous acid is produced. Nitrite can be oxidised or reduced, with product somewhat dependent on the oxidizing/reducing agent...
ions and ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
. Some related fenestrane
Fenestrane
A fenestrane in organic chemistry is a type of chemical compound with a central quaternary carbon atom which serves as a common vertex for four fused carbocycles. They can be regarded as spiro compounds twice over. Because of their inherent strain and instability fenestranes are of theoretical...
s are also found in nature.
Cyclobutane photodimers ("CPD's") are formed by photochemical reactions that result in the coupling of the C=C double bonds of pyrimidines. T-T dimers thymine dimers formed in between two thymines are the most abundant of the CPD's. CPD's are readily repaired by nucleotide excision repair
Nucleotide excision repair
Nucleotide excision repair is a DNA repair mechanism. DNA constantly requires repair due to damage that can occur to bases from a vast variety of sources including chemicals, radiation and other mutagens...
enzymes. In most organisms they can also be repaired by photolyases, a light-dependent family of enzymes. Xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum, or XP, is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of DNA repair in which the ability to repair damage caused by ultraviolet light is deficient. In extreme cases, all exposure to sunlight must be forbidden, no matter how small. Multiple basal cell carcinomas and other skin...
is a genetic disease where this damage can not be repaired, resulting in skin discolouration and tumours induced by exposure to UV light.
Carboplatin
Carboplatin
Carboplatin, or cis-Diammineplatinum is a chemotherapy drug used against some forms of cancer...
is a popular anticancer drug that is derived from cyclobutane-1,1-carboxylic acid.
Preparation
Many methods exist for the preparation of cyclobutanes. Alkenes dimerize upon irradiation with UV-light. 1,4-Dihalobutanes convert to cyclobutanes upon dehalogenation with reducing metals.External links
- Datasheet Link