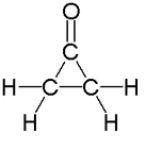
Cyclopropanone
Overview
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with molecular formula C3H4O consisting of a cyclopropane
Cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is a cycloalkane molecule with the molecular formula C3H6, consisting of three carbon atoms linked to each other to form a ring, with each carbon atom bearing two hydrogen atoms...
carbon framework with a ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
. The parent compound is labile with melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
−90 °C and has been prepared by reaction of ketene
Ketene
A ketene is an organic compound of the form R'RC=C=O. The term is also used specifically to mean ethenone, the simplest ketene, where R' and R are hydrogen atoms.Ketenes were first studied as a class by Hermann Staudinger.-Formation:...
with diazomethane
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2. It is the simplest of diazo compounds. In the pure form at room temperature, it is a extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas, thus it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether...
at −145 °C. Derivatives of cyclopropanone are of some interest to organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
.
In organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
the use of cyclopropanone itself is substituted by that of synthon
Synthon
A synthon is a concept in retrosynthetic analysis. It is defined as a structural unit within a molecule which is related to a possible synthetic operation. The term was coined by E.J. Corey...
s like acetal
Acetal
An acetal is a molecule with two single-bonded oxygen atoms attached to the same carbon atom.Traditional usages distinguish ketals from acetals...
s cyclopropanone ethyl hemiacetal or cyclopropanone ethyl trimethylsilyl acetal.
Cyclopropanones are intermediates in the Favorskii rearrangement
Favorskii rearrangement
The Favorskii rearrangement , named for the Russian chemist Alexei Yevgrafovich Favorskii, is most principally a rearrangement of cyclopropanones and α-halo ketones which leads to carboxylic acid derivatives. In the case of cyclic α-halo ketones, the Favorski rearrangement constitutes a ring...
with cyclic ketones where carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
formation is accompanied by ring-contraction.
An interesting feature of cyclopropanones is that they react as 1,3-dipole
1,3-dipole
In organic chemistry, a 1,3-dipolar compound or 1,3-dipole is a dipolar compound with delocalized electrons and a separation of charge over three atoms...
s in cycloaddition
Cycloaddition
A cycloaddition is a pericyclic chemical reaction, in which "two or more unsaturated molecules combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity." The resulting reaction is a cyclization reaction.Cycloadditions are usually described by the...
s for instance with cyclic dienes such as furan
Furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans....
.
Unanswered Questions

