
1,3-dipole
Encyclopedia
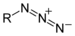 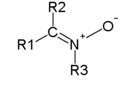  |
| From top to bottom, azides, nitrones, and nitro compounds are examples of 1,3-dipoles. |
In organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, a 1,3-dipolar compound or 1,3-dipole is a dipolar compound
Dipolar compound
In organic chemistry, a dipolar compound or simply dipole is an electrically neutral molecule carrying a positive and a negative charge in at least one canonical description. In most dipolar compounds the charges are delocalized....
with delocalized electron
Delocalized electron
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or one covalent bond....
s and a separation of charge over three atoms. They are reactants in 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
The 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, also known as the Huisgen cycloaddition or Huisgen reaction, is an organic chemical reaction belonging to the larger class of concerted, pericyclic cycloadditions. It is the reaction between a 1,3-dipole and a dipolarophile, most of which are substituted alkenes, to...
s.
Known 1,3-dipoles are:
- AzideAzideAzide is the anion with the formula N3−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid. N3− is a linear anion that is isoelectronic with CO2 and N2O. Per valence bond theory, azide can be described by several resonance structures, an important one being N−=N+=N−...
s - OzoneOzoneOzone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
- Nitro compoundNitro compoundNitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
s - DiazoDiazoDiazo refers to a type of organic compound called diazo compound that has two linked nitrogen atoms as a terminal functional group. The general formula is R2C=N2. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane...
compounds - Some oxideOxideAn oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
s
-
- Azoxide compounds
- Carbonyl oxides (Criegee zwitterions)
- Nitrile oxides
- Nitrous oxideNitrous oxideNitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
- NitroneNitroneA nitrone is the N-oxide of an imine and a functional group in organic chemistry. The general structure is R1R2C=NR3+O- where R3 is different from H.A nitrone is 1,3-dipole in 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions...
s
- Some imineImineAn imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond, with the nitrogen attached to a hydrogen atom or an organic group. If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as a Schiff base...
s:- Azomethine imine
- NitrilimineNitrilimineNitrilimines or nitrile amides are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the general structure R-CN-NR corresponding to an amine bonded to the N-terminus of a nitrile...
s - Carbonyl imines
- Some ylideYlideAn ylide or ylid is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom directly attached to a hetero atom with a formal positive charge , and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds...
s- Azomethine ylide
- Nitrile ylideNitrile ylideNitrile ylides also known as nitrilium ylides, or nitrilium methylides are generally reactive intermediates. Usually, they cannot be isolated. However, a structure has been determined on a by X-ray crystallography. As ylides, they possess a negative charge and a positive charge on adjacent atoms....
- Carbonyl ylide

