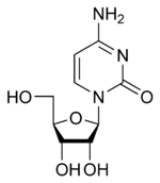
Cytidine
Encyclopedia
Cytidine is a nucleoside
molecule
that is formed when cytosine
is attached to a ribose
ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond
. Cytidine is a component of RNA
.
If cytosine
is attached to a deoxyribose
ring, it is known as a deoxycytidine
.
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
that is formed when cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
is attached to a ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond
Glycosidic bond
In chemistry, a glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate....
. Cytidine is a component of RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
.
If cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
is attached to a deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, more, precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H---3-H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom...
ring, it is known as a deoxycytidine
Deoxycytidine
Deoxycytidine is a deoxyribonucleoside. It is like cytidine, but with one oxygen atom removed....
.

