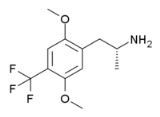
DOTFM
Encyclopedia
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-trifluoromethylamphetamine (DOTFM) is a psychedelic
drug
of the phenethylamine
and amphetamine
chemical classes. It was first synthesized
in 1994 by a team at Purdue University
led by David E. Nichols
. DOTFM is the alpha
-methylated analogue of 2C-TFM
, and is around twice as potent in animal studies. It acts as an agonist
at the 5HT2A and 5HT2C
receptor
s. In drug-substitution experiments in rats, DOTFM fully substituted for LSD
and was slightly more potent than DOI
. Anecdotal reports from human users suggest that DOTFM is a potent psychedelic with an extremely long duration of action, similar to Br-DFLY.
Psychedelic drug
A psychedelic substance is a psychoactive drug whose primary action is to alter cognition and perception. Psychedelics are part of a wider class of psychoactive drugs known as hallucinogens, a class that also includes related substances such as dissociatives and deliriants...
drug
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
of the phenethylamine
Substituted phenethylamine
The substituted phenethylamines are chemical compounds with the 2-phenethylamine chemical structure modified at the phenyl ring, sidechain, and/or amino group. Some of them are psychoactive drugs, including stimulants, psychedelics, opioids, and entactogens, which exert their effects primarily...
and amphetamine
Substituted amphetamine
Substituted amphetamines are a chemical class of stimulants, entactogens, hallucinogens, and other drugs. They feature a phenethylamine core with a methyl group attached to the alpha carbon resulting in amphetamine, along with additional substitutions...
chemical classes. It was first synthesized
Chemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
in 1994 by a team at Purdue University
Purdue University
Purdue University, located in West Lafayette, Indiana, U.S., is the flagship university of the six-campus Purdue University system. Purdue was founded on May 6, 1869, as a land-grant university when the Indiana General Assembly, taking advantage of the Morrill Act, accepted a donation of land and...
led by David E. Nichols
David E. Nichols
David E. Nichols is an American pharmacologist and medicinal chemist.Presently the Robert C. and Charlotte P. Anderson Distinguished Chair in Pharmacology at Purdue University, Nichols has worked in the field of psychoactive drugs since 1969...
. DOTFM is the alpha
Alpha carbon
The alpha carbon in organic chemistry refers to the first carbon that attaches to a functional group . By extension, the second carbon is the beta carbon, and so on....
-methylated analogue of 2C-TFM
2C-TFM
2C-TFM is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in the laboratory of David E. Nichols. It has also been called 2C-CF3, a name derived from the para-trifluoromethyl group it contains.-Chemistry:...
, and is around twice as potent in animal studies. It acts as an agonist
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
at the 5HT2A and 5HT2C
5-HT2C receptor
The 5-HT2C receptor is a subtype of 5-HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin . It is a G protein-coupled receptor that is coupled to Gq/G11 and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR2C denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor, that in humans is located at the...
receptor
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
s. In drug-substitution experiments in rats, DOTFM fully substituted for LSD
LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide, abbreviated LSD or LSD-25, also known as lysergide and colloquially as acid, is a semisynthetic psychedelic drug of the ergoline family, well known for its psychological effects which can include altered thinking processes, closed and open eye visuals, synaesthesia, an...
and was slightly more potent than DOI
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine
2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine is a psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine family. It is also a powerful anti-inflammatory that is effective at doses on the order of 100 micrograms in humans, far below its effective dose as a psychedelic. Despite being a substituted...
. Anecdotal reports from human users suggest that DOTFM is a potent psychedelic with an extremely long duration of action, similar to Br-DFLY.

