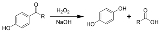
Dakin reaction
Overview
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
redox reaction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
in which an ortho
Arene substitution patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.- Ortho, meta, and para substitution :...
- or para
Arene substitution patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.- Ortho, meta, and para substitution :...
-hydroxylated
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
phenyl
Phenyl group
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group or phenyl ring is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5. Phenyl groups are closely related to benzene. Phenyl groups have six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the...
aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. It can be found in the orchid Gastrodia elata.-Chemistry:The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a...
) or ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
reacts with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
in base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
to form a benzenediol
Benzenediol
Benzenediols or dihydroxybenzenes are organic chemical compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols, and more specifically as polyphenols...
and a carboxylate[3]. Overall, the carbonyl group
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
The Dakin oxidation, which is closely related to the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation
Baeyer-Villiger oxidation
The Baeyer–Villiger oxidation is an organic reaction in which a ketone is oxidized to an ester by treatment with peroxy acids or hydrogen peroxide. Key features of the Baeyer–Villiger oxidation are its stereospecificity and predictable regiochemistry...
, is not to be confused with the Dakin-West reaction
Dakin-West reaction
The Dakin–West reaction is a chemical reaction that transforms an amino-acid into a keto-amide using an acid anhydride and a base, typically pyridine. It is named for Henry Drysdale Dakin and Randolph West . Of special note, the keto-amide product is always racemic.With pyridine as a base and...
, though both are named after Henry Drysdale Dakin
Henry Drysdale Dakin
Henry Drysdale Dakin FRS was an English chemist.He was born in London as the youngest of 8 children to a family of steel merchants from Leeds. As a school boy he did water analysis with the Leeds City Analyst. He studied chemistry at the University of Leeds with Julius B...
.
The Dakin oxidation starts with nucleophilic
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
addition
Addition reaction
An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one....
of a hydroperoxide anion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
to the carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
, forming a tetrahedral intermediate
Tetrahedral carbonyl addition compound
Tetrahedral intermediate is a reaction intermediate in which the bond arrangement around an initially double-bonded carbon atom has been transformed from trigonal to tetrahedral. Tetrahedral intermediates result from nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group...
(2).
Unanswered Questions

