Dark field microscopy
Encyclopedia
Dark field microscopy describes microscopy methods, in both light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. As a result, the field around the specimen (i.e. where there is no specimen to scatter the beam) is generally dark.
technique used to enhance the contrast
in unstained samples
. It works by illuminating the sample with light that will not be collected by the objective lens, and thus will not form part of the image. This produces the classic appearance of a dark, almost black, background with bright objects on it.

 Dark field microscopy is a very simple yet effective technique and well suited for uses involving live and unstained
Dark field microscopy is a very simple yet effective technique and well suited for uses involving live and unstained
biological samples, such as a smear from a tissue culture or individual water-borne single-celled organisms. Considering the simplicity of the setup, the quality of images obtained from this technique is impressive.
The main limitation of dark field microscopy is the low light levels seen in the final image. This means the sample must be very strongly illuminated, which can cause damage to the sample. Dark field microscopy techniques are almost entirely free of artifacts, due to the nature of the process. However the interpretation of dark field images must be done with great care as common dark features of bright field microscopy
images may be invisible, and vice versa.
While the dark field image may first appear to be a negative of the bright field image, different effects are visible in each. In bright field microscopy, features are visible where either a shadow is cast on the surface by the incident light, or a part of the surface is less reflective, possibly by the presence of pits or scratches. Raised features that are too smooth to cast shadows will not appear in bright field images, but the light that reflects off the sides of the feature will be visible in the dark field images.
, in order to allow optical mice to work on transparent glass by imaging microscopic flaws and dust on its surface.
in the study of crystals and crystal defects, as well as in the imaging of
individual atoms.
involves tilting
the incident illumination until a diffracted, rather than
the incident, beam passes through a small objective
aperture in the objective lens back focal plane.
Darkfield images, under these conditions, allow one to
map the diffracted intensity coming from a single
collection of diffracting planes as a function of
projected position on the specimen, and as a function of
specimen tilt.
In single crystal specimens, single-reflection darkfield
images of a specimen tilted just off the Bragg
condition allow one to "light up" only those
lattice defects, like dislocations or precipitates,
which bend a single set of lattice planes in their
neighborhood. Analysis of intensities in such images
may then be used to estimate the amount of that bending.
In polycrystalline specimens, on the other hand,
darkfield images serve to light up only that subset
of crystals which is Bragg reflecting at a given
orientation.
darkfield, but use of a diffracted beam harmonic
rather than the diffracted beam itself. Much higher resolution
of strained regions around defects can be obtained in this
way.
with electrons diffracted into an annular aperture
centered on, but not including, the unscattered beam.
For large scattering angles in a scanning transmission electron microscope, this is sometimes called Z-contrast imaging
because of the enhanced scattering from high atomic
number atoms.
Light Microscopy Applications
In optical microscopy, darkfield describes an illuminationLighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate application of light to achieve some practical or aesthetic effect. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources such as lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight...
technique used to enhance the contrast
Contrast (vision)
Contrast is the difference in visual properties that makes an object distinguishable from other objects and the background. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the color and brightness of the object and other objects within the same field of view...
in unstained samples
Sample (material)
In general, a sample is a limited quantity of something which is intended to be similar to and represent a larger amount of that thing. The things could be countable objects such as individual items available as units for sale, or a material not countable as individual items. Samples of countable...
. It works by illuminating the sample with light that will not be collected by the objective lens, and thus will not form part of the image. This produces the classic appearance of a dark, almost black, background with bright objects on it.
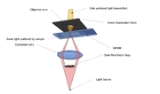
The light's path
The steps are illustrated in the figure where an upright microscope is used.
- Light enters the microscopeMicroscopeA microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
for illumination of the sample. - A specially sized disc, the patch stop (see figure) blocks some light from the light source, leaving an outer ring of illumination. A wide phase annulus can also be reasonably substituted at low magnification.
- The condenser lens focuses the light towards the sample.
- The light enters the sample. Most is directly transmitted, while some is scattered from the sample.
- The scattered light enters the objective lens, while the directly transmitted light simply misses the lens and is not collected due to a direct illumination block (see figure).
- Only the scattered light goes on to produce the image, while the directly transmitted light is omitted.
Advantages and disadvantages

Staining (biology)
Staining is an auxiliary technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast in the microscopic image. Stains and dyes are frequently used in biology and medicine to highlight structures in biological tissues for viewing, often with the aid of different microscopes...
biological samples, such as a smear from a tissue culture or individual water-borne single-celled organisms. Considering the simplicity of the setup, the quality of images obtained from this technique is impressive.
The main limitation of dark field microscopy is the low light levels seen in the final image. This means the sample must be very strongly illuminated, which can cause damage to the sample. Dark field microscopy techniques are almost entirely free of artifacts, due to the nature of the process. However the interpretation of dark field images must be done with great care as common dark features of bright field microscopy
Bright field microscopy
Bright field microscopy is the simplest of all the optical microscopy illumination techniques. Sample illumination is transmitted white light and contrast in the sample is caused by absorbance of some of the transmitted light in dense areas of the sample...
images may be invisible, and vice versa.
While the dark field image may first appear to be a negative of the bright field image, different effects are visible in each. In bright field microscopy, features are visible where either a shadow is cast on the surface by the incident light, or a part of the surface is less reflective, possibly by the presence of pits or scratches. Raised features that are too smooth to cast shadows will not appear in bright field images, but the light that reflects off the sides of the feature will be visible in the dark field images.
Use in computing
Dark field microscopy has recently been used in computer miceMouse (computing)
In computing, a mouse is a pointing device that functions by detecting two-dimensional motion relative to its supporting surface. Physically, a mouse consists of an object held under one of the user's hands, with one or more buttons...
, in order to allow optical mice to work on transparent glass by imaging microscopic flaws and dust on its surface.
Transmission Electron Microscope Applications
Darkfield studies in transmission electron microscopy play a powerful rolein the study of crystals and crystal defects, as well as in the imaging of
individual atoms.
Conventional darkfield imaging
Briefly, imaginginvolves tilting
the incident illumination until a diffracted, rather than
the incident, beam passes through a small objective
aperture in the objective lens back focal plane.
Darkfield images, under these conditions, allow one to
map the diffracted intensity coming from a single
collection of diffracting planes as a function of
projected position on the specimen, and as a function of
specimen tilt.
In single crystal specimens, single-reflection darkfield
images of a specimen tilted just off the Bragg
condition allow one to "light up" only those
lattice defects, like dislocations or precipitates,
which bend a single set of lattice planes in their
neighborhood. Analysis of intensities in such images
may then be used to estimate the amount of that bending.
In polycrystalline specimens, on the other hand,
darkfield images serve to light up only that subset
of crystals which is Bragg reflecting at a given
orientation.
| Animation: darkfield imaging of crystals |
|---|
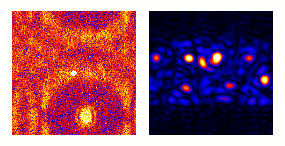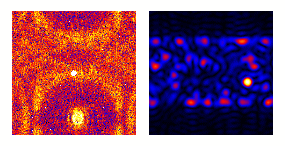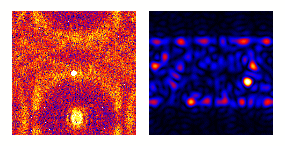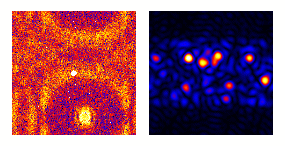 |
Weak beam imaging
Weak beam imaging involves optics similar to conventionaldarkfield, but use of a diffracted beam harmonic
rather than the diffracted beam itself. Much higher resolution
of strained regions around defects can be obtained in this
way.
Low and high angle annular darkfield imaging
Annular darkfield imaging requires one to form imageswith electrons diffracted into an annular aperture
centered on, but not including, the unscattered beam.
For large scattering angles in a scanning transmission electron microscope, this is sometimes called Z-contrast imaging
because of the enhanced scattering from high atomic
number atoms.
External links and references
- http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/stereomicroscopy/stereodarkfield.html
- Molecular Expressions:
- Darkfield Illumination Primer

