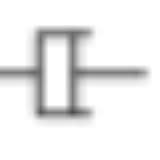
Dashpot
Encyclopedia
A dashpot is a mechanical device, a damper which resists motion via viscous friction
. The resulting force is proportional to the velocity
, but acts in the opposite direction, slowing the motion and absorbing energy. It is commonly used in conjunction with a spring
(which acts to resist displacement). The process and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) symbol for a dashpot is .
A less common type of dashpot is an eddy current
damper, which uses a large magnet inside a tube constructed of a non-magnetic but conducting material (such as aluminium
or copper
). Like a common viscous damper, the eddy current damper produces a resistive force proportional to velocity.
Dashpots frequently use a one-way mechanical bypass to permit fast unrestricted motion in one direction and slow motion using the dashpot in the opposite direction. This permits, for example, a door to be opened quickly without added resistance, but then to close slowly using the dashpot. For hydraulic dashpots this unrestricted motion is accomplished using a one-way check-valve that allows fluid to bypass the dashpot fluid constriction. Non-hydraulic dashpots may use a ratcheting gear to permit free motion in one direction.
 A dashpot is a common component in a door closer
A dashpot is a common component in a door closer
to prevent it from slamming shut. A spring applies force to close the door and the dashpot, implemented by requiring fluid to flow through a narrow channel between reservoirs (often with a size adjustable by a screw), slows down the motion of the door.
Consumer electronics
often use dashpots where it is undesirable for a media access door or control panel to suddenly pop open when the door latch is released. The dashpot slows the sudden movement down into a steady and gentle movement until the access door has opened all the way under spring tension.
Dashpots are commonly used in dampers and shock absorbers. The hydraulic cylinder in an automobile shock absorber is a dashpot. They are also used on carburettors, where the return of the throttle lever is cushioned right before the throttle fully closes and then is allowed to fully close slowly to reduce emissions of sudden deceleration (compared to deceleration without a dashpot)
Large forces and high speeds can be controlled by dashpots. For example, they are used to arrest the steam catapults on aircraft carrier
decks.
Relay
s can be made to have a long delay by utilizing a piston filled with fluid that is allowed to escape slowly.
and Kelvin-Voigt
models of viscoelasticity
use springs and dashpots in series and parallel circuits
respectively. Models containing dashpots add a viscous, time dependent, element to the behavior of solids allowing complex behaviors like creep
and stress relaxation to be modeled.
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
. The resulting force is proportional to the velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
, but acts in the opposite direction, slowing the motion and absorbing energy. It is commonly used in conjunction with a spring
Spring (device)
A spring is an elastic object used to store mechanical energy. Springs are usually made out of spring steel. Small springs can be wound from pre-hardened stock, while larger ones are made from annealed steel and hardened after fabrication...
(which acts to resist displacement). The process and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) symbol for a dashpot is .
Types
Two common types of dashpots exist - linear and rotary. Linear dashpots are generally specified by stroke (amount of linear displacement) and damping coefficient (force per velocity). Rotary dashpots will have damping coefficients in torque per angular velocity.A less common type of dashpot is an eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
damper, which uses a large magnet inside a tube constructed of a non-magnetic but conducting material (such as aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
or copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
). Like a common viscous damper, the eddy current damper produces a resistive force proportional to velocity.
Dashpots frequently use a one-way mechanical bypass to permit fast unrestricted motion in one direction and slow motion using the dashpot in the opposite direction. This permits, for example, a door to be opened quickly without added resistance, but then to close slowly using the dashpot. For hydraulic dashpots this unrestricted motion is accomplished using a one-way check-valve that allows fluid to bypass the dashpot fluid constriction. Non-hydraulic dashpots may use a ratcheting gear to permit free motion in one direction.
Applications

Door closer
A door closer is a mechanical device that closes a door, in general after someone opens it, or after it was automatically opened. Choosing a door closer can involve the consideration of a variety of criteria...
to prevent it from slamming shut. A spring applies force to close the door and the dashpot, implemented by requiring fluid to flow through a narrow channel between reservoirs (often with a size adjustable by a screw), slows down the motion of the door.
Consumer electronics
Consumer electronics
Consumer electronics are electronic equipment intended for everyday use, most often in entertainment, communications and office productivity. Radio broadcasting in the early 20th century brought the first major consumer product, the broadcast receiver...
often use dashpots where it is undesirable for a media access door or control panel to suddenly pop open when the door latch is released. The dashpot slows the sudden movement down into a steady and gentle movement until the access door has opened all the way under spring tension.
Dashpots are commonly used in dampers and shock absorbers. The hydraulic cylinder in an automobile shock absorber is a dashpot. They are also used on carburettors, where the return of the throttle lever is cushioned right before the throttle fully closes and then is allowed to fully close slowly to reduce emissions of sudden deceleration (compared to deceleration without a dashpot)
Large forces and high speeds can be controlled by dashpots. For example, they are used to arrest the steam catapults on aircraft carrier
Aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship designed with a primary mission of deploying and recovering aircraft, acting as a seagoing airbase. Aircraft carriers thus allow a naval force to project air power worldwide without having to depend on local bases for staging aircraft operations...
decks.
Relay
Relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal , or where several circuits must be controlled...
s can be made to have a long delay by utilizing a piston filled with fluid that is allowed to escape slowly.
Viscoelasticity
Dashpots are used to form models of materials that exhibit viscoelastic behavior, such as muscle tissue. MaxwellMaxwell material
A Maxwell material is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named for James Clerk Maxwell who proposed the model in 1867. It is also known as a Maxwell fluid.- Definition :...
and Kelvin-Voigt
Kelvin-Voigt material
A Kelvin–Voigt material, also called a Voigt material, is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named after the British physicist and engineer William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin and after German physicist Woldemar Voigt.- Definition :The Kelvin–Voigt...
models of viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain instantaneously when stretched and just...
use springs and dashpots in series and parallel circuits
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
respectively. Models containing dashpots add a viscous, time dependent, element to the behavior of solids allowing complex behaviors like creep
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep is the tendency of a solid material to slowly move or deform permanently under the influence of stresses. It occurs as a result of long term exposure to high levels of stress that are below the yield strength of the material....
and stress relaxation to be modeled.
External links
- brief description by Julius O. Smith III of Stanford University's CCRMA

